Through this post we bring you through this excellent article the spanish baroque painting, characteristics, genres and much more about this type of art that was made during the XNUMXth century and the first half of the XNUMXth century, considering it the golden age of Spanish painting. Don't stop reading it!

What is Spanish Baroque Painting?
Spanish baroque painting stands out due to the excess of idealized beauty and integrated with Mannerist deformations, allowing the narrative fact without the loss of ornamentation according to the demands of the counter-reformist church.
It takes for the year 1610 the natural models of the artist Caravaggio of Italian origin, together with the tenebrist lighting, determining the dominant style of Spanish baroque painting of the first part of the 1603th century, then the arrival of Rubens is essential between the years 1628 and XNUMX.
Where he demonstrates the massive wave of the transmission of his works together with that of his disciples, this influence is nuanced thanks to the nuances of Titian with his loose brushstroke technique that is typical of one of the main representatives of Spanish baroque painting such as Velázquez. .
The influences of the Flemish order are combined in Spanish Baroque painting thanks to the new currents that come from the Italian nation with respect to expert artists in the art of fresco such as Colonna and Mitelli in the year 1658 and then Luca Giordano in the year 1692. .
Although in this period a general crisis was unleashed that affected the Spanish nation due to the migration of a large number of inhabitants to the new continent coupled with the casualties caused by the multiple wars and the expulsion of the Moors from the Spanish nation.

In addition to the diversity of plagues and epidemics that affected the population of Spain despite all these vicissitudes, it is the Golden Age in Spanish Baroque painting due to the multiple works of great quality and originality of the first row images that they made.
Main characteristics of Spanish baroque painting
With the intention that you can locate in a practical way the most representative characteristics of Spanish Baroque painting, we will explain in detail in this section everything related to this interesting topic.
In relation to Clients and Patrons
The main clientele was the church, which requested a large number of artistic works to decorate the multiple religious temples and demanded a large number of works from the artists.
Demonstrating the importance of Spanish Baroque painting in the counter reform of the church using art as a weapon in favor of the Catholic Church.
Thanks to them, the painters who worked for this dogma were unable to express art as such since they had to comply with religious requirements specifically in the choice of subjects to paint.
In addition, the church demanded the models to be made and supervised whether the artistic work of Spanish Baroque painting was in accordance with the interests that they expected.
Although the painters who worked for the Catholic Church enjoyed excellent economic income as well as an excellent reputation and renown by making the exhibition of their works public.
Another client was the Cortes, specifically the reign of Felipe IV, where he was actually a patron. An example of this is the excerpt from Rubens' letter to a friend where he states the following:
“… Here I dedicate myself to painting, as I do everywhere… I have made an equestrian portrait of His Majesty that has pleased him very much. It is true that painting delights him…”
"... in my opinion this prince is endowed with excellent qualities, I have personal contact with him... as I stay in the palace he comes to see me almost every day..."

One of the examples of Spanish baroque painting is the decoration of the new Palacio del Buen Retiro, which allowed the increase of significant artistic works for the ornamentation of the Salón de los Reinos where excellent portraits can be seen.
The equestrian portraits made by Velázquez appear as well as a variety of artistic paintings of the battles won by the armies of Felipe IV, as well as the cycle referring to The Labors of Hercules made by Zurbarán.
In the city of Rome, several artists were requested, among which Claudio de Lorraine and Nicolas Poussin stand out in regard to series of landscapes where figures are observed for the Gallery of Landscapes.
Likewise, the artists Giovanni Lanfranco, Domenichino and other artists were commissioned to make more than thirty-four paintings regarding the history of Rome in the city of Naples, among which The Combat of Women by José de Ribera stands out.
The prohibition of transferring artistic works to other royal palaces was carried out and due to Olivares' haste to complete the decoration, works from collectors had to be acquired to reach the sum of 800 works that had to hang on the walls of this infrastructure.

Among the sellers of these artistic works was the artist Velázquez who in 1634 sold the king the artistic work La Tunica de José and La Fragua de Vulcano that he painted in the Italian nation, which is a work that represents Spanish Baroque painting.
He also sold other works, including foreign works, such as a copy of the Danae made by Titian, as well as four landscapes, god allegorical works to still lifes and two other pictorial works related to flowers.
After that, it was required to decorate the Torre de la Parada where a large number of representative works of Spanish Baroque painting were placed, being the number of sixty-three paintings with mythological motifs which were commissioned in 1636 from the artist Rubens.
This painter was in charge of giving the designs and monopolized the execution of fourteen pictorial works in relation to landscapes as well as views referring to real sites were made by artists of Spanish origin such as Félix Castelo, José Leonardo.
In addition to Velásquez, who contributed works related to Aesop and Menippus, as well as the portrait of Mars, being one of the great examples of Spanish Baroque painting.
The Alcázar also received a large number of new works referring to Spanish Baroque painting, showing admiration for its themes and some protests were even formalized, as was the case in 1638.
From the city of Rome, the pictorial works The Bacchanal of the Andrios and The Offering of Venus were transferred, being two works of great admiration by the artist Titian. A great number of protests were forged among the artists of the city.
In addition, a reorganization of the funds was required among the artists who participated, Velázquez, a great representative of Spanish Baroque painting, was made a priority regarding the criteria of aesthetics.
Therefore, the ground floor of the palace contains the so-called Titian Vaults, where thirty-eight pictorial works were integrated.
In addition to the poetry that Felipe II requested from Titian himself in conjunction with The Bacchanal and other works of art of Venetian origin such as The Three Graces by Rubens, Eva by the artist Dürer.

Other works belonging to Ribera such as the famous Jordaens in addition to Tintoretto where female figures stand out, mainly referring to the nude and with the intention of being able to complete this series of paintings, Velázquez needed to move to the Italian nation in the year 1648.
With the order to purchase sculptures and hire a professional dedicated to fresco painting, Angelo Michele Colonna and Agostino Mitelli stand out for this.
Work continued on the Alcázar and in 1649 Francisco Camilo was commissioned with a series of scenes known as Ovid's Metamorphosis, which were not to the king's liking.
Also noteworthy in Spanish Baroque painting are the scenographic ornaments referring to the theatrical performances, as can be seen in the Buen Retiro, and in them was the workmanship of the Italian-born engineers Baccio del Bianco and Come Lotti.
Those who were in charge of introducing the stagecraft in addition to the games of Tuscan alterations, being the director of the royal theaters Francisco Rizi, today drawings related to the curtains are preserved.

Other artists also participated, such as the Granada-born José de Cieza, who was a painter of perspectives and thanks to this he obtained the coveted title of Painter of the King.
In Spanish Baroque painting, the ephemeral decorations related to triumphal arches and facades with festive intentions stand out, which were sponsored by the City Council or by intellectual guilds, which was another source of income for artists.
But in this type of works it was observed that they were of a profane order but they did not stop representing Spanish baroque painting, among them the entries in Madrid of Mariana of Austria stand out, she was the second wife of Felipe IV.
In addition to the two wives of Carlos II, being María Luisa de Orleans and María de Neoburgo, where artists specialized in relief participated, such as Claudio Coello.
With regard to the clientele in the private sphere, with regard to Spanish Baroque painting, little can be said, due to the few data available, it is possible to speak specifically of the nobility that was interested in decorating their private chapels.
Although some members of the high nobility who were close to the king who were in charge of performing functions in regions of Italy as well as in Flanders had the possibility of becoming creditors of large collections of artistic works.
An example of this can be seen with the viceroys of Naples who acquired works of Spanish baroque painting by Ribera, then Alonso Cano who became a creditor of works by Olivares, being original patrons with regard to the collection of works in Europe.
One of the researchers of Spanish baroque painting named Carducho comments that there were around twenty collectors of great importance in Spain at that time, such as the Marquis of Leganés who felt a strong attraction to Flemish painting.
It is also possible to mention Juan Alfonso Enríquez de Cabrera who was Admiral of Castile and received from his mother Vittoria Colonna a large number of religious works where original works and some copies of Rubens, Correggio, Tintoretto and Titian were evident.
Many of the upper class preferred works by foreign artists, which meant that the works carried out by Creole artists from Spain were reduced.

Although it should be noted that many works were without the signature of their author and when they were carried they were not always the artist's own but rather a crude copy, such as the case of the Marquis del Carpio, his collection oscillated around two thousand pieces.
Among these works, the Venus of the Mirror by Velázquez, a great artist of Spanish Baroque painting, stood out. There were also works by other artists such as Angelo Nardi and Juan van del Hamen.
In addition, in his inventory there were also second-rate works such as Gabriel Terrazas, Juan de Toledo and even copies of great artists such as Rubens, Velázquez, Tiziano that were made with great mastery by Juan Bautista Martínez del Mallet.
With respect to the collection that the Dukes of Benavente had acquired, works referring to Flemish and Italian painting were observed, although the bulk of the collection was made up of works of Spanish Baroque painting by Murillo, around forty pictorial works.
Another collection of great exceptional beauty was that of Admiral Juan Gaspar Enríquez de Cabrera who was the protector of Juan Alfaro by order of his funds to build a museum.

These paintings were distributed in various topical rooms referring to nations, as well as still lifes and seascapes. Likewise, great works by influential masters are evident, such is the case of Rafael, Rubens, Ribera, Pedro de Orrente and Bassano.
Each artist with his own piece elaborated also highlights in Spanish baroque painting the Dream of the Knight of Pereda as well as works by other artists such as Carreño and Antolinez.
Little is known if in the other social classes it was possible to know if they enjoyed collecting works related to Spanish Baroque painting, although the possession of pictorial works as part of the household trousseau was common.
According to the Toledan record of the inventories of the second half of the XNUMXth century that are currently preserved, it is possible to speak of a genre of paintings that were kept in the homes of the other social classes where the majority belong to topics of a religious nature.
Artists and their consideration in society
It is important to highlight the little social consideration given to artists since they considered this trade something mechanical and it was only until the XNUMXth century that they were recognized.
Well, in the previous century they were underestimated, such is the case of the arduous effort on the part of Velázquez to be admitted to the Order of Santiago in order to seek social recognition.
It is important to note that the custom of starting the profession at an early age did not favor intellectual training, and few artists care about acquiring cultural training.
Among the exceptions to this rule, Francisco Pacheco stands out in Spanish Baroque painting, who was Velázquez's teacher and who endeavored to surround himself with intellectuals with whom he maintained communication through letters.
Another was Diego Valentín Díaz in the city of Valladolid where he had a library consisting of five hundred and seventy-six (576) volumes.
There were artists who were totally illiterate, such is the case of Antonio de Pereda who, according to Palomino, did not know how to read or write, but he liked to be read to him by books referring to general culture.

According to the Council of Trent, the church was in charge of establishing new rules regarding morality which were much more demanding.
Among them, nudes were prohibited, so several treatises on chastity were published, disapproving the act of painting nudes.
It is observed that at that historical moment of Spanish baroque painting, some nudes were used to represent Eve and Adam as well as other holy martyrs, as well as in the churches in the courts, a large number of nudes were observed in artistic works.
For this reason, Fray Juan De Rojas y Auxa proposed to cover these artistic works with veils when the ladies were in the presence of these paintings.
Therefore, this taboo in relation to the nude was influencing the works of some artists, such as Francisco Pacheco, who advised artists to only imitate the heads and hands of models and do the rest in front of prints or statues.

Although in the mid-seventeenth century most art academies encouraged artistic study through a living model in most cases male.
An example of this can be evidenced in the Principles to Study the Noble Art of Painting in the year 1693 created by José García Hidalgo.
Various Genres in Spanish Baroque Painting
A great diversity of representative genres of Spanish Baroque painting were observed in art and in this interesting article we will explain each one of them, being the following:
Religious Painting
According to the words of Francisco Pacheco regarding religious painting, it is a representative genre of Spanish Baroque painting and expresses the following:
“…the main purpose of painting was to persuade men to piety and lead them to God…”
So you can evidence the realistic aspect of Spanish baroque painting in regards to the religious sphere in the first half of the XNUMXth century.
The naturalist currents were quickly accepted, so the artist feels faithful to religion when it is part of the fact that he captures in artistic works.
The space of greatest honor for Spanish Baroque painting was the main altarpiece of the religious sanctuaries, although in the smaller altarpieces works were also placed in the chapels and lateral naves.
An example of this is the altarpiece of El Escorial, which is divided into streets and bodies in a mixed way, where Spanish Baroque painting and sculptures can be seen.
Then, in the second half of the XNUMXth century, the imposition of huge altarpieces is observed, eliminating the varied scenes to focus on a central scene, being the historical moment of religious painting and at the end of the century it is only relegated to the attic.

The main body of the altarpiece is made up of carved wood, being a great stage of Spanish Baroque painting and thanks to the influence of the Italian Luca Giordano who was in the Spanish nation, the painting of frescoes began in the vaults of religious temples.
Therefore, Spanish Baroque painting makes representations of triumphal scenes, such as the Apotheosis of San Hermenegildo by Francisco de Herrera, better known as El Mozo.
Another example of Spanish Baroque painting in the religious sphere, such as Saint Augustine, produced by Claudio Coello. These works are now in the Prado Museum. In these works, compositions are observed where diagonal lines dominate and full of great strength.
Images of saints are observed in Spanish baroque painting, specifically those of greater devotion in the Catholic Church of various sizes and repetitions were frequent in the same workshop among the favorite saints are the following:
- St. Teresa of Jesus
- St. Ignatius of Loyola
- the penance
- San Pedro
- The Magdalena
- San Jeronimo
- The charity
- Almsgiving
- Saint John of God
- Saint Elisabeth of Hungary
- Martyrs (witnesses to the Catholic faith)

Regarding the cult of the Virgin and the cult of Saint Joseph, which were promoted thanks to the words of Saint Teresa of Jesus, increasing the cult as the Protestant church fought with the Catholic faith.
Being representative images of Spanish baroque painting, among which La Inmaculada stands out in the Spanish region, the main ones to acquire these works were the disputed monarchs in defending the dogma that had not yet been conceptualized by the Pope.
Due to this, artistic paintings referring to the Eucharist were made in Spanish Baroque painting, as can be seen thanks to the artist Claudio Coello in his artistic work Adoration of the Sacred Form that is located in El Escorial.
From what is observed that the Spanish Baroque painting was used to confront the ideas of the Protestant religion, an example of this is the Last Supper where the consecration of the Eucharist is encouraged.
Likewise, the miracles of Christ reflected the various works of mercy, as can be seen in the series of paintings made by the artist Murillo for the Hospital de la Caridad in Seville, demonstrating great importance in Spanish Baroque painting.
It is important to highlight that few allegorical images of the Old Testament are observed, since there were reservations of this reading to the faithful of the Catholic faith and the topics that are taken in the first instance refer to the coming of Christ or allegorical to them.
As is the case of the Sacrifice of Isaac where a meaning analogically manifests itself of the passion of Christ and is represented thanks to Spanish baroque painting.
The Profane Genre
You should be aware that other genres were found in Spanish Baroque painting, although the one that is best known corresponds to religious themes.
Since the church was his main client and the money paid for it was very rewarding for the artists of this artistic movement.
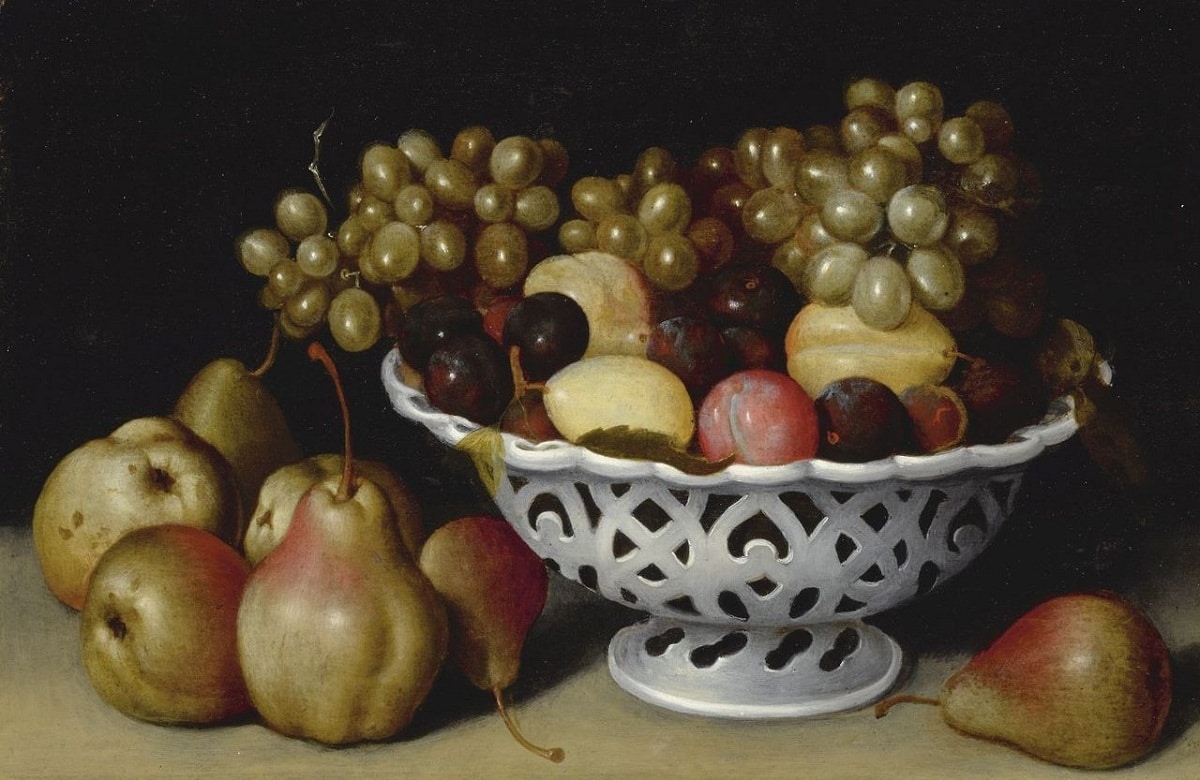
So we can talk about other genres in Spanish Baroque painting such as portraits and still lifes. Although since 1599 the expression referring to still life painting has been found in documents.
One of the qualities of the austere Spanish still life is opposed to the ostentatious kitchen tables of Flemish origin and it is thanks to the artist Sánchez Cotán that it is defined as a genre made up of simple compositions where geometric figures, hard lines and gloomy lighting are used.

Such was the success of this artistic genre of Spanish Baroque painting that other artists supported him in this form of painting that became part of the royal courts, being the following artists of great renown:
- Felipe Ramirez
- Alexander of Loarte
- Francisco Burgos Mantilla
- Juan van der Hamen and Leon
- Francis Barrier
- Juan Fernandez better known as the Labrador
- Antonio Ponce
- Juan de Espinosa
- Francisco Palacios
The Sevillian school also helped shape the qualities of the still life genre, with Velázquez and Zurbarán being the main representatives of Spanish Baroque painting. It is essential to emphasize that these still lifes were not free from the influence of the Italian region as well as Flemish.
The genre of the Spanish still life underwent a transformation in the mid-seventeenth century when, thanks to the Flemish influence, the images represented were more ostentatious and complex than the initial ones, a development in the composition is observed in a theatrical way with allegorical content.

An example of this form of Spanish baroque painting can be seen in the flower paintings made by Juan de Arellano and even in the artistic work named Vanitas by the artist Antonio de Pereda and another great artist Valdés Leal.
The foreign influence is observed because this genre of the Spanish still life is framed in the austerity and sobriety of its forms that changes with the Flemish and Italian influence.
Although Velázquez dedicated time and attention to the Spanish still life genre, it obtained few cultivators and was disqualified by Carducho. Some works by Loarte and other artistic paintings attributed to Puga can be mentioned.
In the mid-seventeenth century, Murillo represented beggar children demonstrating street life in a scene from Spanish baroque painting, beginning the genre of portraiture in a way that was far removed from the elitist nobility of Europe.
In this form of Spanish Baroque painting, the Greek influence is fused, so this genre mixes its roots with the Italian school of Titian as well as the Spanish-Flemish painting represented by the artist Antonio Moro and Sánchez Coello.
It shows a simple composition with little ornamentation but that allows us to perceive the human experiences of its protagonists, giving dignity to the portrait as opposed to the counter-reformation, they should not necessarily be captured in images of figures of great renown.
Well, a street child can be portrayed as the monarch of a nation with regard to the genre of the portrait of Spanish baroque painting, a worthy example of this artistic work is El pie varo also known as patizambo made by José de Ribera in the year 1642.
One of the qualities that stands out the most in Spanish Baroque painting with respect to the portrait genre is its austerity compared to other schools, since it represents the soul of the human figures that are captured on the canvas.
A certain point of distrust and melancholy is observed before what life holds from a natural style at the moment of capturing the features of the model far removed from the classicism that most of the theoreticians of the moment defended.
One of the qualities of the counter-reformation is the predominance of the real as opposed to what would be ideal, and it is the genre of the portrait of Spanish Baroque painting.
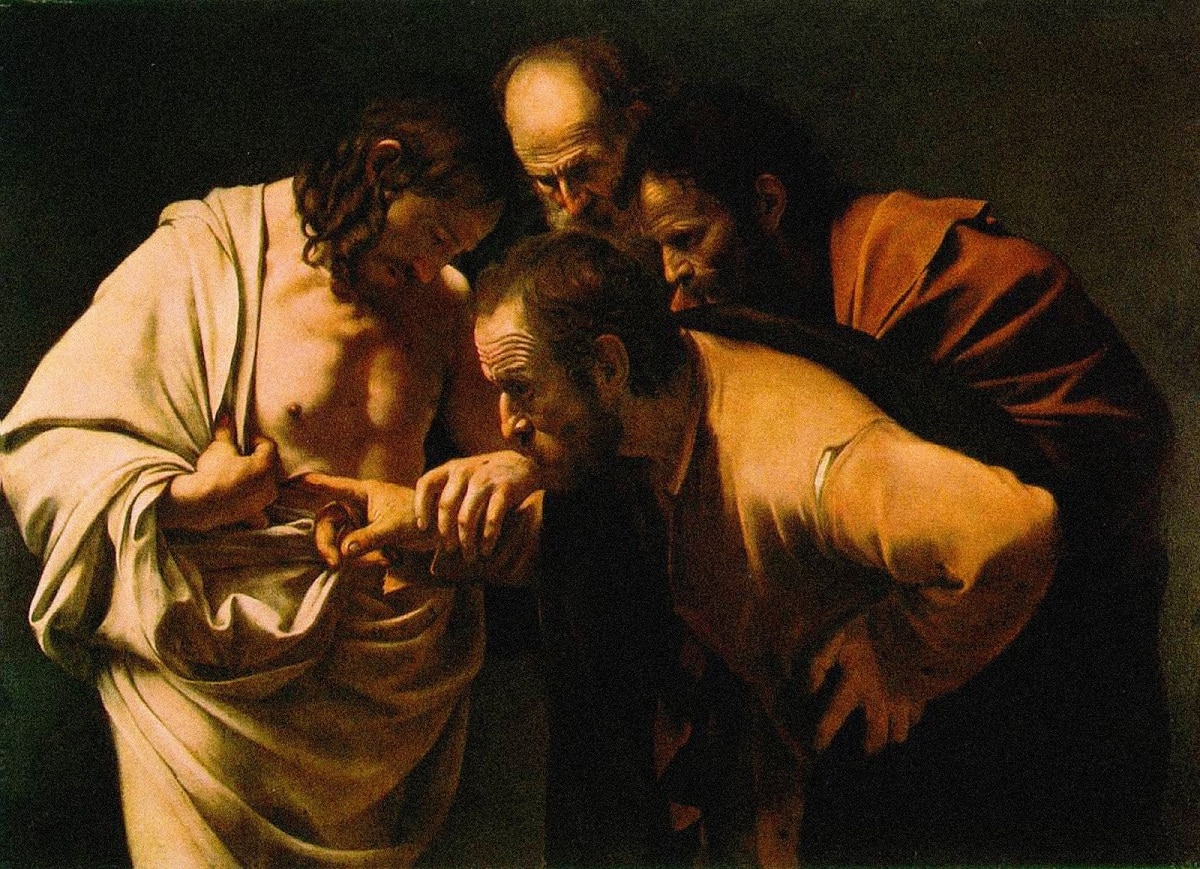

Consolidating in the XNUMXth century with the artistic works of Velázquez as well as the works referring to portraits by Ribera, Zurbarán, Juan Ribalta, this quality was maintained in the artistic works of Goya.
With regard to the portrait genre in Spanish Baroque painting, there are few works related to the mythological or historical field and these examples have been part of collecting.
In relation to the XNUMXth century, the rise of works related to the mythological field stands out in the XNUMXth century, which were not only exhibited on the walls of the palaces, being available to the entire society, allowing a wide range of icons.
With respect to the paintings related to the landscape, which were called countries in Spanish baroque painting, they were treated with less impulse because the human figure was at the pinnacle of art.
According to Carducho's criticism, the landscapes were suitable for residences in the countryside or places of retreat and would be mostly enriched with some sacramental or profane image, which he exposed in his treatise called Dialogues of Painting.

This point of view coincides with the words expressed by Pacheco in regards to his research called Art of Painting where he comments that the landscapes made by foreign artists.
Among them, Cesare Arbasia, Muziano and Brill stand out, who learned this technique from the illustrious Spanish artist Antonio Mohedano, expressing the following:
"... it is a part of painting that should not be despised... but they are matters of little glory and esteem among the ancients..."
According to the investigations that have been carried out, they show that this genre was very important for collectors and, unlike Holland, in the Spanish nation there are no authentic representatives, although the following can be mentioned:
Ignacio de Iriarte, who was active in Seville, as well as Francisco Collantes and Benito Manuel Agüero in the city of Madrid, are noted for their landscape paintings with or without figures, in addition to Antonio del Castillo from Cordoba.
Schools of Spanish Baroque painting
In the first half of the XNUMXth century, large production centers were observed with regard to the movement of Spanish Baroque painting, the main ones being located in the city of Toledo, Seville, Valencia and Madrid.
It is important to note that in the second half of the XNUMXth century, the Toledo and Valencia schools declined in hierarchy, increasing the value of the works of Spanish Baroque painting in the city of Madrid and Seville, but there were always artists of some importance in the various regions of the Spanish nation.
The school in the city of Madrid
At the beginning of the 1575th century, both in the city of Madrid and in Toledo, a range of artists influenced by foreign artists from the Italian nation who came to the Spanish nation to work in the great Monastery of El Escorial, among them Eugenio Cajes stands out between the years 1634 and XNUMX.
In addition to the artist Vicente Carducho, between 1576 and 1638, due to the construction of this distinguished religious temple, great artists of Spanish Baroque painting were trained.
As is the case of Sánchez Cotán as well as Francisco Ribalta who were engrossed with the artistic work of Orazio Borgianni.

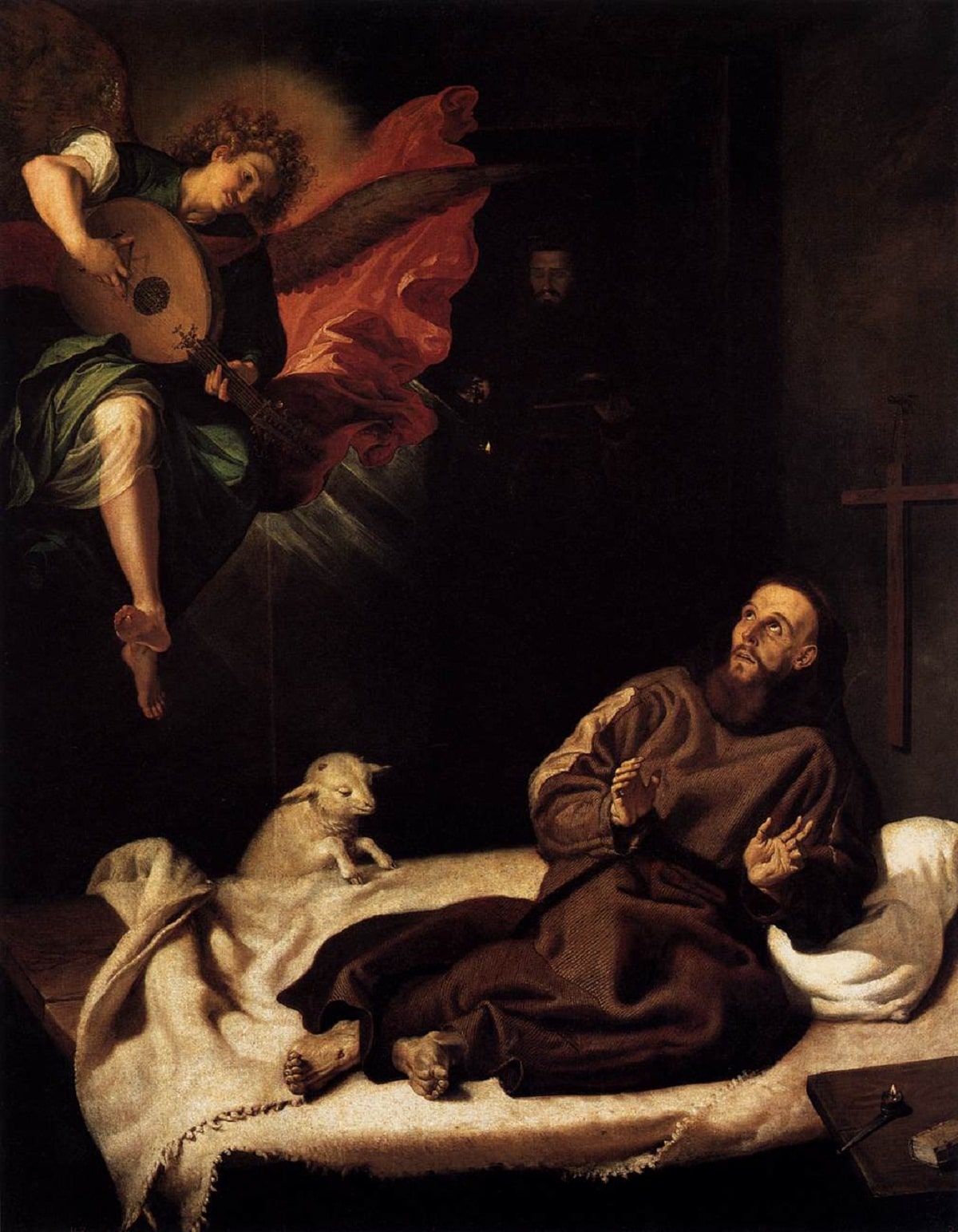
In addition to the pictorial works of Carlo Saraceni which were won for the Cathedral of Toledo thanks to Cardinal Bernardo de Sandoval y Rojas who was a collector and very attentive to all the artistic trends coming from the Italian nation.
Referring to religious topics with great realism in Spanish baroque painting without eliminating the ornament that many in the city of Rome reproached the great artist Caravaggio.
Among those that stand out Juan van der Hamen between the years 1596 and 1631 who was in charge of capturing still lifes as well as religious canvases.
In addition to portraits typical of Spanish Baroque painting, he is followed by the great artist named Pedro Núñez del Valle, who called himself the Roman Academician.
Who was influenced by the classicism of the Bolognese artist Guido Reni who was inspired by Caravaggism and was in charge of capturing landscapes and topics of the religious sphere.

We can also name Juan Bautista Maino between the years 1578 and 1649 who, when traveling to Italy, was impressed with the artistic works of Caravaggio and the artist Annibale Carracci, who was characterized by using light colors and sculptural figures.
The Toledo City School
You should know that in the city of Toledo an artistic school of Spanish baroque painting began, where Juan Sánchez Cotán (1560-1627) stands out, who was an eclectic artist as well as diverse, who highlights his still lifes where fruits and vegetables are evident.
He did not know the work of Caravaggio like Juan van der Hamen who were characterized by a genre similar to that of the Dutch painters such as Clara Peeters and Osias Beert.
As well as artists of Italian origin, such as Fede Galizia, who were contemporary and their interest was in tenebrist lighting.
They were not interested in the complex still life illustrations of other artists of Dutch or Flemish origin. Therefore, Sánchez Cotán's compositions in relation to still lifes are simple, some pieces placed geometrically in the space of the canvas.
It is commented that Sánchez Cotán orders its elements according to the proportion and harmony according to Neoplatonism, although no writings have been found referring to it.
Only naturalism is used to capture as evidenced in the work Still Life with Fruits where he captures a still life containing quince, melon, cucumber and cabbage this work belongs to the Fine Arts Gallery in San Diego.
In this work, the simplicity of four fruits is observed on a geometric frame in the lower part of the left side, highlighting the black color in the center of the canvas as well as in the right half, highlighting the details.
It is a work of Spanish Baroque painting that draws the attention of viewers thanks to the architectural frame where the fruits fit.
Like the pieces referring to hunting, alluding to the cupboards typical of the Spanish region of that historical moment, it also stands out for the illusionist perspective that it gives to the work.
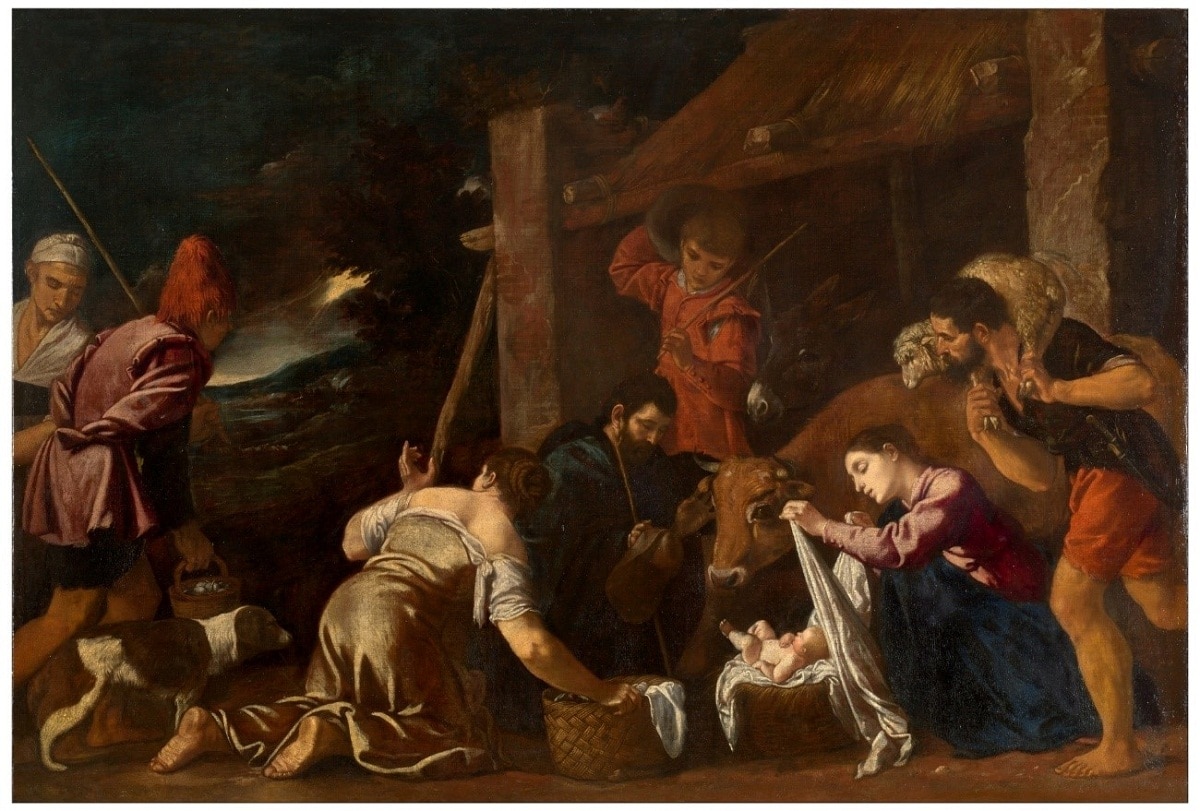

Another of the Spanish Baroque painting artists are Pedro Orrente and Luis Tristán, who was a disciple of the Greco artist when he moved to the Italian nation between 1606 and 1611.
It is characterized by a training in the tenebrist style of a personal court as well as eclectic, highlighting among its works the main altarpiece of the church of Yepes in the year 1616.
Regarding the artist, Orrente also lived in the Italian nation between 1604 and 1612, where he was in charge of working in the Bassano workshop in the city of Venice.
His work carried out in the cities of Murcia, Valencia and Toledo stood out in religious themes, highlighting the realism of the figures, objects and animals.
As is the case of Saint Sebastian in the Cathedral of Valencia in the year 1616 as well as the Apparition of Saint Leocadia in the Cathedral of Toledo in the year 1617.

The school of Spanish baroque painting in Valencia
The tenebrist style artists Francisco Ribalta (1565-1628) and José de Ribera (1591-1652) stand out in this school. They are classified in this Valencian school beginning in the XNUMXth century.
The artist Ribalta was residing in the city of Valencia since 1599 and in this locality the painting had the characteristics of the artist Juan de Juanes.
Ribalta's style was conducive to the counter-reform since in his works a simple composition centered on the characters that showed implicit emotion typical of Spanish Baroque painting was observed.
Among his pictorial works stand out The Crucified Embracing Saint Bernard as well as Saint Francis Comforted by an Angel which are in the Prado Museum.
Another of his works is The Holy Supper of the altarpiece of the Colegio del Patriarca as well as the altarpiece of Portacoeli which is in the Museum of Valencia where San Bruno stands out.
Among his great students, his own son Juan Ribalta stands out, who died very young, as well as Jerónimo Jacinto Espinosa.
His works stand out such as The Miracle of Christ of the Rescue of the year 1623 as well as the Death of San Luis Beltrán in the year 1653 the Appearance of Christ to San Ignacio of the year 1658.
It is important to note that José de Ribera, although he is included in the Valencian school, always worked in the Italian nation since 1611, he was not in Valencia and while in Rome he had contact with the influence of the artist Caravaggio, taking tenebrist naturalism.
His pictorial works highlight the simplicity of apostles and philosophers where he emulated expressions including wrinkles. He settled in the city of Naples and had contact with Velázquez regarding chiaroscuro, which was attenuated by the influence of Venetian classicism.
Among the works that stand out from this great artist of Spanish Baroque painting is La Magdalena Penitente, which is kept in the Prado Museum.

Like the Martyrdom of San Felipe, El Sueño de Jacob, Santísima Trinidad, San Andrés and Inmaculada Concepción, these works belong to the Agustinas de Monterrey in the city of Salamanca.
Another of the representative works of Spanish Baroque painting is La Cartuja de San Martino in the city of Naples, the Communion of the Apostles also captured some canvases referring to landscapes that belong to the collection of the Dukes of Alba in the Palace of Monterrey .
He was also in charge of capturing religious topics commissioned by the Spanish viceroys in the city of Naples as well as mythological themes such as Venus and Adonis, Apollo and Marsyas, The Visit of the Gods to Men, Silenus Drunk without forgetting a series of portraits.
Such is the case of the equestrian of Don Juan José of Austria and the well-known portrait El pie varo that responds specifically to the taste of the moment in Spanish baroque painting, as well as The Bearded Woman for the III Duke of Alcalá.
Regarding the Andalusian School
At the beginning of the 1564th century in the city of Seville, traditional painting with Dutch influence was in vogue, its best representative being the Mannerist artist Francisco Pacheco, who was the father-in-law and teacher of the great Velázquez (1654-XNUMX).

He was a erudite painter who was in charge of making a treatise under the title The Art of Painting that was published after his physical absence. It is essential that you know that a clergyman named Juan de Roelas (1570-1625) was the artist who included colorism to the Venetian artistic style in the city of Seville.
Due to this fact, he is considered the father of Spanish Baroque painting in Lower Andalusia. His works stand out for the bright and colorful Baroque style that has its antecedent in Mannerist style painting.
Among the works that stand out from this representative of Spanish baroque painting, the Martyrdom of Saint Andrew stands out, which is in the Museum of Seville.
You should know that this first generation of artists who represent Spanish Baroque painting ends with Francisco Herrera better known as El Viejo (1590-1656) being the art teacher of his own son Herrera El Mozo.
According to the investigations carried out, this artist with the surname Herrera would be part of the transition from mannerism to the Baroque movement.
Of which he was a promoter thanks to his artistic qualities such as the vertiginous brushstroke and the realism typical of Spanish Baroque painting.
It is essential that you understand that the city of Seville was in full economic boom thanks to trade with America where great artists of Spanish Baroque painting were trained, such as Zurbarán, Velázquez and Alonso Cano.
With regard to Francisco de Zurbarán (1598-1664), he is the maximum representative of Spanish Baroque painting in the religious sphere, for which he was known in his time as the painter of the friars.
His still lifes also stand out, although he devoted himself to them occasionally. One of his qualities is the dark style where he includes a simple and realistic composition of the objects and people that he captured on his canvases.
They highlight large series of artistic works referring to different religious orders of Catholic dogma, among which the Carthusians of the city of Seville stand out, as well as the Hieronymites of the Sacristy of the Monastery of Guadalupe. Among his works stands out:
- Friar Gonzalo de Illescas
- Immaculate
- Friar Pedro Machado
- The Mass of Father Cabañuelas
- Saint Hugo in the Refectory of the Carthusians
- The Vision of Father Salmerón
- Temptation of Saint Jerome
- Santa Catalina

With respect to another great representative of Spanish Baroque painting, Alonso Cano (1601-1667) is considered the founder of the Granada Baroque school. In the first instance, he was a tenebrist, then he changed this style.
Well, he got to know Venetian painting in the royal collections when he was appointed chamber painter thanks to the Count-Duke of Olivares. It is essential that you know that Alonso Cano and Velázquez were friends and classmates.
In the workshop of the master Francisco Pacheco, where he welcomed idealized forms as well as the classic ones, he did not like the realism of his contemporaries.
Among the most representative works of this artist of Spanish baroque painting are the canvases referring to the Life of the Virgin that are currently in the Cathedral of Granada.
Velázquez and his influence on Spanish baroque painting
In this century is the maximum figure of Diego Velázquez being one of the great creative geniuses of the Spanish Baroque painter. This great artist was born in the city of Seville in the year 1599 and died in the city of Madrid in the year 1660.

He demonstrated a great mastery of light and darkness, he was a great portraitist of Spanish baroque painting, with respect to his portraits, he not only captured kings and their families on canvas, but also other figures such as court jesters. .
With respect to these characters, he highlights them with great decency and formality in his profession, he proved in his time to be a great artist recognized by other artists of great renown.
Such is the case of Vicente Carducho, although he was immersed in classicism, he dismissed naturalism as a minor art.
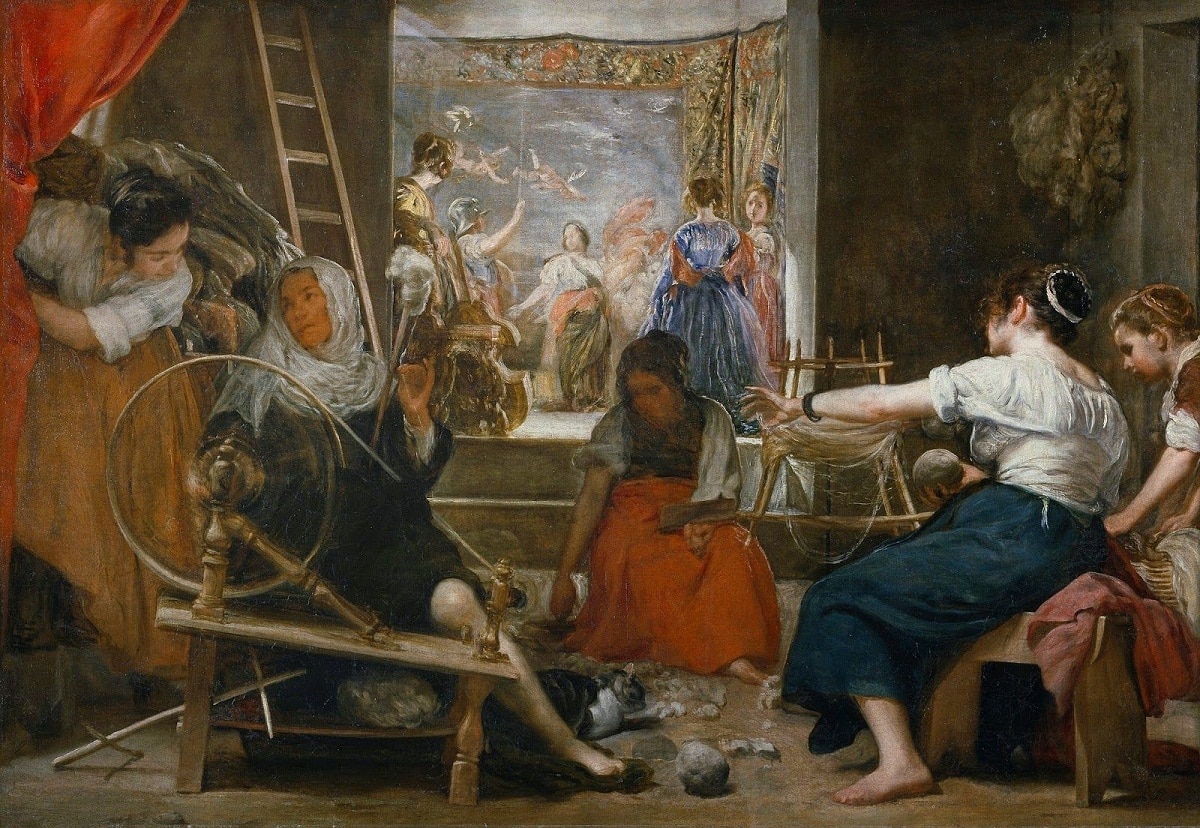
In his beginnings in the city of Seville, the artist Diego Velázquez was in charge of capturing images referring to genre scenes where other painters such as Francisco Pacheco and Antonio Palomino called or cataloged as Still Lifes.
Where they made models of kitchen paintings which were created by artists of Flemish origin such as Beuckelaer and Aertsen from the south of the Netherlands.
That it was under the domain of the Austrians, so there was a great commercial economic boom between the regions of Flanders and Seville.
Being these images the initials in giving fame to this artist because he did not make simple works but genre scenes which can be evidenced in various museums of the Spanish nation.
Highlighting how fascinating these very striking artistic compositions were for European society, among them stand out:
- The Lunch created in 1617 in the Hermitage Museum
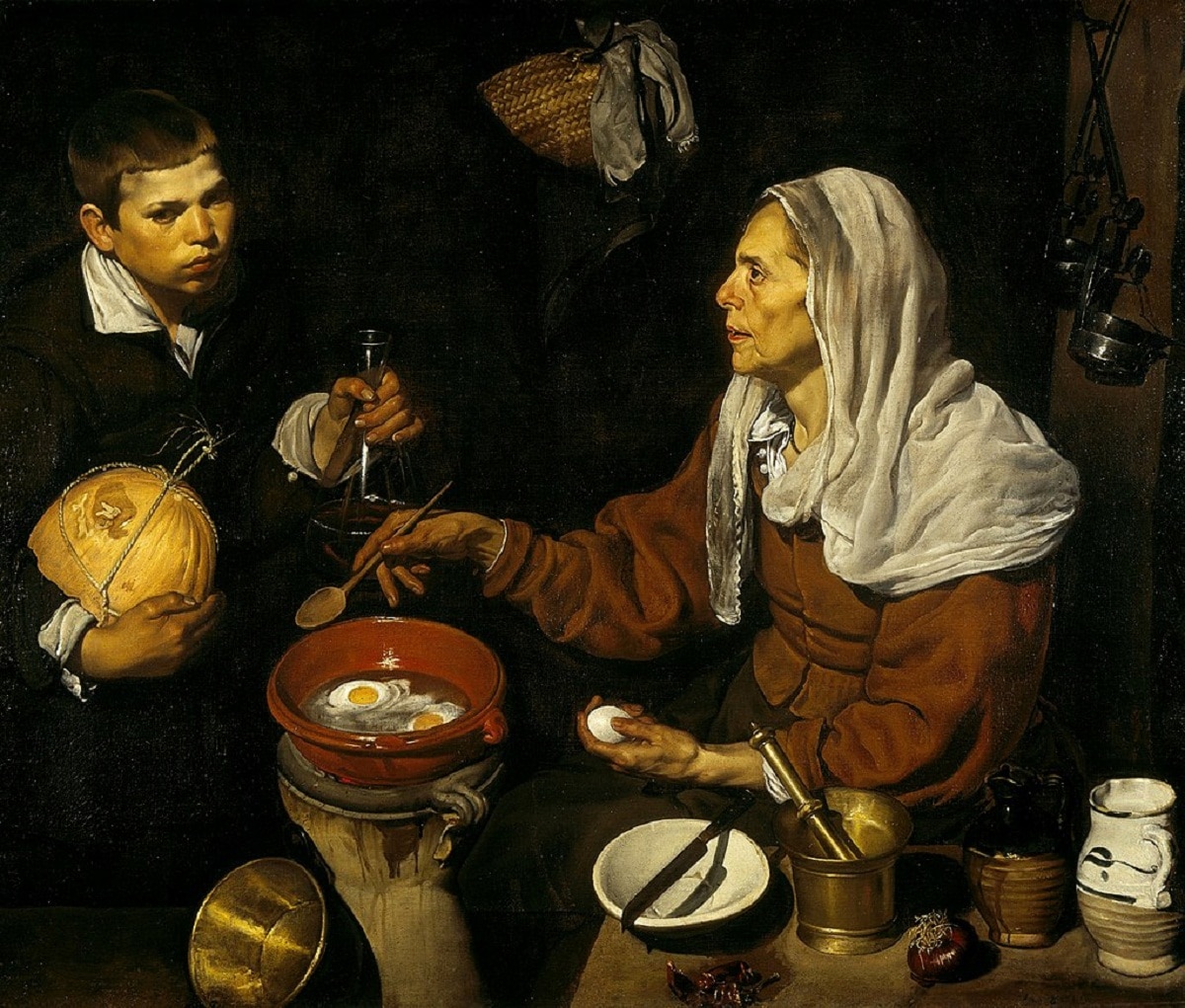
- Old woman frying eggs the year 1618 which is in the National Gallery of Scotland
- Christ in Marta's house from the year 1618 located in the National Gallery of London
- The Aguador de Sevilla created in the year 1620 and is located in the Apsley House
In these scenes, details referring to the distinctive still lifes can be seen where jars made with elements such as ceramics as well as fish are presented.
In addition to eggs with great realism on a canvas that is characterized by the dark atmosphere where he uses a palette with few colors.
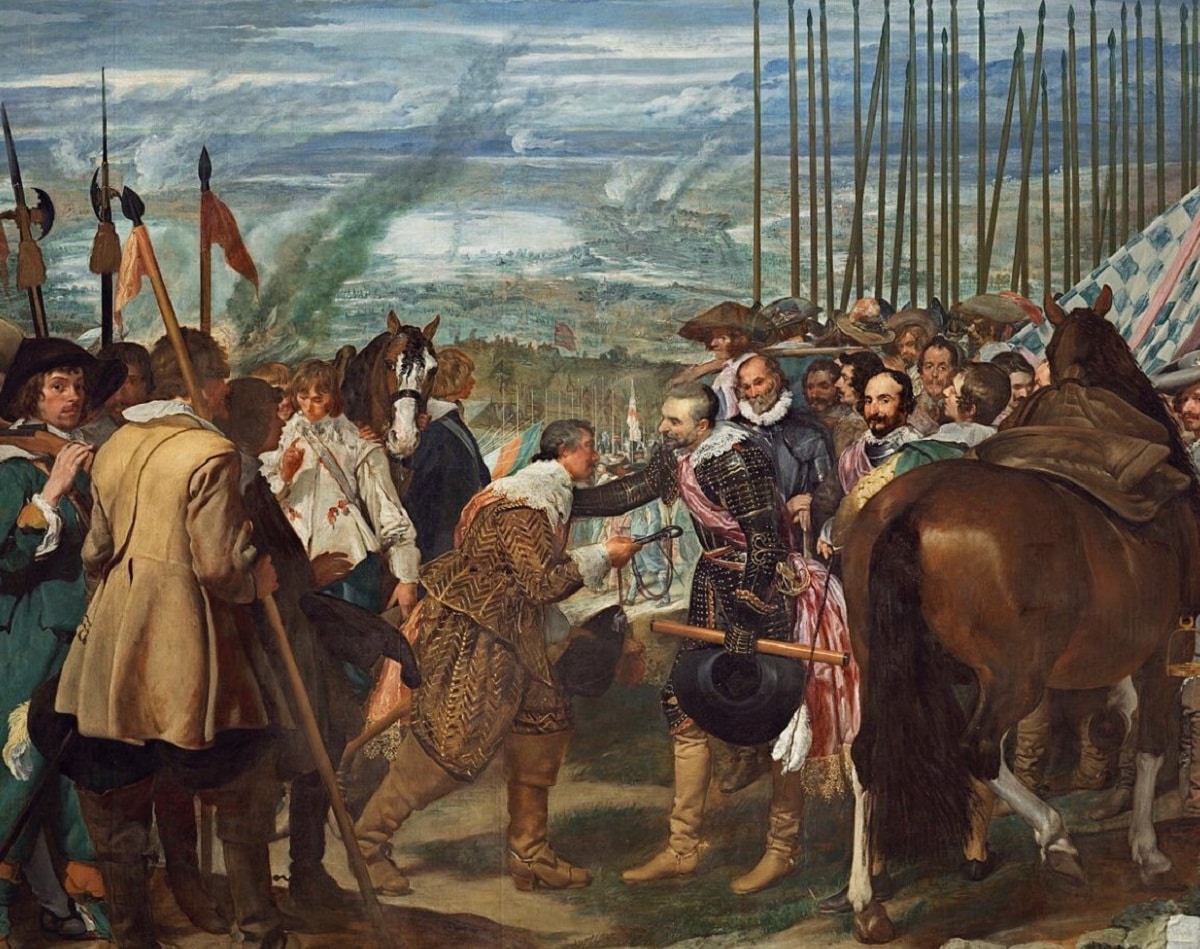
You should be aware that this artist Diego Velázquez not only made artistic works related to the religious sphere, he was also in charge of capturing courtly portraits as well as historical themes, among which The Surrender of Breda stands out.
He also showed excellent work in Spanish baroque painting referring to mythological themes, where The Triumph of Bacchus, The Fable of Arachne, The Forge of Vulcano, among others, stand out.
Among his great creativity are still lifes and landscapes as well as some female nudes typical of this art, such as the Venus of the Mirror.
This great artist of Spanish baroque painting is influenced by the tenebrism of Caravaggio as well as by the great Rubens, allowing the fusion of these currents that stand out in this work of great realistic character typical of Velázquez.

He showed great artistic creative ingenuity in the handling of light and space in Spanish Baroque painting, due to this he is considered a highly relevant figure of tenebrism in the first half of the XNUMXth century and of the Baroque movement in the second part of it. century.
One of its main characteristics is the realistic effect of great depth, showing in its canvases an atmosphere where a dust floats between the figures.
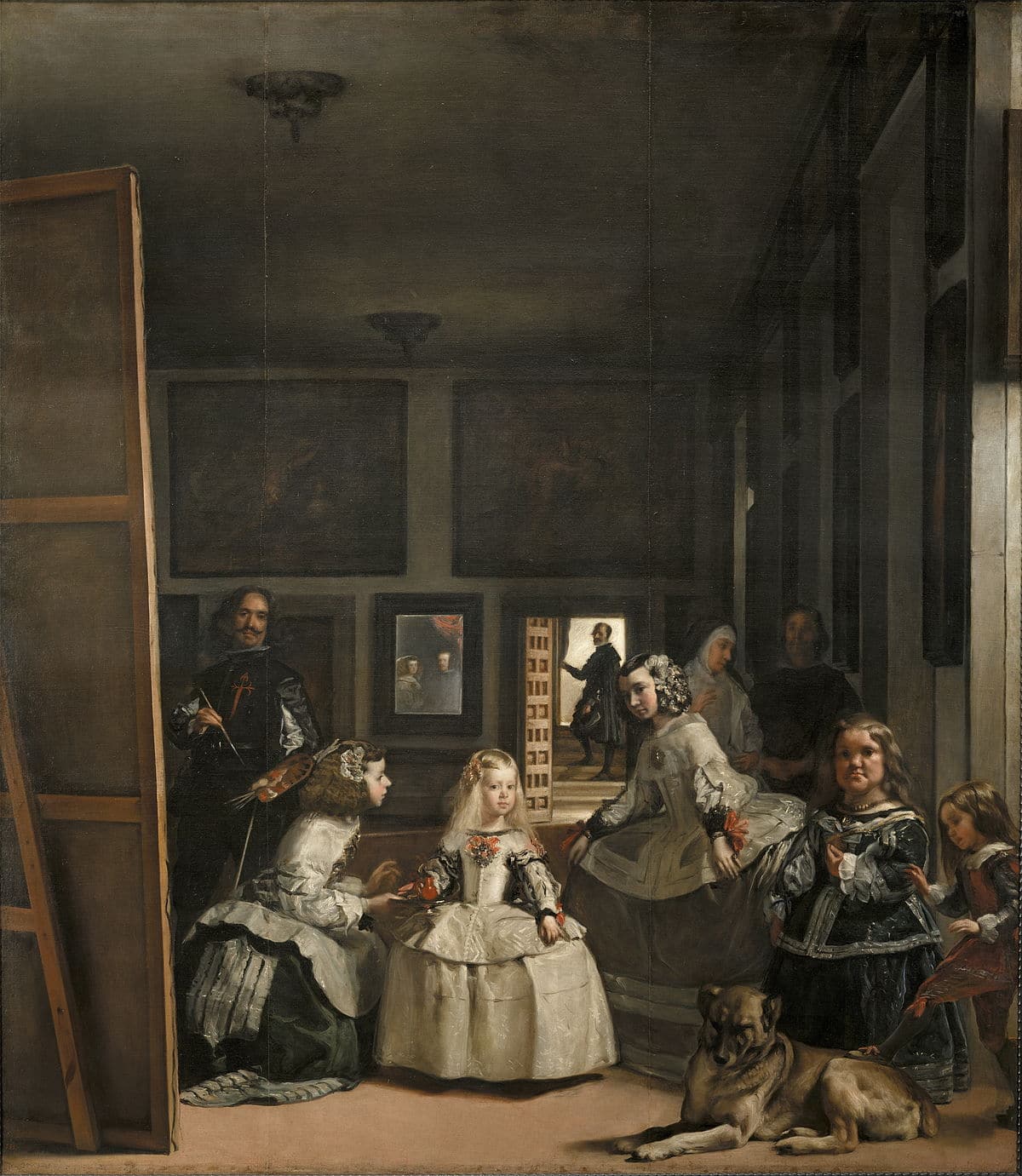
That he captures on his canvases demonstrating a great command of volatile perspective as highlighted in one of his great works Las Meninas.
Amongst Velázquez's works are other great artists, such as the painter Juan de Pareja (1610-1667).
And that of his son-in-law Juan Bautista Martínez del Mazo (1605-1667) who was his assistant after learning the style and became an independent artist.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=macuJDysm0k
Regarding the Second Half of the XVII Century
At this stage of Spanish Baroque painting, it is no longer under the domain of Caravaggio, but the influence of the Flemish Baroque movement of the Rubensian court, as well as the Italian Baroque, is evident.
Other types of paintings are evident where light and shadows do not stand out but a penetrating chromatism is taken into account that alludes to the school of Venetian origin.
In addition, a theatricality is included in Spanish baroque painting, which is something very unique in this Spanish baroque painting.
This type of Spanish baroque painting is used to express the triumph of the Church thanks to the counter-reformation and at the same time it is used to cope with the decline of the Spanish empire.
Added to this art is the ornamental fresco painting on extensive walls and even on the vaults of religious temples and in the imperial courts.

Effects of scenes and optical illusions are observed, themes referring to vanitas enter with the intention of demonstrating to the spectators.
The vanity of earthly objects refers to the fragility of life and how brief its existence can be, hence the importance of enjoying it.
Unlike the Dutch vanitas, in Spanish Baroque painting the religious sphere is reinforced by using supernatural topics for the attention of the faithful of the Catholic Church.
The Madrid School
A transition is observed in Spanish baroque painting from tenebrism to full baroque and among the best representatives of this Madrid school.
Juan Andrés Rizi (1600-1681) stands out among the artists, as well as Francisco de Herrera, better known as El Mozo (1627-1685), son of Herrera El Viejo.

With regard to Francisco Herrera el Mozo, he studied from a very young age in his father's workshop, who was in charge of giving him the first teachings of Spanish Baroque painting, then at a considerable age he moved to Italy and returned to Spain again in 1654.
Upon his return, he spread what he had learned about the decorative baroque of Italian origin, as highlighted in the artistic work San Hermenegildo that is in the Prado Museum, his influence was such that he received the position of president of the Seville Academy.
It is essential that you know that the president of this Academy was presided over by Murillo, although he was absorbed in his artistic work in the city of Madrid with respect to Spanish Baroque painting.
Another of the artists who also represented Spanish Baroque painting at this time was Antonio Pereda (1611-1678) who focused on the religious sphere in various churches and convents in the city of Madrid.
He was in charge of capturing a few vanitas where he expresses the speed with which earthly pleasures end, demonstrating qualities that bring him closer to the still life genre, turning it into a subgenre of it.
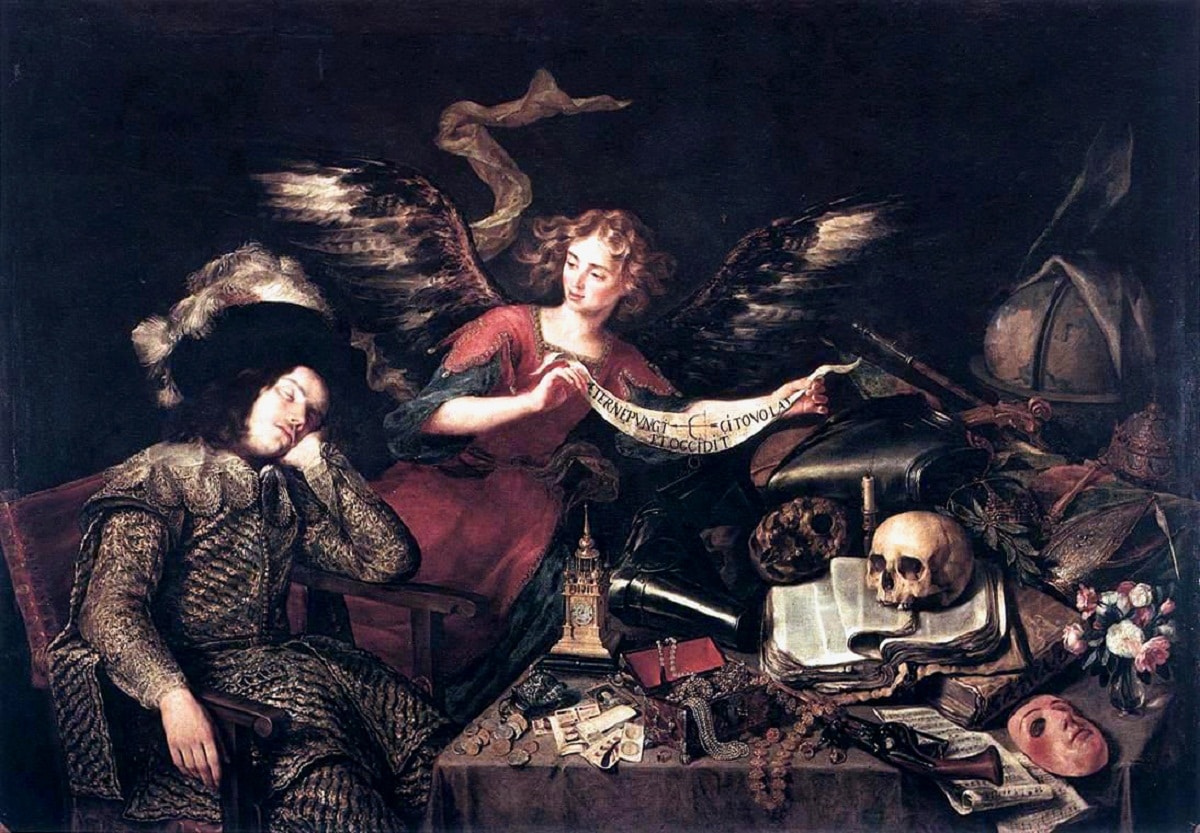
Remember that still life refers to still life and one of this type of Spanish baroque painting by this great artist is El Sueño del Caballero which is in the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando.
Where the gentleman is shown sleeping while in his surroundings a range of vanities typical of this world is observed, highlighting the insignia that grant power such as the globe of the planet earth and crowns, as well as highly appreciated objects such as jewels, money and books.
All this around the skulls and flowers that soon lose their beauty and wither, you can also evidence the light of a candle that is half used, demonstrating that the time of life is fleeting and the angel certifies it because he wears a ribbon that has a few drawings and an inscription:
“…AETERNE PUNGIT; I CITE VOLAT ET OCCIDIT… Time always wounds, flies fast and kills…”
This is like a warning to viewers of Spanish Baroque painting where the artist Antonio Pereda wishes to express through art the following:
“…The fame of great deeds will vanish like a dream…”

Another example that can be evidenced is the artistic work Allegory of the Vanity of Life that is in the Kunsthistorisches in the city of Vienna.
The work shows a figure with wings and around it the topics of the previous work are repeated, such as the globe, skulls, a clock, as well as money.
Although in other representative works of Spanish baroque painting in terms of vanitas they may contain few elements such as the skulls and the clock.
As can be seen in the Zaragoza Museum where he will accommodate them according to his creative ingenuity, allowing complex compositions.
Spanish baroque painting of this second half of the century is represented by several artists, among which we can mention the following:
- Francisco Rizi (1614-1685) who was the brother of Juan Ricci
- Juan Carreño de Miranda (1614-1685) being the second best portraitist
- Diego Velázquez is the best portraitist of Spanish baroque painting, his paintings of the widowed queen Mariana of Austria and Charles II being very famous.
- Mateo Cerezo (1637-1666) disciple of Velázquez and admirer of Titian as well as Van Dyck

We can mention other representative artists of Spanish Baroque painting, such as José Antolínez, who was a student of the artist Francisco Rizi.
Who had a great influence of Venetian and Dutch origin was the author of various works in the religious field, highlighting his artistic works referring to the Immaculate Conception.
The influence of Velázquez is observed with regard to the color palette used where silver colors are selected. We can also tell you about Sebastián Herrera Barnuevo who was a student of the artist Alonso Cano.
In addition to being an architect, he was a painter and sculptor. His artistic works related to portraiture stood out, demonstrating a style similar to the Venetian school, as is the case with Veronese and Tintoretto.
To finish with the Madrid school, one of its last representatives of Spanish Baroque painting corresponds to the Madrid-born artist Claudio Coello (1642-1693) who specialized as a court painter.
Although his best artistic works are related to the religious sphere as well as drawing and perspective influenced by Velázquez.
Plus a great theatricality that alludes to the artistic works of Rubens such as the work The Adoration of the Sacred Form as well as the Triumph of Saint Augustine.
The Andalusian School
The Spanish baroque painting that is represented by the artist Murillo as well as another great artist named Valdés Leal who were the founders in the year 1660 of the Academy of Seville where a large number of painters were affiliated.
The full name of this great representative of Spanish baroque painting is Bartolomé Esteban Murillo (1618-1682). He is especially admired for his work referring to the Immaculate Conception as well as the representations with great feeling of the Child Jesus.
Although in his historical moment Murillo was highly appreciated thanks to the genre scenes, such is the case of the boys who demonstrate how to live in marginality, examples of them are: Children eating fruit and the Child looking out the window.

Demonstrates a transformation of Spanish baroque painting, leaving behind the tenebrist style with regard to its first period, the following works are recognized: La Sagrada Familia del Pajarito and the Cycle of the Convent of San Francisco in the city of Seville.
Then, through his artistic works, it is evident that the brushstroke becomes lighter and is enriched with the color palette, allowing a much looser and more agile brushstroke.
It is observed that Murillo captured images that were adapted to the taste of bourgeois society where the canvases represent artistic works with soft themes without drama, eliminating the negative aspects of daily life.
With regard to the religious sphere of Spanish Baroque painting, Murillo made a large number of artistic works, including The Martyrdom of Saint Andrew, The Good Shepherd, Rebeca and Eliezer, Saint Justa and Rufina, The Annunciation, as well as various versions referring to The Immaculate Conception. Conception.
This last image became an emblematic model that continued to be copied throughout the century without neglecting the half points he made for the Sevillian church named Santa María La Blanca con el Sueño del Patricio without forgetting the very elegant portraits similar to those by the artist Van Dyck.

We can also mention the artist of Cordoba origin Juan de Valdés Leal (1622-1690) two of his works are well known today as is the case of the Decadences he created for the Hospital de la Caridad in the city of Seville.
They are excellent complex compositions where the triumph of death over life is observed. Death is symbolized through skulls and skeletons while vanities are represented through books and armor.
Where it shows that death does not make class distinctions as it is stated in the work Dances of Death. It is observed that Valdés Leal's style is dynamic and even violent where he is in charge of giving priority to color over the drawn work.
In relation to the eighteenth century
With regard to the first years of the XNUMXth century, it is observed that Spanish baroque painting is maintained until a new artistic movement known as Rococo is introduced, which has great influence from the French nation.
In the mid-eighteenth century, the Bourbons arrived in the Spanish nation and were responsible for bringing a large number of foreign artists to the Spanish court, including Louis-Michel Van Loo, Michel-Ange Houasse and Jean Ranc.
Despite this, in various regions of the Spanish nation, the work of the School of Seville was continued, as is the case of the disciples of the artist Murillo until the year 1750 and although the court produced transformations with regard to painting.
In religious temples and the regional nobility remained faithful to Spanish Baroque painting, which is why a continuity of this art is observed until the XNUMXth century.
Among the artistic figures that represent the transition from Spanish Baroque painting is Acisclo Antonio Palomino (1655-1726) who was in charge of a great artistic activity during the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries.
He first began the religious profession but it was abandoned thanks to his passion for Spanish Baroque painting. He moved from his hometown of Córdoba to the city of Madrid in 1678 where he received classes from the artists Claudio Coello and Carreño.
After ten years of study and practice in the year 1688 this great artist ascends to the position of painter of the king for that reason he receives among his assignments to paint the vaults of the Chapel of the City Hall of the city of Madrid work that he carried out between the years 1693 and 1699 .

He also worked together with another great painting artist such as Luca Giordano who taught him everything related to the Baroque of Italian origin.
In the years 1697 and 1701 he is in charge of making the frescoes of the Church of the Santos Juanes located in the city of Valencia then in another period of time 1705 and 1707 he is commissioned to decorate the Convent of San Esteban in the city of Salamanca.
With respect to the beginnings of this artist, it is framed in the style of the Madrid School with the influence of the artist Claudio Coello but after the interaction with Gordano he clarified the color palette that he used in Spanish Baroque painting.
After that, he was in charge of making sublime complex compositions where he demonstrated an excellent mastery of the sketch.
We can mention another figure of great relevance in Spanish baroque painting of this historical moment, such as Miguel Jacinto Meléndez, who lived in the city of Madrid and knows Palomino.

He was also promoted to the position of painter to the king in 1712 and was commissioned to make portraits of Felipe V and his family as well as the religious sphere thanks to the influence of Claudio Coello and Francisco Rizi.
Adding to his Spanish baroque painting great care and color that infers Rococo influence, being an example of this the following artistic works The Annunciation made in the year 1718 in addition to The Holy Family in the year 1722.
With respect to the city of Valencia, the artist José Vergara Gimeno (1726-1799) stands out. He was also in charge of assuming the influence of Palomino with regard to Spanish Baroque painting.
Specifically in its extensive and complex compositions made through the fresco technique, it was updated through the formulas used by another artist of great importance, such as Juan de Juanes y los Ribalta.
He was in charge of creating other new artistic styles that allowed him to introduce it into the neoclassical and he was in charge of founding in 1768 the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Carlos.
In the company of his brother Ignacio and this institution will allow him to give dignity and respect to the normative studies of Spanish Baroque painting.
To end this great century of Spanish baroque painting is the Catalan-born artist Antoni Viladomat who collaborated with a great artist of Italian origin.
Being Ferdinando Galli Bibbiena at the time when the city of Barcelona was the seat of the court of Archduke Carlos of Austria.
Who was a candidate for the Spanish crown thanks to his influence on the Spanish nation, the rise of the style of the artist Antoni Viladomat was observed, where he oscillated a fusion with the naturalism of the School of Seville and Spanish Baroque painting.
Among the paintings that stand out by this artist are those made inside the chapel of Los Dolores de Mataró in 1722, the serial scenes referring to the life of San Francisco that are today in the National Museum of Art of Catalonia in the year 1727.

Another of the artistic works in which this great artist stood out refers to still lifes and genre scenes, among which we can mention the Four Seasons found in the National Art Museum of Catalonia.
Spanish baroque painting in the viceroyalties of America
As evidenced in the Spanish viceroyalties in the continent of America, the first influence that was observed in Spanish baroque painting was related to the tenebrism of the school of Seville.
Among those that appear is the influence of the artist Zurbarán, part of his artistic works referring to Spanish Baroque painting in the nations of Mexico and Peru can still be seen.
Which can be seen in the artistic works of painters of Mexican nationality, such as Sebastián López de Arteaga and José Juárez.
You can also appreciate the work of the Bolivian artist Melchor Pérez de Holguín. With respect to the Peruvian nation, specifically in the city of Cuzco where the influence of the School of Seville is observed, it was interpreted in a unique way with the use of highly appreciated materials such as gold.

In addition to the very peculiar style of the natives of the American continent that enriched Spanish baroque painting with respect to the Cuzco School of painting, it emerged thanks to the Italian-born painter Bernardo Bitti in 1853.
For which he introduces mannerism in America among the pictorial works that stand out from this historical moment are Luis de Riaño was a student of Angelino Medoro who was in charge of making the murals of the Andahuaylillas temple.
Other artists of native origin who stand out in Spanish Baroque painting include Basilio Santa Cruz Puma Callao, Diego Quispe Tito.
Like Marcos Zapata who was responsible for making the fifty paintings of enormous volume that are responsible for dressing the high arches that the Cathedral of Cuzco presents.
With respect to the eighteenth century in relation to the altarpieces made in sculpture, they are supplanted by artistic works of Spanish baroque painting in the American continent, and there was also at this historical moment a boom in the demands for artistic works with respect to the civil sphere.
Especially in the genre of portraiture by the aristocratic society of the time in the American continent, as well as the Catholic Church, he was an excellent client for the artists of Spanish Baroque painting.
You should know that the main influence of Spanish baroque painting comes from Murillo and in some cases the influence of other artists can be observed, such is the case of Cristóbal de Villalpando who obtains his influence thanks to the artist from Valdés Leal.
Regarding this type of Spanish baroque painting of this historical moment in the American continent, it is highlighted through emotion, its forms are sweeter and among the artists Gregorio Vázquez de Arce, a native of the Colombian nation, stands out.
In relation to the Mexican nation, great artists of Spanish baroque painting stand out, such as Miguel Cabrera and Juan Rodríguez Juárez. It is essential that you understand that the moment of greatest boom of this art occurred between the years 1650 and 1750.
Several artists of great prominence in Spanish baroque painting take place simultaneously in various regions of the American continent, among which Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico and Peru stand out.
In addition, Spanish baroque painting in this American continent was impregnated by the mythological sphere where the triumphal arches that are built at the entrance of the residences of the viceroys and other characters of noble society stand out.
Without forgetting the preponderance of capturing scenes from the Bible where the counter-reformation is promoted, an example of this was the city of Quito under the orders of the Dominican friars as well as the Jesuits.
Legacy of Spanish Baroque Painting
It is essential that you take into account that Spanish Baroque painting marks an interesting point in the history of art thanks to its great influence in the region of Spain.
This current was of great importance throughout the European continent during the XNUMXth century and part of the XNUMXth century, with Spanish Baroque painting being a new way of expressing art.
In a historical moment where the plague causes a large number of deaths and the Catholic Church faces its first crisis.
That he tries to solve thanks to the counter-reformation and thanks to Spanish baroque painting, the passion for faith, peace and services such as mercy is captured, demonstrating great spirituality in the religious sphere.
So the Catholic Church tried to find in Spanish Baroque painting a way to make the faithful believe in Christian dogma by making a realistic similarity of what was expressed in artistic works.
Although an exaggeration was observed in the proportions of the images made in Spanish Baroque painting, which served to give intention of movement thanks to the optical illusion, for which it was later underestimated by a large number of artists.
The use of chiaroscuro stands out in Spanish baroque painting, being the contrast that is observed in his artistic works, allowing a fusion.
Between the dark areas and the areas that are fully illuminated, remember that it is a work with great luxury in the use of the color palette.
The colors used are intense and highlights the use of gold and silver in the scene captured on the canvas with the incorporation of contrasting colors.
Such is the case of burgundy, violet and red showing a sumptuous exaggeration and pleasing to the eye of the viewer, the presence of black is common for the contrast of Spanish Baroque painting.
Conclusion
During the mid-seventeenth century and the first part of the eighteenth century, Spanish baroque painting reached a moment in history imbued with genius and creativity, which is why it is known as the Golden Age.
Thanks to the diversity of artistic disciplines, although the Spanish nation is in a serious economic and health crisis, great schools of Spanish Baroque painting are developed in various regions of the country, such as Valencia, Madrid, Seville and Toledo.
One of the main qualities of Spanish baroque painting is realism thanks to the play of light and shadow coupled with the complex compositions that allow an optical illusion that generates movement in the works captured on the various canvases.
The Catholic Church, thanks to the counter-reformation movement, uses Spanish Baroque painting to increase the faith of the believers of this dogma, allowing a growth of the faithful in relation to the Protestant church.
It is essential that many artists of the Spanish nation took the influence of Caravaggio and tenebrism to capture great artistic works on their canvases.
You should know that Diego Velázquez is the maximum representative of Spanish baroque painting, among the works that stand out the most from his hard work are The Triumph of Bacchus in the year 1628, Venus and the Mirror elaborated in the year 1647.
His important works are followed by Las Meninas, which he produced in 1656, not to mention a mythological work of great prominence, such as the Fable of Arachne, which he produced in 1657.
After Spanish Baroque painting, a new movement arose in the second half of the XNUMXth century from the nation of France, which spread throughout the European continent, such as Rococo.
If you found this article interesting, I invite you to visit the following links:


