In this article we bring you relevant information about the mesopotamian art. Also, what is the origin of the Sumerian civilization and how it was enhancing its culture through the study and Mesopotamian art? Keep reading and find out more!

Mesopotamian art
Mesopotamian art refers to a region or locality which is located in the Middle East and is located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, that is why the word Mesopotamia translated into Spanish means "The land between two rivers" this territory is It will extend throughout the area of both rivers, having very fertile lands and it will coincide with non-desert areas found in present-day Iraq. Although the term Mesopotamia was used in ancient times.
That is why it should be noted that Mesopotamian art will be a geographical and chronological division of the city during ancient times, since many cultures refer to the artistic expressions that occurred in Mesopotamia. From the Neolithic period that is located in the sixth century BC until there was the fall of Babylon against the Persians in the year 539 BC.
Throughout this period, various civilizations developed, such as Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian (or Chaldean), Kassite, Hurrian (Mittani) and Assyrian (Assyrian art). After thousands of years passed, there was a great domain of Lower Mesopotamia and Upper Mesopotamia in the entire region. Until the Persian Empire began to form, which had a much higher spatial order than the Empire of Alexander the Great and Hellenism.
Mesopotamian art had various routes of contact even long before the time of the Persians. It also had connections with the Roman era and with Hellenistic art, there were many ways of contact, among which diplomacy, trade and war stand out.
There was also a connection between Mesopotamian art and various civilizations that lived in the Ancient Near East, such as the arts of the Hittite civilization, the art of the Phoenician civilization and the art of the ancient civilization of Israel. Other civilizations that stood out at that time for their art and had connections with Mesopotamian art are the art of India, the art of Egypt, the art of the Levant of the Mediterranean and many areas of the Central Asian region.
In Mesopotamian art, there was a great endogenous cultural diffusion, as well as the use of various materials and artistic techniques for the development of different works of art, for which it contributed to many scientific advances, which highlight the potters' ovens that were more efficient and then it gave way to the design of glazed ceramic kilns and metallurgy kilns.
Among the social and cultural advances of Mesopotamian society was the birth of a society dedicated to writing and religions, institutions were created that were governed by the government that directed the city. Many art specialists have come to affirm that a very complex civilization.
Currently, much Mesopotamian art is preserved, but it is a subject that has brought a lot of controversy because many archaeologists and orientalists, since the beginning of the XNUMXth century, took the most valuable pieces of Mesopotamian art to different museums on the European continent and the United States. .
That is why there are currently collections of Mesopotamian art in several European museums, including the British Museum in London, the Louvre Museum in Paris and the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
While currently the findings that have been made on Mesopotamian art have directed the works to the National Museum of Iraq, but the war that exists in that country has caused deterioration and looting of the existing pieces that have a price of no less than 10 thousand American dollars.
History of Mesopotamia
In the civilization of the region of Mesopotamia during the years 6000 and 5000 a. C. livestock and agriculture were imposed, that was the entrance to the Neolithic period where the new production strategies that were being designed in the initial Neolithic area were implemented.
These strategies were developed and spread throughout the region, among which Lower Mesopotamia stands out, which resulted in many cities developing more than others, among which the city of Buqras, Umm Dabaghiyah and Yarim stand out, and then the cities of Tell es-Sawwan and Choga Mami, giving way to a new culture that was called Umm Dabaghiyah.
Later this culture was replaced by the Hassuna-Samarra cultures, located between 5600 BC to 5000 BC and between 5600 BC to 4000 BC, the Halaf culture emerged. With the passage of time around the year 3000 a. C in the region of Mesopotamia writing began to be used. But its main purpose was to keep the administrative accounts of the community.
The first writings that were found by archaeologists were made in clay, the use of clay was very frequent in the Mesopotamia area, the writing was made up of several drawings in the form of lines that are known as pictograms.
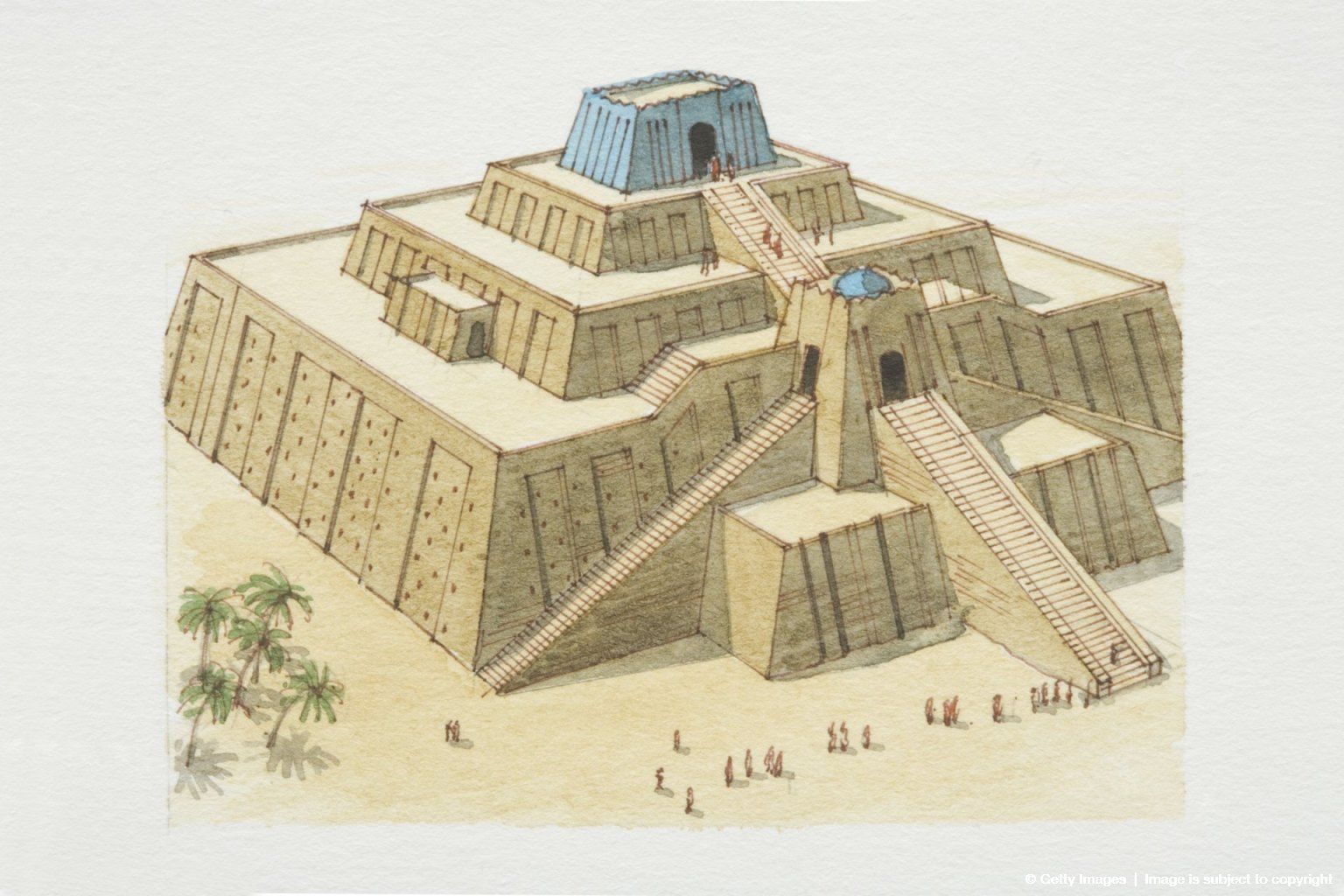
Urban civilization in the Mesopotamian region continued to make technological advances during the Obeid period which is set between 5000 BC and 3700 BC. These technological advances focused on new developments in the Mesopotamian art of ceramics. and in irrigation. The first urban temples for the worship of the gods also began to be built.
Once the Obeid period is over, the Uruk period is born. In this period, the urban civilization of Mesopotamia began to settle in the region, making great technical advances such as the wheel and calculation. Where the calculations were written down on clay tablets to keep an order. This would be the first representations that would be made of writing in Mesopotamia.
The Sumerians
In the year 3000 BC, the civilization of the Sumerians began to develop several cities in the lower part of Mesopotamia, among which Eridu, Ur, Ea, Uma, Kish, Lagash and Uruk stood out, which were also known as city-states. .
The main economy and food source of these cities was based on irrigation. These cities were governed by an absolute king who would have a position known as a vicar. Because he had the power to communicate with the gods and protect the cities from different natural hazards.
In the history of the Sumerians, it stands out that it was a civilization in cuneiform writing and they built great temples for the worship of their gods, which meant a great advance in Mesopotamian art.
The Archaic Dynasty Period
While the Uruk civilization that lived in the region of Mesopotamia was acquiring great advances in Mesopotamian culture and art, it was giving birth to the Sumerian culture. Because many of the techniques that were used in Mesopotamian irrigation, economy and art were being used in various cities and in the new territories that were being occupied in the other regions of Mesopotamia.
Many of the new cities are going to stand out because they built walls. But the studies carried out by archaeologists have described that they were raised by the various wars that took place at that time. It also highlights writing as a Mesopotamian art, since it was used in the administrative area, as in the technique to write dedications on the statues that they offer to their gods.
It is necessary to emphasize that there are many Sumerian royal lists. But this history is not very well documented since it is very unknown because there were many kingdoms with dates that are impossible and in the XNUMXth century BC the kings began to make royal lists since those monarchs wanted to know what their lineage was from epic times.
That is why many of the kings of the archaic dynasty may be true but many others are not, they were invented by other kings and there is no historical evidence that they have existed and there are no physical figures of these kings.
The Akkadian Empire
Around the same year 3000 BC, the Semitic civilization was known as nomads who were inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula, and they spread north to found new civilizations such as the Amorites, the Phoenicians, the Israelites and the Arameans. While in the region of Mesopotamia the Semitic peoples, the civilization that had the greatest influence were the Akkadians.
During the year 2350 BC, a king known as Sargon I of Akkad, who had Akkadian lineage, invaded the city of Kish and seized the power to rule it. The first thing he did was found a new capital. Which he called Agade and this gave rise to start several battles to conquer all the Sumerian cities. He defeated the king of these cities known as Lugalzagesi.
All this was known as the first empire in the history of the world and would be led by the successors of Sargon who had to face the continuous revolts that were carried out to overthrow the Empire. Among the kings who stood out the most was his grandson and conqueror Naram-Sin. It was a period where the culture of the Sumerians declined and the culture of the Akkadians rose.
But in the year 2220 BC the Empire fell due to the many revolts they had to face and the nomadic invasions of the Amorites and the Gutis, when the empire fell the entire region was dominated by these tribes. That promoted its culture and its art in the different city states of Mesopotamia. Where he emphasized the most was in the main city Agade that all its surroundings were destroyed.
The Sumerian chronicles dating from that period describe these events as very negative for society as a group of barbarians and mountain dragons that came to the city to destroy everything in their path. But some archaeologists have shown that this fact was not so bad, because in several cities there was a great flourishing in Mesopotamian culture and art.
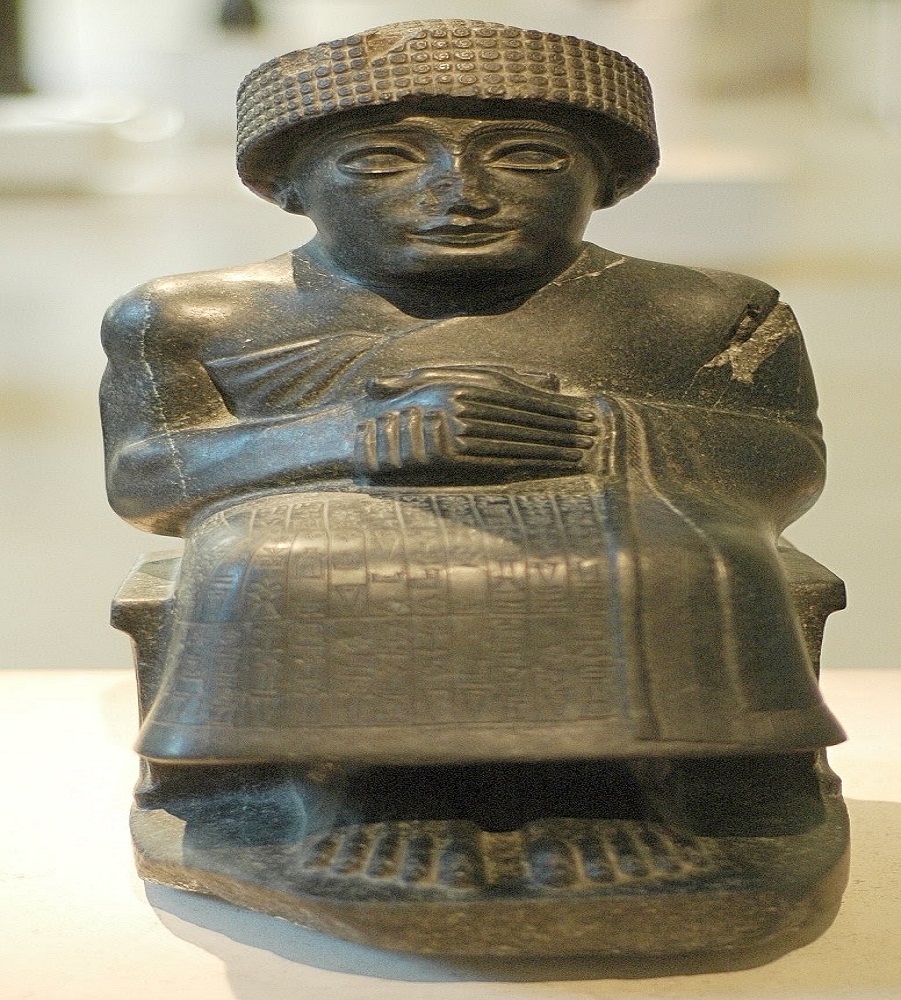
A very clear example of this fact occurred in the city known as Lagash, during the rule of the ruler Gudea, who emphasized Mesopotamian art, raising its quality since the works that were made in this Lagash city had very high quality materials. and they came from cities far away such as Lebanon or diorite, gold and carnelian from the Indus Valley.
Due to this characteristic, archaeologists think that the trade was not, since the transfer of this material was going to be very expensive. That is why many people who lived in the southern cities wanted to buy the freedom of their relatives in exchange for valuable materials for the development of the Mesopotamian economy and art. The cities of Uruk and Ur during the XNUMXth and XNUMXnd centuries prospered greatly and their dynasty was highly respected.
The Sumerian Renaissance
In the tablet found by the researchers it is named Utu-hegal, who was the king of the city of Uruk. Who is listed in the years 2100 BC because he led his army to defeat the rulers of the city of Gutis in Sumerian territory. But he did not know how to take advantage of this success since shortly after he was dethroned by Ur-Nammu, who was the king of the city of Ur.
Then the city became a hegemonic city in the entire Mesopotamian region during the third dynasty of the Ur. Although many specialists have called it the rebirth of the Sumerian culture. The Sumerian empire that emerged through hegemony lasted as long as the empire of the Sargon dynasty.
After this, the theory of the unified Empire germinated in the region of Mesopotamia where the monarchs adapted to the system of government of the Akkadians who called themselves "the kings of Sumer and Acad" in the city Ur-Nammu where the kingdom will be in charge of the son Shulgi who faced the eastern kingdom of Elam and the nomadic tribes of the Zagros.
Then his son Amar-Suen takes power, then the brother named Shu-Sin takes power. To finish with the Ibbi-Sin. As the third king in succession to the throne of the civilization of the Sumerians. But in this reign the civilization of the Amorites who come from Arabia who become strong due to the advancement of their technology and culture until in 2003 BC the last Sumerian empire falls in the region of Mesopotamia.
Then the culture that will predominate in the region of Mesopotamia will be that of the Babylonian civilization that inherited many characteristics and customs of the Sumerians.
The Amorite dynasty
When the hegemony of the city of Ur fell, this time the same history of darkness was not repeated for the population, since this stage was marked by an ascent of the dynasty of the Amorites who had greater culture and were more prepared to live in a better environment. civilization.
During the first 50 years of civilization, the Amorites lived in a city known as Isin, which tried to impose itself on the entire region of Mesopotamia but without any success. Then in the year 1930 BC, the monarchs of the city of Larsa launched to invade other cities in the region, attacking the city of Elam and Diyala as their main objective, ending with the city of Ur.
But the objective was not fully achieved since he did not obtain complete control of the Mesopotamia region. But he obtained a clear hegemony from the Paleo-Babylonian Empire of Hammurabi, but his hegemony fell between the years 1860 and 1803 a. C since the city of Uruk with its army decide to challenge the hegemonic power they had for the leadership they exercised throughout the region.
In the city of Elam, the culture of the Akkadians made the kingdom of this city much stronger, which was introduced more into the politics that was exercised in the Mesopotamian region.
While in the well-known northern Mesopotamia stronger cities arose that were reformed by the trade and economy that was practiced between the southern cities and that of Anatolia, where the kingdom of Assyria will stand out, where it will expand throughout the territory until reach the Mediterranean led by the king of Shamshi-Adad I.
The paleobabylonian empire
According to the investigations carried out, Hammurabi came to the throne in the year 1792, where the city of Babylon was of little importance to the region of Mesopotamia. During that time the pharaoh will begin a policy of expansion throughout the region. In one of his first strategies was to liberate the city of Ur in the year 1786.
After facing his army and overthrowing the king of Larsa, known as Rim-Sin. He also seized control of the city of Uruk and of Isin. With the help of various armies that joined his cause. In the year 1762, he defeated the coalition that existed between the cities that were on the banks of the Tigris River.
So that after a few years they decided to invade and conquer the city of Larsa after this maneuver the king could proclaim himself as the governor of the city of Sumer and Acard. This title had been used in the times when he led Sargon of Akkad. And it began to be used by each monarch who began to occupy the throne either by conquest or by succession. Throughout the region of Mesopotamia.
With the passage of time, the image of the monarchs became widespread, since the various conquests but also the use of a construction activity and maintenance of various irrigation systems and in the elaboration of a system of laws that had to be fulfilled as the well-known Hammurabi code.
In the year 1750 BC, the monarch Hammurabi died, giving his entire empire to his son Samsu-Iluna, who had to face several battles against the Kassite nomads. This situation is repeated several times until in the year 1708 BC, in the reign of Abi-Eshuh. Many problems of the house nomads had multiplied.
This pressure was frequent throughout the seventeenth century BC, the empire was wearing down until the last attack of the Hittite king, Mursili I, settled the empire which fell under the power of the nomadic Kassites.
Characteristics of the History of Mesopotamian Art
To develop a bit of the history of Mesopotamian art, we must study the first studies and investigations that were carried out in the year 1786 by the well-known vicar and general Joseph de Beauchamps, who had to wait several years to be able to carry out the first real excavation in the Mesopotamia region.
Although these excavations were motivated by a French consul known as Paul Émile Botta, who was in the city of Motul. They focused on carrying out excavations in the city of tell Kuyunjik, but they did not give good results since it was close to the city of Nineveh and a villager suggested that they move the investigation and excavations further north of the city where they found works of art. Mesopotamian as were bas-reliefs of the Syrians.
This gave way to one of the most important early finds of Mesopotamian art that had only been named after the Bible. From that point on, various investigations and excavations began to find more evidence of Mesopotamian art and culture.
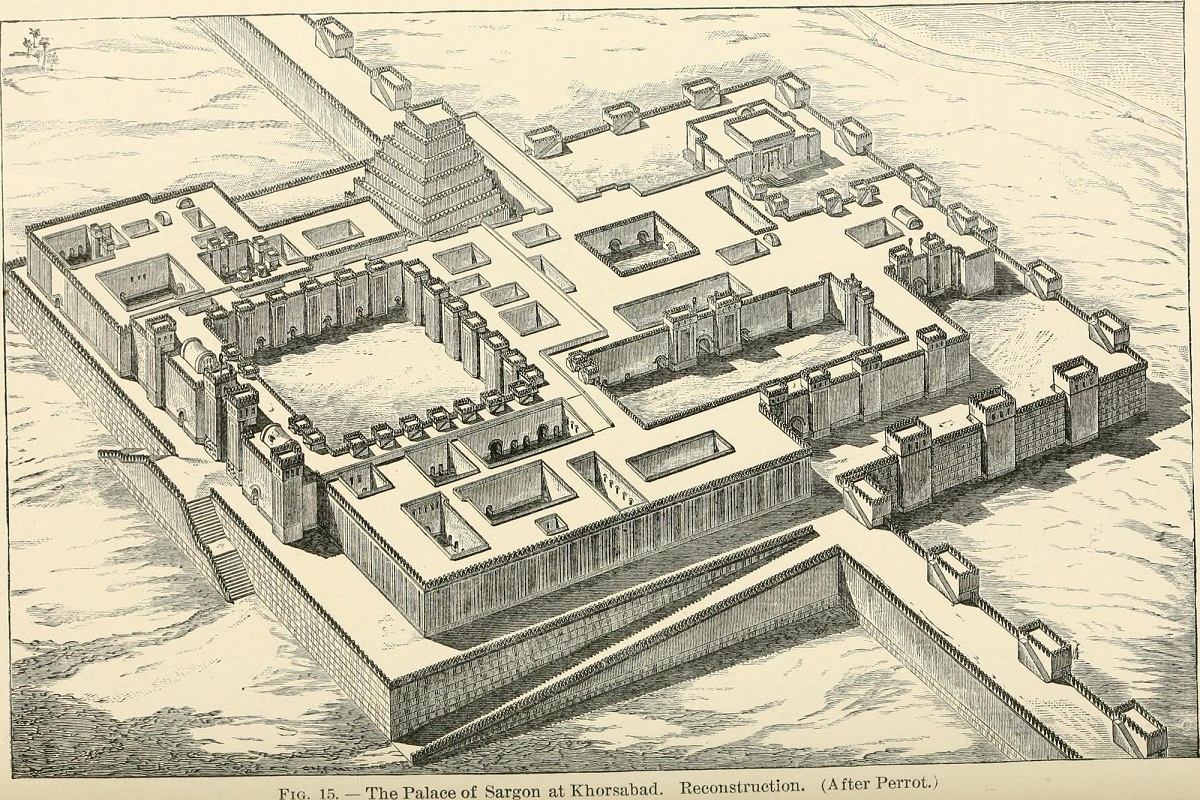
This also started a rivalry between the French and the English. Since the English, in the investigations they were carrying out, managed to find the beginning of the Ashurbanipal library, while the French managed to find the palace of Sargon II in Khorsabad.
But these finds had a sad end as several works of Mesopotamian art as well as many relics of the culture were taken on a boat down the Tigris River. This ship sank and more than 230 boxes of Mesopotamian material and art were lost at sea.
Then excavations began to be carried out in the south of the region in order to find more Mesopotamian art, with this they found the ruins of the cities of Uruk, Susa, Ur and Larsa. When the year 1875 arrived, evidence of the Sumerian civilization was found, as well as several works of Mesopotamian art.
In the beginning of the XNUMXth century, a large number of remains of various statues from the city of Gudea belonging to Mesopotamian art were obtained. In this period the Americans began to be interested in carrying out excavations together with the Germans to find treasures and Mesopotamian art to sell to various collectors who were interested in Mesopotamian art.
Culture in the Mesopotamia Region
Throughout the region of Mesopotamia, its culture and its Mesopotamian art was one of the pioneers in several branches of knowledge, one of the first characteristics was the development of cuneiform writing, since in principle it was very pictorial by which Mesopotamian art was developed. . In the field of law, the first codes of ethics were created.
While in architecture technology and innovation advanced and there were great advances such as the design of vaults and domes, they also had so much knowledge that they created a calendar that consisted of 12 months and 360 days a year. In the field of mathematics they had great mastery and certainty when using hexadecimal numbering.
Many of the characteristics of Mesopotamian art. As well as its culture, there is much to discover and continue to study, this being one of the civilizations that exerted great influence on several civilizations that were very close and that is why it began to build and develop a Western culture.
Sciences Developed in Mesopotamian Art
One of the most used sciences in Mesopotamian art was the use of mathematics through the use of hexadecimal numbering and the decimal numbering system centuries later. The first application that was given to the different numbering systems was in the economy and in commerce.
Since they began to use mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division to perform different mathematical calculations. At the beginning of the II millennium BC, his mathematics advanced to the point of using equations up to the third degree. They also knew a value very close to the number pi.
As well as the use of powers and roots in mathematical operations. Similarly, in the region of Mesopotamia they used calculus to determine volumes and surfaces in the main geometric figures.
The civilization also made use of astronomy to relate it to Mesopotamian art, since the Sumerians made studies and determined that other planets and mobile objects existed. In addition to many stars. But the civilization that focused the most on developing astronomy were the Babylonians who had the ability and knowledge to foresee phenomena in advance.
With this knowledge the Babylonians adopted a very exact lunar calendar where they included an extra month to adjust it to the solar calendar. Among the various investigations that existed, several treatises on medicine and many geology lists were found where there were several classifications of the different materials that they knew.
Literature Related to Mesopotamian Art
Before there was a strict development of literature with the written language that was widely used to write down the different transactions that were carried out in the administrative area to run an organization in the commune. But over time they were giving another application to literature and writing since it was related to Mesopotamian art.
Writing was used to write down and explain the different events, catastrophes, myths, legends that were occurring in the civilization of Mesopotamia and all these vicissitudes were related to Mesopotamian culture and art. Therefore, it is important to note that Sumerian literature reached three major themes such as Mesopotamian art, such as lamentations, myths, and hymns.
Of which the hymns were composed of different stories that recounted the different characteristics of the gods of Mesopotamia, among which Enlil the father God and progenitor of the other minor gods stood out; The goddess Inanna who was known as the goddess of love and friendship. But by making her angry she was the goddess of war.
Also featured was the fresh water god known as Enki who was always at odds with the mountain goddess Ninhursag. All of these hymns were part of Mesopotamian art and culture. While the hymns were used to perform songs of praise and ceremony to the gods and kings in the different cities and temples of Mesopotamia.
Lamentations were used as Mesopotamian art to recount the accidents and catastrophes that were happening throughout the Mesopotamia region and record everything that happened.
Many of these stories are based on events that occurred such as wars or natural phenomena such as floods or due to the impressive construction of temples or statues for a particular God or king that was distorted over time. That is why literature is a Mesopotamian art since it was based on different poems.
The Religion Practiced in Mesopotamia
It should be noted that throughout the region of Mesopotamia the religion that was practiced was polytheistic, since in each city its main God and a set of minor gods were worshiped, although there were common gods that were worshiped by the population due to their characteristics. . The main gods that were worshiped in the region of Mesopotamia were:
- Anu: god of the sky and father of the gods.
- Enki: god of the Earth
- Nannar: God of the Moon
- Utu: God of the Sun (around 5000 BC he was called Ninurta).
- Inanna: goddess Venus
- Ea: creator of men
- Enlil: god of the wind.
This being a great influence and support for Mesopotamian culture and art, for which it should be noted that in the XNUMXth century BC, King Hammurabi decided to unify the entire region of Mesopotamia into a single state. From which he established the city of Babylon as the capital and center of Mesopotamian economy, culture and art. He placed the God Marduk as the main god of worship and worship in the entire Mesopotamian region.
This god held great responsibility in the civilization of Mesopotamia since he was in charge of reestablishing the great celestial order that meant making the land emerge from the sea and carving the body of humans similar to that of the gods and being able to distribute the domains of the universe between all of them.
An important point to highlight in Mesopotamian art based on religion was that the gods were related to different jobs that they carried out in civilization such as livestock, clothing, writing, among many other activities. This gave way to religion being very broad throughout the Mesopotamian region and for many people of that time and today it is very interesting and is an object of study as religion, culture and as Mesopotamian art.
In the region of Mesopotamia, highlighting that it was located between two rivers, its land was very fertile, that is why the civilization that occurred in that territory became nomadic peoples who came there to become farmers and ranchers, developing their own culture and their art. Mesopotamian that has surprised many people throughout history for its different styles and forms that they applied.
For all this, it can be highlighted that Mesopotamian art has enough unity in terms of its intentionality of everything it has meant and has resulted in a rigid, geometric and very closed style of art. Since Mesopotamian art will stand out for its practice and use and not for its aesthetics since it has always been developing to fulfill a service with Mesopotamian society.
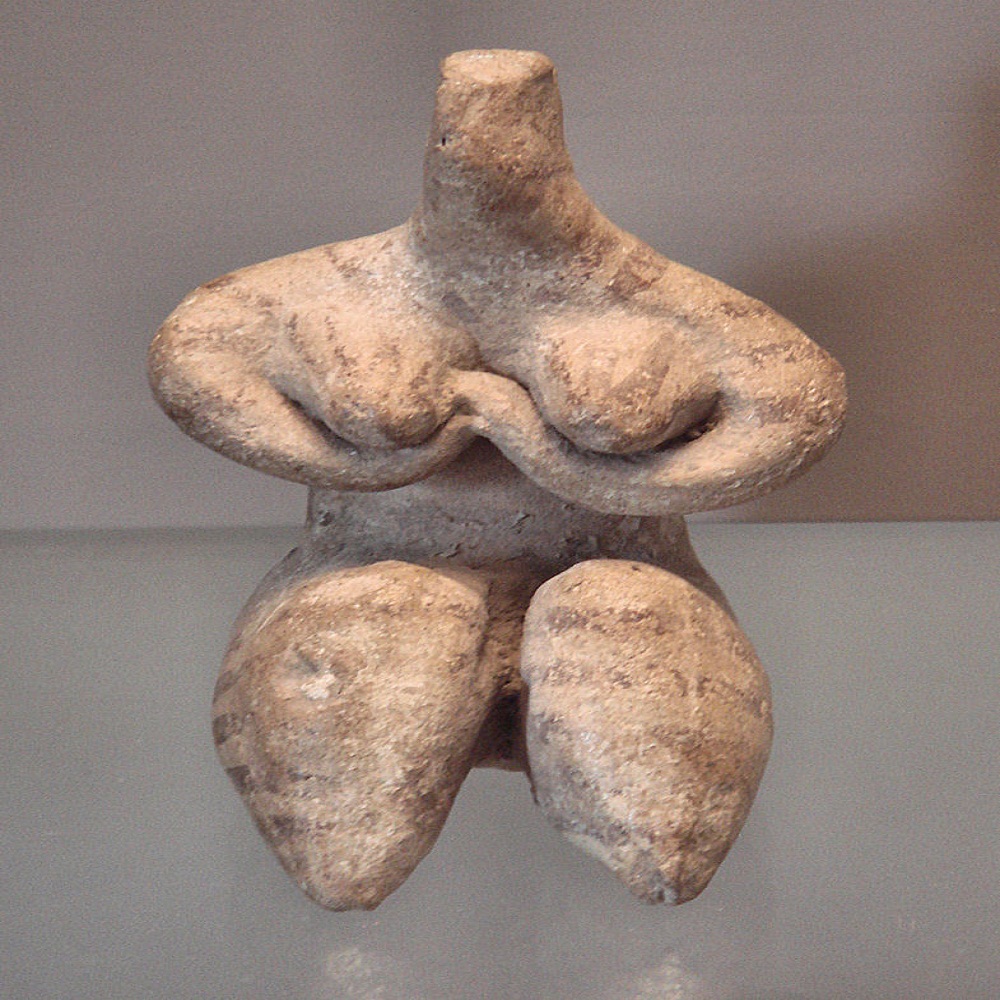
The Sculpture that was Practiced in Mesopotamia
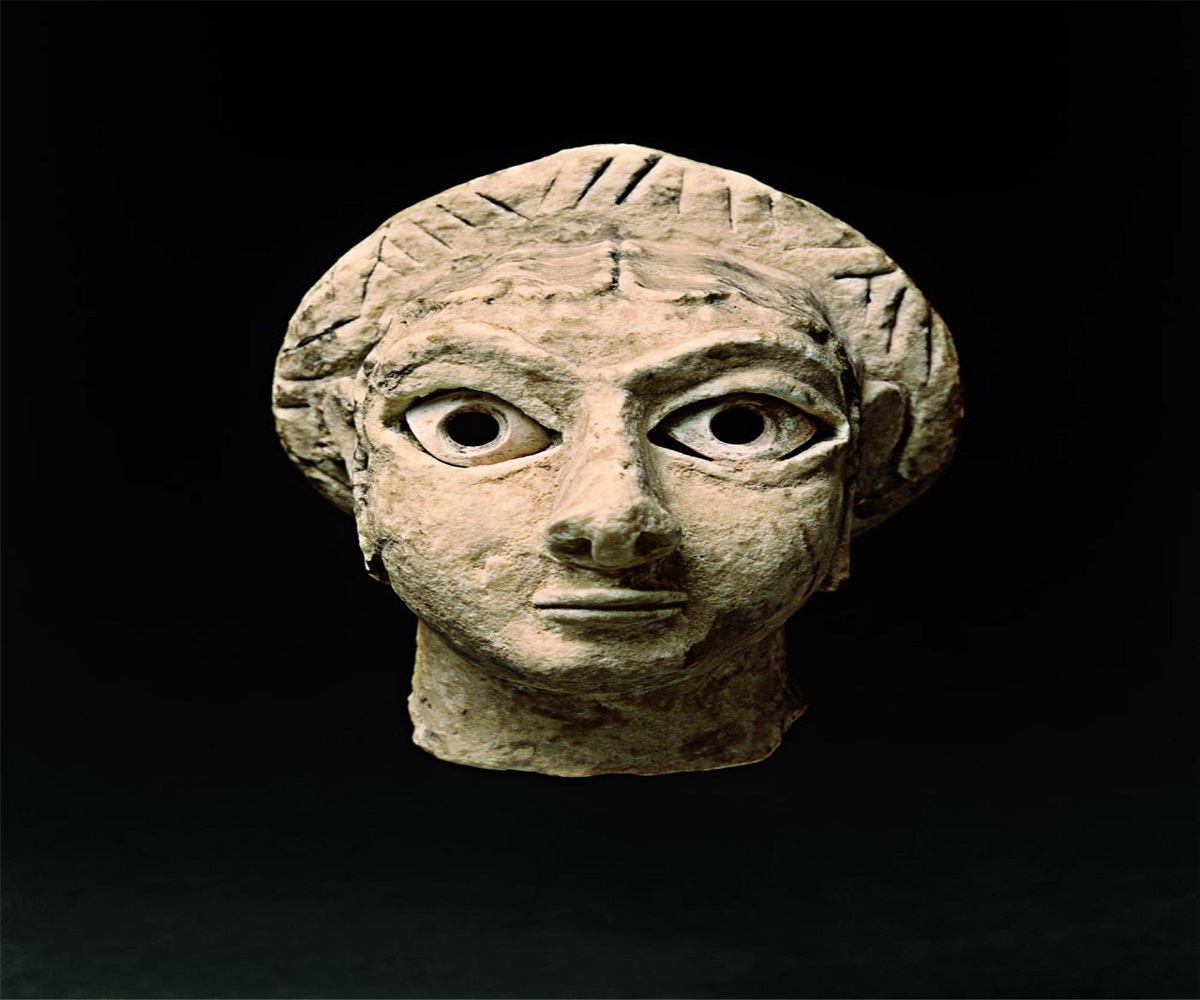
In Mesopotamian art, one of the most practical artistic techniques was sculpture, since many artisans made representations of the gods, kings and various government officials, but always emphasizing individualized people who almost always placed the person's name on them. the one that made this sculpture.
One of the most outstanding characteristics of sculpture as Mesopotamian art is that the statue was sought to replace the person rather than represent it, since it had features that stood out from the person, such as the face and head, and were disproportionate to the person. the normal figure of the person.
At that time, what became known as conceptual realism was developed in Mesopotamian art, which consisted of simplifying and regularizing the forms of the human body thanks to the use of the technique that was called the law of frontality, which was based on performing the sculpture that the left and right sides were symmetrical,
Many of the sculptures were developed in a kind of geometric cylinder very similar to the cone. That is why the different representations that were made did not surround the reality that was lived. Of which many artisans began to make sculptures of the animals they worshiped with greater realism than the sculptures of people.
Many themes that were treated in Mesopotamian art for sculpture were the making of monumental bulls that were very realistic since they were very stabilized. These bulls represented fantastic monsters in Mesopotamian art, but they were also revered as geniuses and protectors of society. Mesopotamian and that they had supernatural powers.
The main techniques used in Mesopotamian art were based on the use of monumental relief, parietal relief, stele, seal, and glazed brick relief. They also developed new ways of sculpting stone and developing stories on temple walls based on different drawings that are part of Mesopotamian art.
The sculptures in the Mesopotamian art were made in scale to the reality of the people, but the executing artists of the Mesopotamian work of art gave it some symbology that made it stand out or a meaning beyond what the people of the same civilization could perceive. . That is why the sculptures in Mesopotamian art were the categories where the disappeared civilization of the Mesopotamia region stands out the most.
The model with which the different sculptures in Mesopotamian art were designed was that the hands were always crossed over the chest, the head of the person was shaved in the sculpture and the torso or back of the figure was uncovered or a kind of mask was placed on it. of mantle The theme was based on the people who were noted in the Mesopotamian civilization. As well as in the power of faith and the expressions they had.
While other characteristics of sculpture in Mesopotamian art was the use of bas-relief that was used to narrate stories of military wars and the most shocking events that had to be narrated so that future society would know the events.
As well as the religious motifs that were performed to the different gods that were worshiped in society were the main characteristics of Mesopotamian art.
Painting in Mesopotamia
Painting in Mesopotamian art did not stand out much due to the characteristics of the Mesopotamia region, that is why there are very few works of art, however the art made in Mesopotamia is very similar to the art that was practiced in the Magdalenian period of prehistory. . Since the technique that was used in the region of Mesopotamia was the same as the parietal relief. There was no perspective and the works had only a decorative purpose.
In the different paintings and engravings that the archaeologists found in the investigations carried out, a hierarchy of the paintings was shown according to the size of the people who were painted in the Mesopotamian work of art. Since those who had the highest position such as monarchs and high officials were painted larger than other people.
But it should be noted that in Mesopotamian art, painting was used to decorate and embellish architecture but it lacks perspective and is chromatically poor, there are only red, blue and white colors. Using the tempering technique that is appreciated in decorative mosaics and tiles. The most recurrent themes used in Mesopotamian art were scenes of sacrifices, rituals and wars that were very realistic.
Other paintings found from Mesopotamian art were paintings of animals, geometric figures, monsters and people with animal heads that were used for decoration in the different houses and temples and did not contain shadows.
Architecture in the Region of Mesopotamia
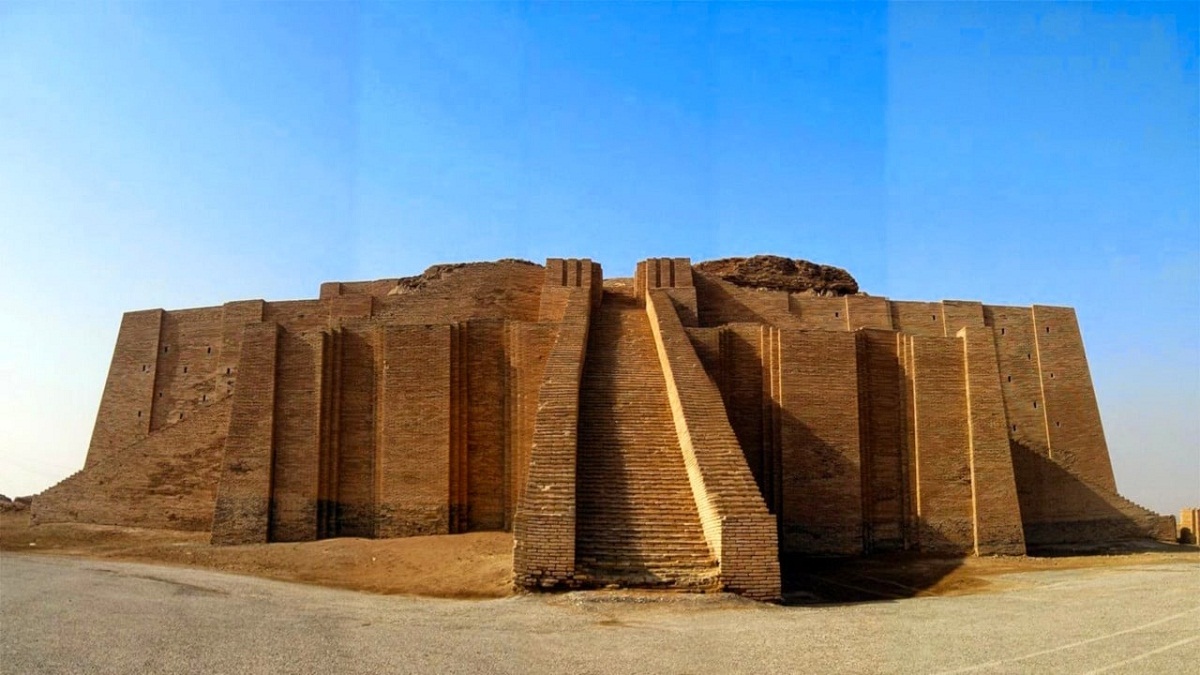
It should be noted that the architecture in Mesopotamia was very particular as Mesopotamian art due to all the resources and materials that were used, that several of the constructions were based on two basic systems which were the lintel and the vault.
The architecture of Mesopotamia was based on building mosaics with very bright colors, among which green, black and bicolor stand out, which were designed by the same artisans who design very creative murals, the light was obtained through the ceiling since many temples they had no windows.
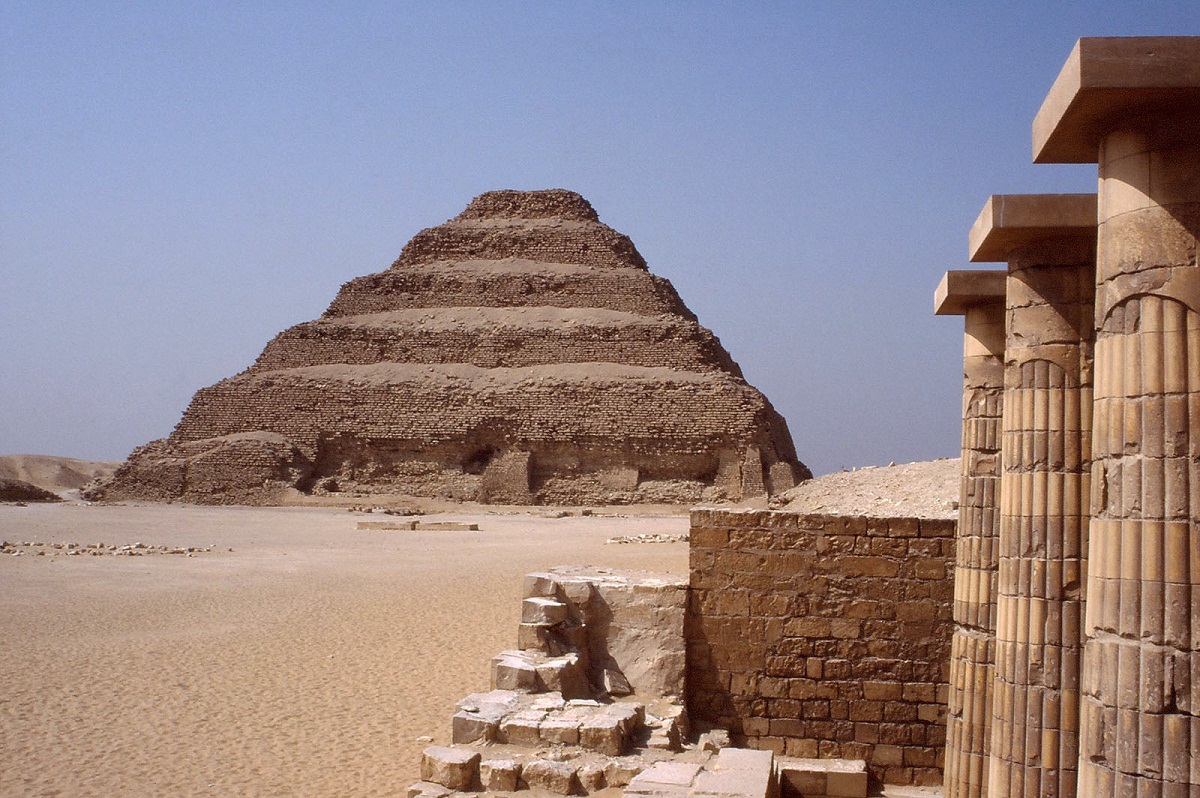
But in the civilization of Mesopotamia they were very concerned about what happened in earthly life and did not pay much attention to the world of the dead, so the constructions that had the greatest representation were the palaces and temples.
That is why in the temples they were dedicated for many things such as the political, religious and economic spheres. In addition, these temples had large extensions of land to practice agriculture and there were herds of sheep and cattle. In some temples there were deposits and warehouses to store the different crops.
Of course there were also workshops where the utensils, the bronze and copper statues were made. As well as the ceramic statues that represented a lot of cultural value in Mesopotamian art.
The priests of the different temples were the ones who organized the trade of the city since they employed the peasants, the artisans and the shepherds to sell the merchandise that was in the temples and these people were paid with small plots of cereal cultivation , dates or wool.
In addition, the people known as the ziggurats had houses with large rooms to accommodate people who came from nearby cities to exchange products and thus promote the economy of the cities. It should be noted that urban planning began to be regulated in several cities, one of the main ones being the city of Babylon and the city of Nebuchadnezzar II.
While the engineering works highlighted the network of canals that were made to join the waters of the Tigris River and the Euphrates River. With this they propitiated agriculture, irrigation and navigation. The main characteristics that we can find in the monuments are:
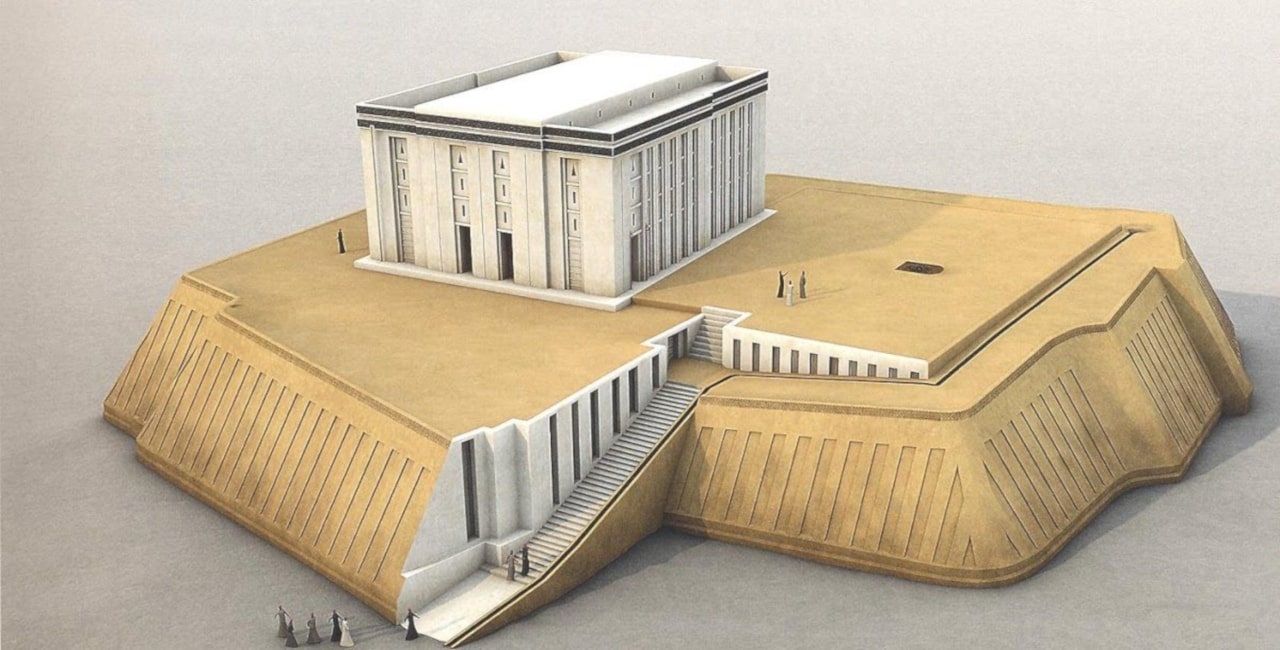
The palace: since in Mesopotamian art there was no exact form of the palaces, but rather they were a series of buildings that had different sizes and were united by several corridors, corridors and galleries that were connected by large patios and with walls around for protection. from town.
Many of these palaces were designed in a quadrangular construction that had a very simple patio which received sunlight and ventilation and were raised by large brick terraces that could be reached by large ramps or stairs and had a drainage system. very well designed to protect itself from the different floods that were carried out by the flooding of the rivers.
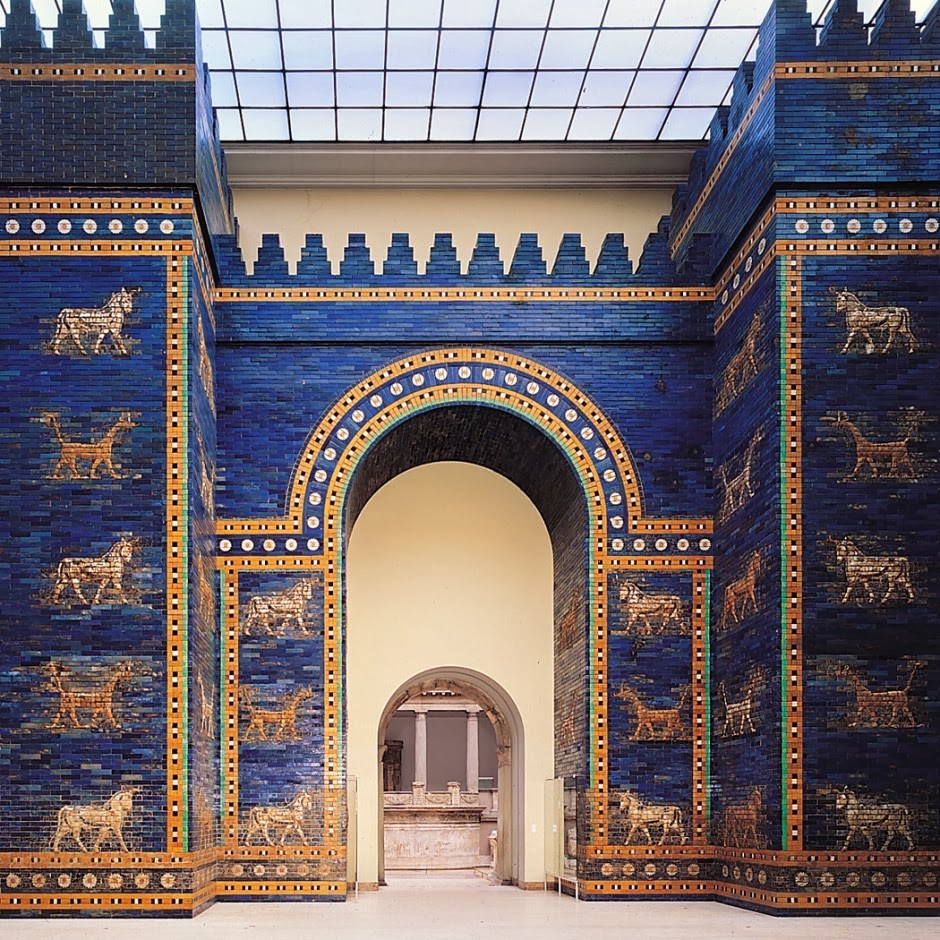
The gates of the palaces were designed with fine bronze sheets that were surrounded by statues of winged bulls with the heads of people that were a very important feature of Mesopotamian art. The walls of the palaces were decorated with frescoes on a lime base, lined with glazed bricks. Which made Mesopotamian art stand out in a very fluid way.
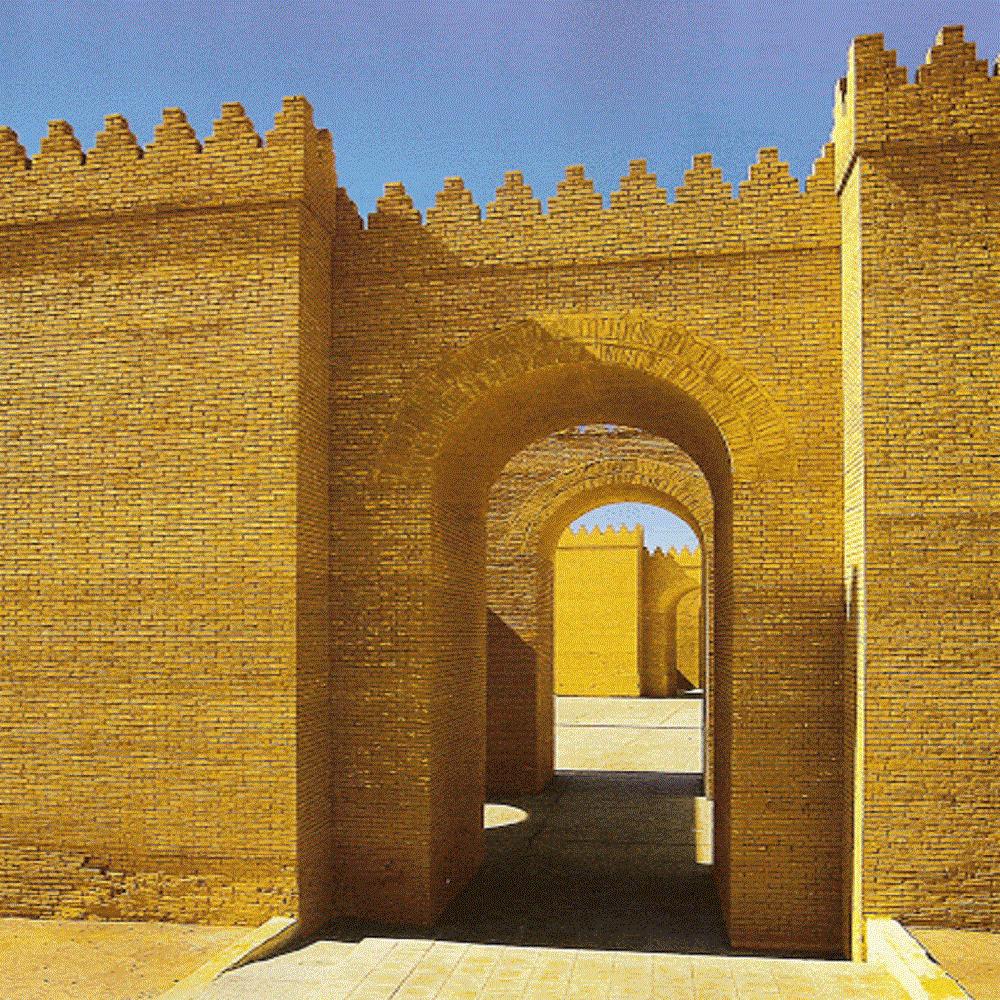
The walls: The cities in the region of Mesopotamia were protected by great walls to protect themselves from invasions. They were also designed at right angles that were reinforced from stretch to stretch with square towers. The entrances to the cities had to be made through the main entrance which was heavily fortified and quite secure,
In order to open the gates of the city, they were designed in the form of a vault with a large cannon in the middle and on the sides were placed large statues of winged bulls with human heads that were a very important feature of Mesopotamian culture and art.
The tombs: From the point of view of Mesopotamian art and architecture, the tombs did not have great interest in the population of Mesopotamia since they were designed as simple brick vaults which had several chambers, which had a small monument on the outside of each chamber. that represented some contribution to the deceased who were there.
While inside the tombs, various artifacts were found as gadgets of great importance in Mesopotamian culture and art. Since there was furniture as well as the dead bodies of ladies, musicians, servants, coachmen and guards who were immolated in groups that reveal that they had very rare funeral customs in these towns of the Mesopotamia region.
If you have found this article on Mesopotamian art important, I invite you to visit the following links: