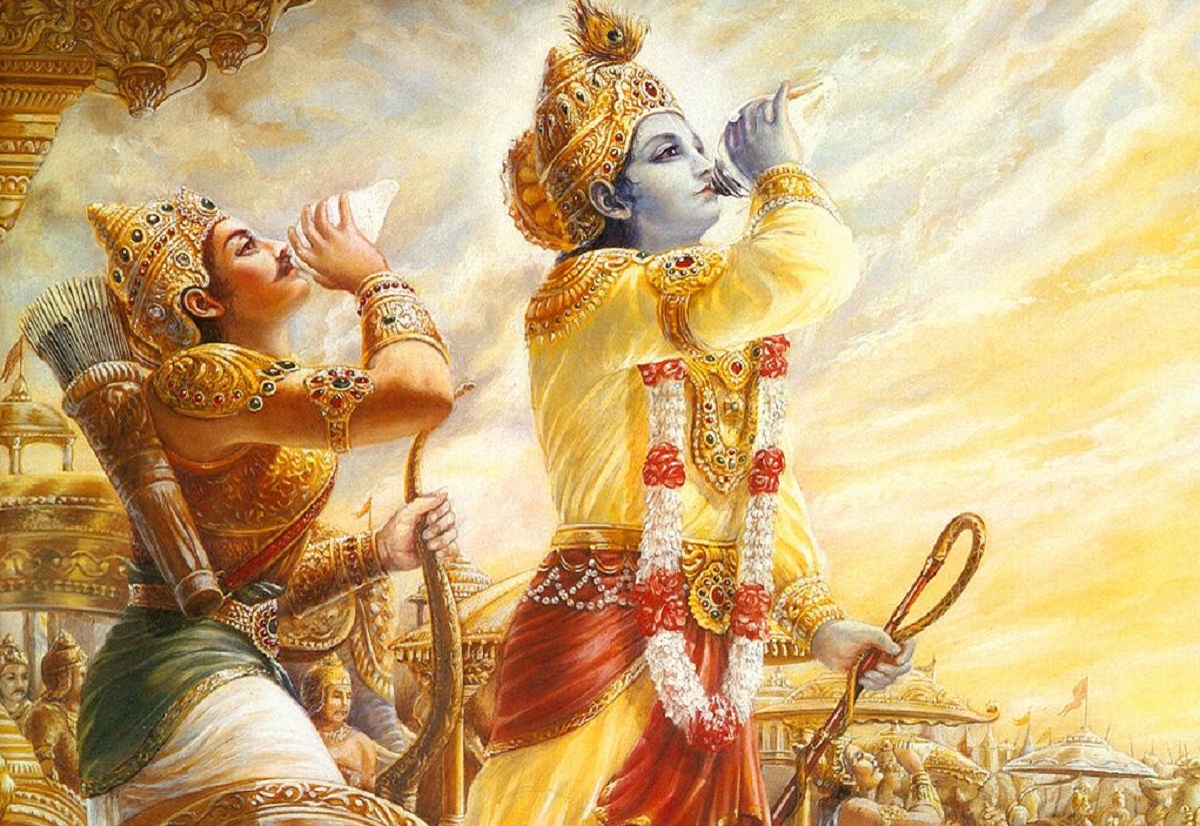
Through this post you will learn more about the hindu art, fundamentals, plastic arts and much more of this complex multicultural society dedicated to the religious sphere and its interaction with nature as part of the universal order. Through this interesting article. Don't stop reading it!

What is Hindu Art about?
In the first instance you should be aware that Hindu Art is made up of its interests, rites and ideologies of the multicultural society according to existence where aspects such as perfection, transformation coupled with eternity and time are taken.
Various religions being integrated into Hindu Art, such is the case of Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism and Christianity, interacting with nature to seek a sacred order by including mountains, trees and rivers.
It is important to note that Hindu Art comes from the rich culture of the various peoples who entered the territory, starting with the natives whose skin is dark, being the ancestors of the Dravidians as well as other cultures.
Among them from Australia, the Mesolithic Mediterranean, Armenians, Mongols, Aryans who were in this nation in 1500 BC as well as the Greeks and Persians between 600 and 300 BC.
Not to mention the Parthians and post-Mongols who entered between 50 and -300 BC, then there are the Huns who entered the Hindu territory in the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries, as well as the Arabs between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries without forget the Turko-Afghans between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries.
It is also necessary to highlight the incursion made by the Turko-Mongols between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries, as well as the British between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries, which is why this great diversity of cultures has led to Hindu Art being so rich and diverse according to each of its regions.
Hindu Art has managed to spread thanks to Buddhism, especially in Southeast and Central Asia, being influential in cultures such as Japan and China, and in the West it is known about this art thanks to the Expedition of Alexander the Great.
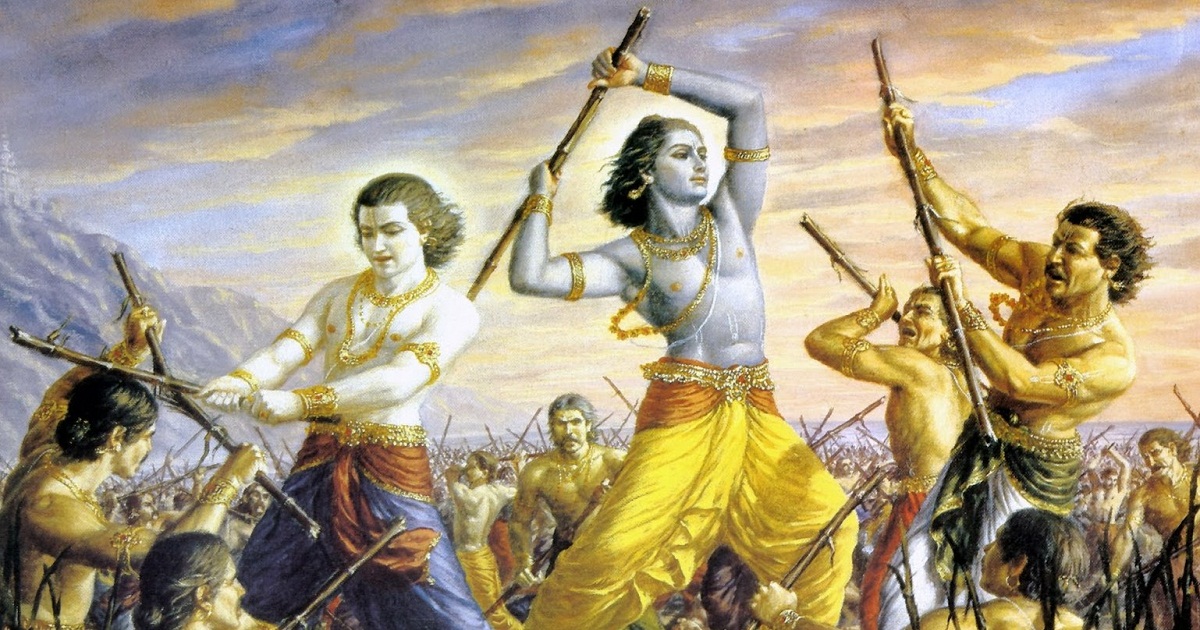
Where they were able to appreciate the technical, artistic and cultural advancement of this civilization expressing the narrative character in Hindu Art where images with great sensuality are observed, demonstrating aesthetic refinement.
Primary Characteristics of Hindu Art
It is important to note that the main qualities of Hindu Art that differentiated it from other styles that emerged in this nation throughout its history are the following:
- They had a great mastery of drawing
- great freedom of expression
- Art is consolidated in the aesthetic needs specifically in the rituals of the population
- With regard to voluptuousness and sensuality, they were totally premeditated
- In his works the dual conflict between life and death is observed in addition to eternity and time
- The main topics that stand out in Hindu Art were related to religion and the elements that make up nature as a sacred entity.
Basis of Hindu Art
As you can see, Hindu art is impregnated with religious manifestations, allowing humans to connect with deities, as can be seen in the architectural structures.
Where the interest is not the mark of the artist but the integration of the natural environment with the deities standing out in the fine arts, as is the case with sculpture as well as painting and, as we mentioned, architecture.
Creating own styles of Hindu Art in sculpture through the techniques and styles that were evolving integrating nature into his works, unlike Western man who has been in charge of adapting nature to his designs.
Hindu Art is in charge of designing its works according to the nature that surrounds it, as can be seen in the cave sanctuaries where they excavated the rock and in the caves, demonstrating great skill in their designs.
Therefore, in Hindu Art, nature is a sacred topic, hence the scenes where mountains, trees and rivers integrate, as well as the Sun called Surya, the Moon Chandra, the rain Indra and the fire Agni.
In addition, the monsoon climate was part of Hindu Art thanks to its cycle and duality, which was reflected in the personality of each of the inhabitants of this region, which allows them to coexist with opposing and conflicting styles.
Among these styles are naturalism, realism, abstraction and idealism present in the works of Hindu Art, allowing the use of an eclectic art among the first settlers of Negroid descent who formed the ethnic group or natives called Dravidians.
Which were located south of the nation of India, although the Aryans arrived and then the Muslims, they have always reiterated their darker complexion thanks to the symbology such as the indigo blue on the skin of the deities.
Like the use of sandstone in constructions with the intention of creating a darker visual effect in relation to stone and marble.
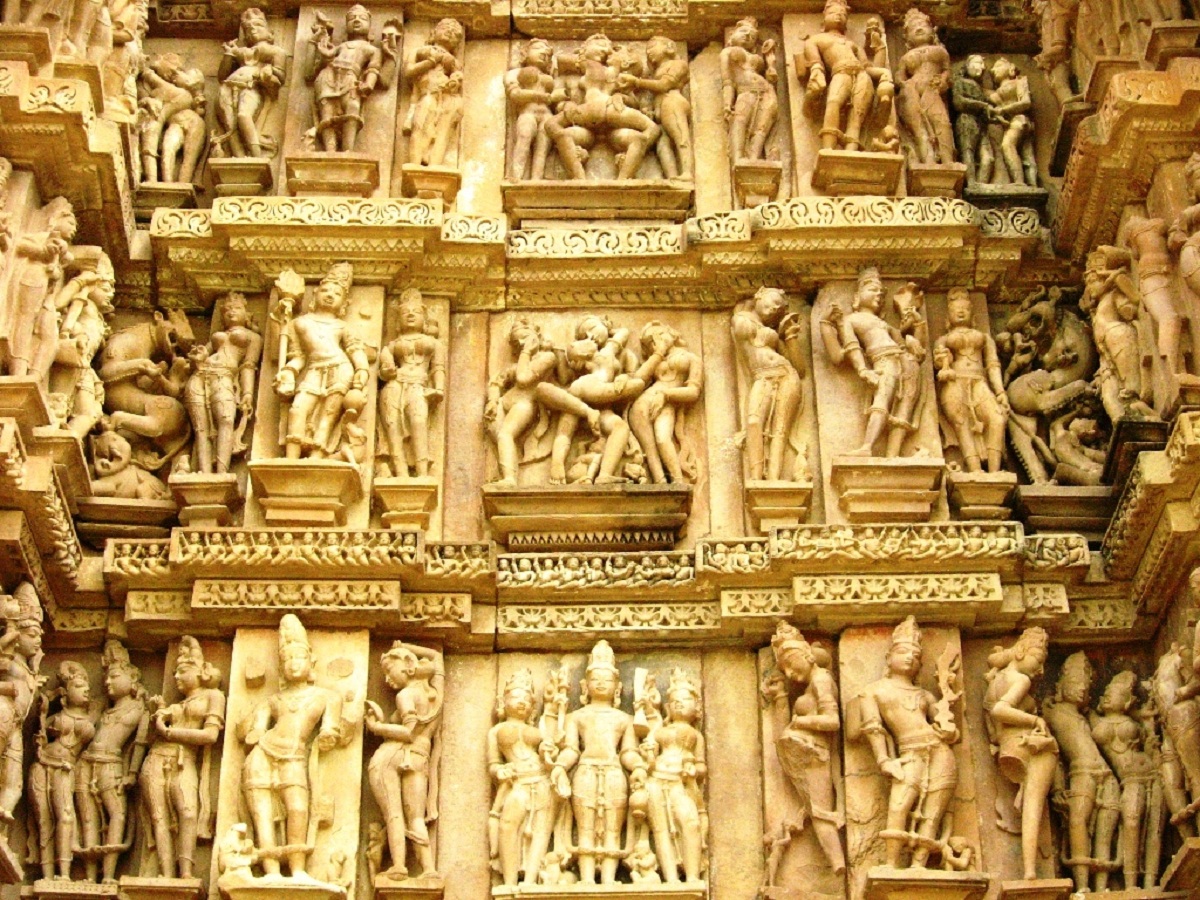
Even one of the phases of greatest interest for the Western world with respect to Hindu Art is the representation of eroticism without any type of taboo, demonstrating that for this civilization sexual relations are a form of prayer between human beings and deities.
Spirituality through the Deities
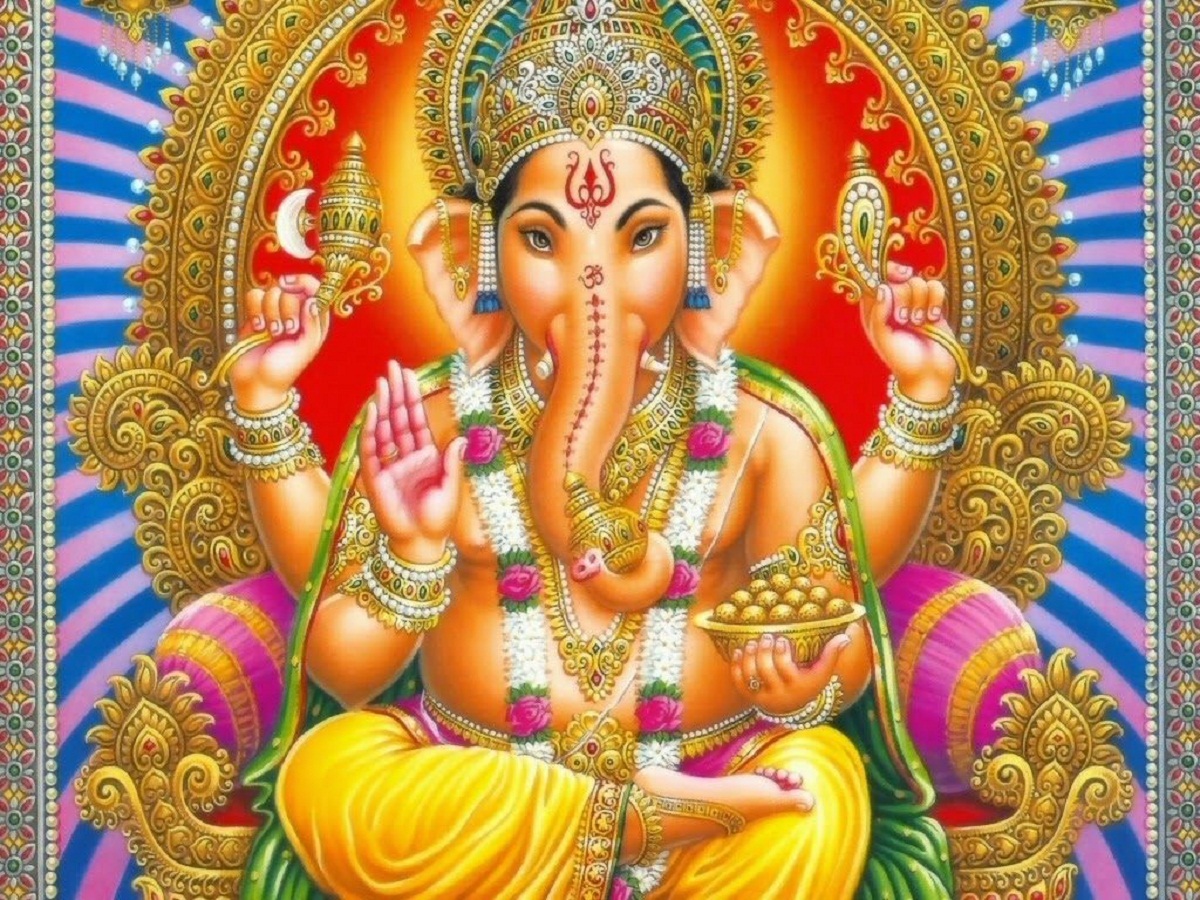
Being a way of being able to transcend in relation to spirituality, the lingam cult is demonstrative, which is the representation of the male sex in addition to the ioni symbolizing the female sex.
Being typical of the rituals of the Neolithic era regarding fertility and are typical of Hindu Art, the Lingam being the creative power of the deity Shiva, being the main one worshiped in religious temples.
Where a pillar is evident which ends its design in the form of a glans from a naturalistic to abstract form referring to a cylinder that alludes to the phallus.
This phallus has eyes simulating a face or up to four faces with respect to the tradition of the Dravidian culture, which are the oldest of Hindu Art, are associated with the four main elements of nature such as Water, Air, Earth, Fire and Wind. .
On the other hand, ioni symbolizes the Mother Goddess named Sakti, including Parvati, who is the deity that represents the fertility of nature and is Shiva's wife, since her natural geometric representation is the triangle, making the similarity with the vagina.
For what is observed in Hindu Art, the lingam together with the ioni forms a concave figure from which the lingam stands out, demonstrating the unity within the duality that is observed in the universe.
The creative source that transforms sexual energy into mental energy from feeling to spirituality. This is achieved in the culture of Hindu Art from the regular practice of yoga.
Therefore, these rituals were merged with a series of tantra that simply seeks the truth through the energy transmitted by the body of human beings.
Being the body of the people the spiritual enhancer through the sexual energy known in this culture as kundalini, there are also the stories or narrations of the Kama Sutra, which is the book dedicated to love being represented by Hindu Art.
Specifically through the discipline of sculpture where there is evidence of a large number of mithuna or scenes of erotic relevance such as can be seen in the sanctuaries of Khajuräho and Konärak.
So the aesthetics of Hindu Art was perfected from the Gupta period where they were responsible for analyzing, studying, classifying a large number of writings.
Vedic calls which correspond to sacred texts of this culture that were transmitted orally from the year 1500 before the era of Christ.
These sacred texts were of great importance in the development of Hindu Art, specifically those known under the name of Vastu – Sastras, which are treatises related to architectural constructions for the deities.
Principles of Aesthetics according to Painting
There are also other treatises named Silpa – Sastras related to the disciplines of painting and sculpture to be able to physically transcribe the language of the deities.
Therefore, the Gupta were in charge of studying the techniques and norms that govern the Hindu Art, including the materials, styles and images that demonstrated their iconography, among them the Sadanga can be mentioned. Where six principles of aesthetics in relation to painting are established:
- Rüpa – bheda entrusted in the science of forms
- Pramani that gives meaning to the relationships that you want to capture
- Bhava which is the science related to feeling
- Lavanna vojanam which corresponds to the sense of grace
- Sadrisyam concerning the sciences of comparisons
- Varnika – bhanga which refers to the science of colors over time two more principles were introduced such as the Race that refers to the quintessence known as taste and Chanda that corresponds to the rhythm in artistic works
As far as race is concerned, it is present in the emotions of the natives of Hindu Art with the intention of capturing an art that is capable of moving that arouses emotions before the viewer.
Therefore, nine characteristics related to emotions are distinguished in Hindu Art and they are represented through a color in a specific way, being the following:
- Sringara is the color black and represents Love in the erotic aspect
- Vira represented by the color red and is the heroic race symbolizes the Value
- Raudra is represented by the color red and connotes a furious rasa which symbolizes Anger.
- Hasya is the color white is the cosmic rasa and symbolizes Joy
- Adbhuta represents the color yellow, it is an admiring rasa and symbolizes Amazement.
- Karuna is represented by the color gray and is a repulsive rasa corresponding to Pain
- Bibhasta for this emotion the color blue is used and being a repulsive rasa that symbolizes Disgust
- Bhayanaka is represented with the color black is a fearful rasa symbolizes Fear
- Sänta is used for its representation of the color white and symbolizes the serene rasa that is Peace.
You will be able to observe in Hindu Art that these nine emotions in turn produce the various attitudes and postures called asana in the sculptures and images made through painting.
Being the Samabhanga a posture that is evident as rigid but at the same time balanced, the artists performed it both standing and sitting, it symbolizes serene spirituality and you can see in the images that have been made of Buddha and other deities such as Vishnu.
Another of the postures is Äbhanga being a slightly inclined appearance that translates as a being in meditation and is a very characteristic posture of Bodhisattvas and other lower-ranking deities.
Tribhanga is a posture that alludes to a triple flexion which shows sensuality as well as spirituality, it is very common to be evidenced in the images of Apsaras and Yaksis.
Finally, there is the Tribhanga posture where an extreme inclination is evident, which denotes violence in the images as well as a certain drama.
It is widely used to represent the God Shiva and the Lokapäla who serve the obligation of being the guardians of the world are in charge of guarding and protecting the four cardinal points.
Evolution of the Plastic Arts
In this section you will find the evolution of Hindu Art from its beginnings. Continue reading this interesting article so that you know in detail how it acquired the techniques and skills that are so appreciated.
The Prehistory of Hindu Art
Remains have been evidenced such as utensils that come from the paleolithic era made with quartzite and flint, it is finely carved or polished and corresponds to the same era of the utensils that have been found in the European region, which are of lower quality.
In the Bhimbetka region, very close to the town of Bhopal, around a thousand caves have been found, which contain a great variety of cave paintings 7000 years before the Christian era.
The images show the routine of the people who lived in the caves where dance, rituals, births and funerals are evident.
In addition, animals such as elephants, bison, turkeys, tigers and rhinoceroses are detailed since 2003 this territory was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
Already in the Mesolithic era, a large number of tools very similar to crescent-shaped blades have been collected from the regions of the Near East and Eastern Europe as well as North Africa.
Another territory that is very important to highlight is the Deccan where a large number of tombs of the megalithic model have been found.
In the town of Baluchistan, which is located in the north of India, painted pottery and objects made with metal have been found that are from the IV era before the Christian era.
But not only that, there are also paintings in other regions such as Raigarh which are similar to those found in the town of Cogul in Spain where animals such as deer, elephants, oxen are evident.
In addition, in an archaeological excavation in the town of Karnataka, a cemetery was discovered where the coffins were made with stones.
We can also comment on the archaeological centers that correspond to the regions of Adichanallur and Brahmagiri belong to the neolithic era A type of ceramic with red and black colors has been found, as well as dolmens.
For this reason, a classification of the ceramics that have been found has been made, such as the red one belonging to the hematite of the Banas culture, another one of gray color concerning the Ganges River Basin and a highly polished black one from the Jariana region and Delhi.
The Indus Culture
Around the year 2500 before the Christian era, the first civilization of Hindu Art was created in the Neolithic era. It is important to remember that this part of the nation of India Zagros belonged to the commercial route that integrated the Mediterranean with the Far East.
So many towns benefited as shown in the archaeological sites made by John Marshall in the year 1920 in the Mohenjo - Daro region in what is now known as Pakistan.
Due to the findings made, the contact with Mesopotamia was evidenced, developing a writing system that for the moment has not been deciphered.
On that site there were about nine cities which were superimposed, demonstrating its excellent urban planning, including the technical evolution regarding the sewerage construction of the structures.
In addition to parallel streets, everything is organized through a regular symmetric planimetry. These buildings were made with baked clay and brick, all the houses enjoyed the element as vital as water.
Traces of vaults made with the use of bricks have even been found. The city was walled and made up of terraces.
Where the public buildings were distributed, such as the baths, the cloisters and the palaestras, but without observing the remains of sanctuaries or castles.
It is important to highlight that in these archaeological sites a great variety of stamps made with steatite have been found where images of animals and even amazing monsters are observed with great realism and great precision.
It is said that they would be thanks to the influence of the Mesopotamian culture, sculptures and ceramics were even found, in addition to utensils made with gold, brass, copper and silver, the bronze knives with very curved blades stand out, which are very characteristic of this culture. .
With respect to ceramics, it was made through the use of lathes ornamented with geometric figures, in addition, the ability of textile art specifically of printed cotton was found.
Therefore, the trade stands out due to the presence of objects made with lapis lazuli from Afghanistan, gold and silver from Persia and Jade from the Chinese nation.
Even in archaeological sites in the Mesopotamia region, red chalcedony beads have been found that come from the Indo culture.
In relation to sculpture, a wide range of images made in terracotta have been found where animals, cars and people are symbolized, many of them without clothes and with symbols related to sex such as the lingam and the ioni referring to fertility rituals.
Even sculptures made in bronze, such as the Mohenjo-Daro dancer, where a rounded anatomical figure is detailed, and in limestone, such as the Priest-King of the same region, where the thick lips, fringed beard and eyes are highlighted. ripped similar to Asian ethnicity.
Vedic Stage
At this historical moment, the Aryan peoples entered the nation of India, which is why they influenced religious traditions, this people is the one who introduces the Sanskrit language as well as the ability to work with iron.
It also presents the unknown animal horse by the Hindu culture and they were in charge of creating small kingdoms divided by castes and the priests occupied an important rank known by the term Brahmans.
Thanks to the Sanskrit language, great epic poems such as the Mahabharata and the Ramayana arose, as well as the philosophical writers known as the Upanishad.
Which allowed the development of Hinduism being a religion of mythological topic where practices related to esotericism were integrated.
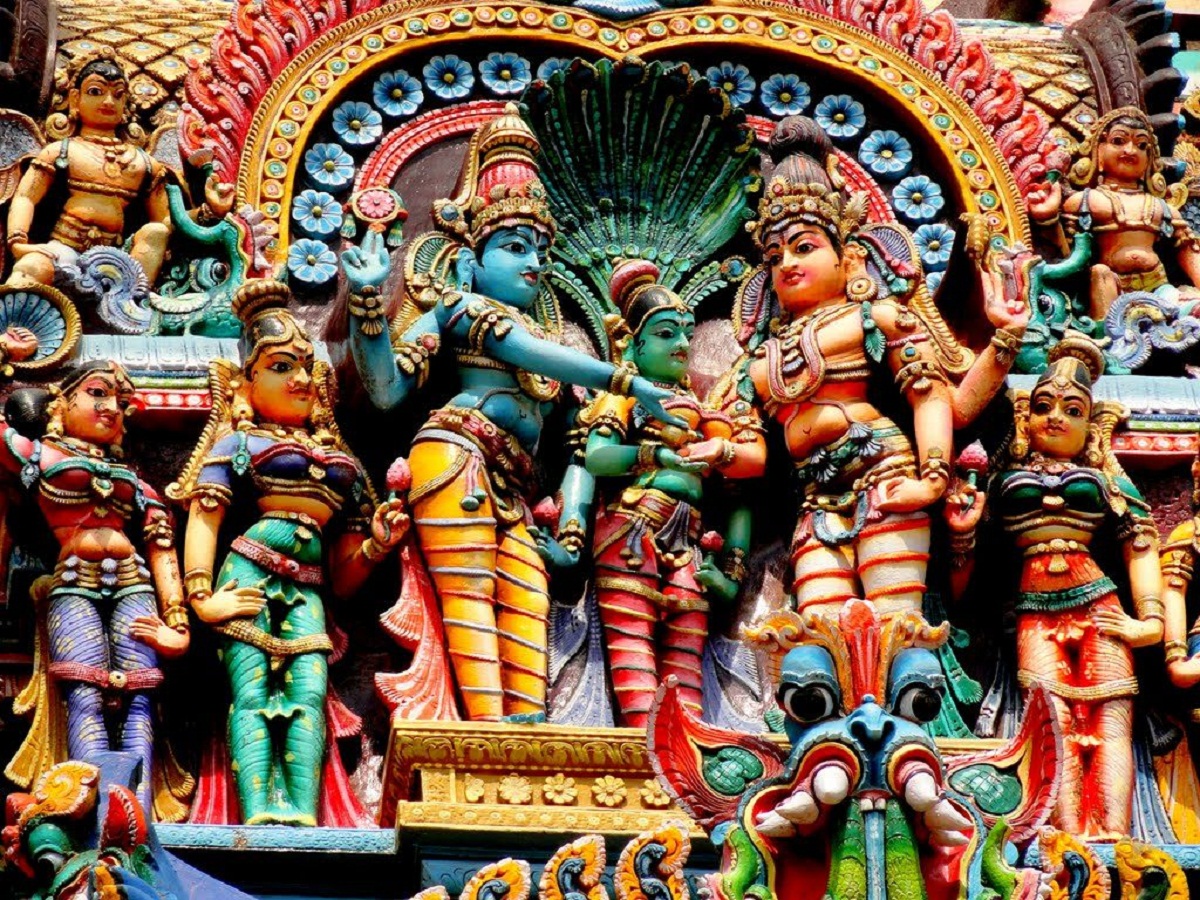
The main deities of Hinduism are Siva and Vishnu and even other concepts of abstract notion such as Brahman, which is the soul of the world.
In addition to atman that corresponds to the human soul without forgetting Maia, an energy that deceives human souls and makes them live in the material world.
The intention of the Hindu religion is to bring the atma closer to the Brahman in order to free Karma and avoid the succession of reincarnations stipulated by the actions of the individual in his life and they originate the caste system of the Hindu territory.
Being the brahmins the caste belonging to the priests and politicians, the chatrias It is the caste that corresponds to the military and the rulers, then they follow the caste vaisias which is related to merchants and farmers.
Then they are followed by you will sweat belonging to the slaves and finally the dalits which refers to outcasts as well as outsiders who are untouchables.
According to the remains that have been evidenced in the archaeological sites according to this period, few objects have been found and bronze was used in them.
Other ceramics, with little information between this stage and that corresponding to Mauryan art, since perishable materials were used, such as wood and baked clay, leaving no great vestiges of this period.
Around the XNUMXth century before the Christian era, Buddhism arose in addition to Jainism, both religions offered people the salvation of their souls and put an end to reincarnations.
For its part, Buddhism allows through meditation and the practice of asceticism leads people to the paradise that is nirvana.
In this culture, while Jainism practices five abstentions such as jina - kalpa which means not to kill, ahimsa refers to not lying, sattva means not to steal.
Asteya refers to not abusing sex and brahmacharya related to not coveting and at the end of this stage the famous expedition of Alexander the Great to India was made around the year 326 before the Christian era.
Allowing contact with Greek culture, Hindu art was impregnated with Greek art as well as Persian art, demonstrating a surprising fusion in its religious images.
Hindu Art and Buddhism
This dynasty was in charge of expelling from the region of India the favored ones of Alexander the Great who occupied the central part of this region and the Deccan peninsula.
The Buddhist culture as you have already understood the Hindu Art unfolded to the teachings of the Buddha as endorsed in the dharma and between the exchanges that originated between the nations of Persia, Egypt, Sri Lanka, Greece and Southeast Asia.
The stone replaces the brick in the constructions demonstrating a more fortified structure as is the case of the rock sanctuaries of the Baräbar region as well as the Asoka palace in the town of Pätaliputra.
Presenting as qualities the monolithic columns called stambha where polished stoneware was used and the bell-shaped capital simulating the lotus flower.
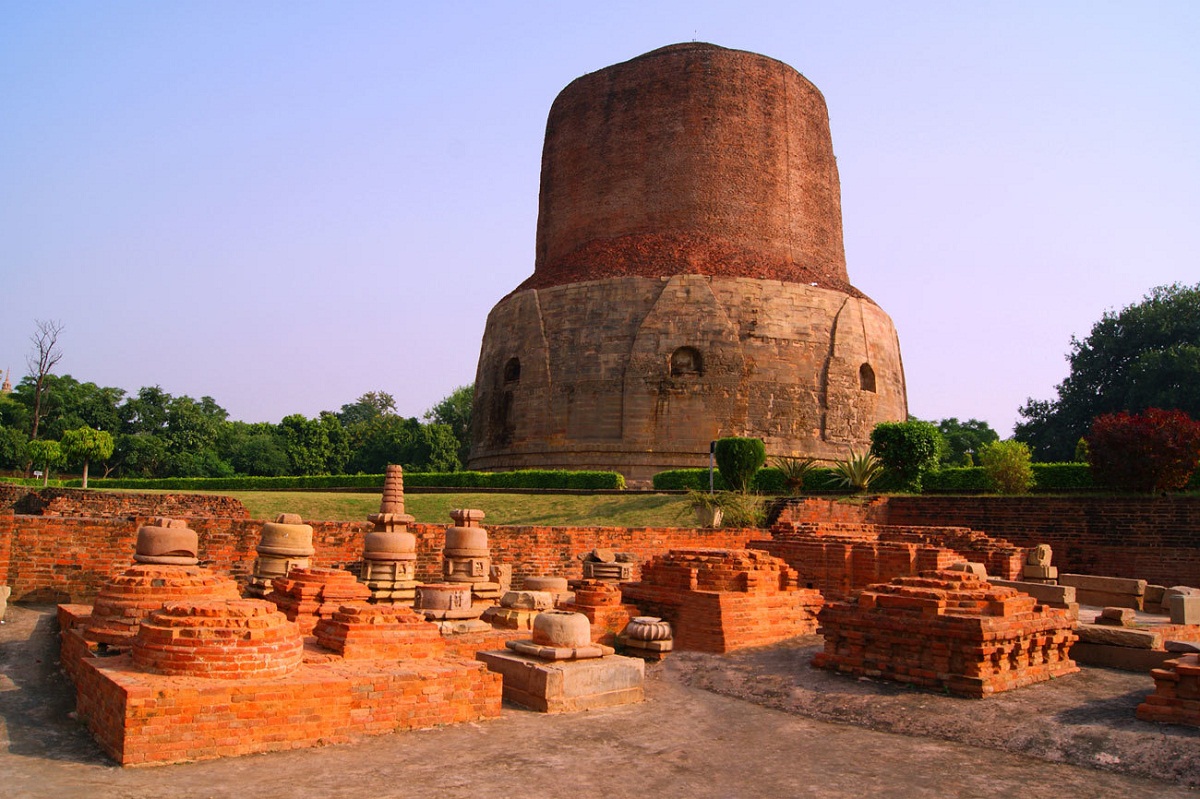
An animal sculpted in relief was also made, such is the case of the Capital of the Lions in the Särnäth region in the XNUMXrd century before the Christian era.
It is important to note that this image was made of sandstone and today is part of the national coat of arms of this nation. These well-known columns were erected in the government of King Asoka throughout his reign and the inscriptions declared his devotion to Buddha.
Forgoing any act of violence, the columns hovered around ten meters high and the figures were carved mainly lions.
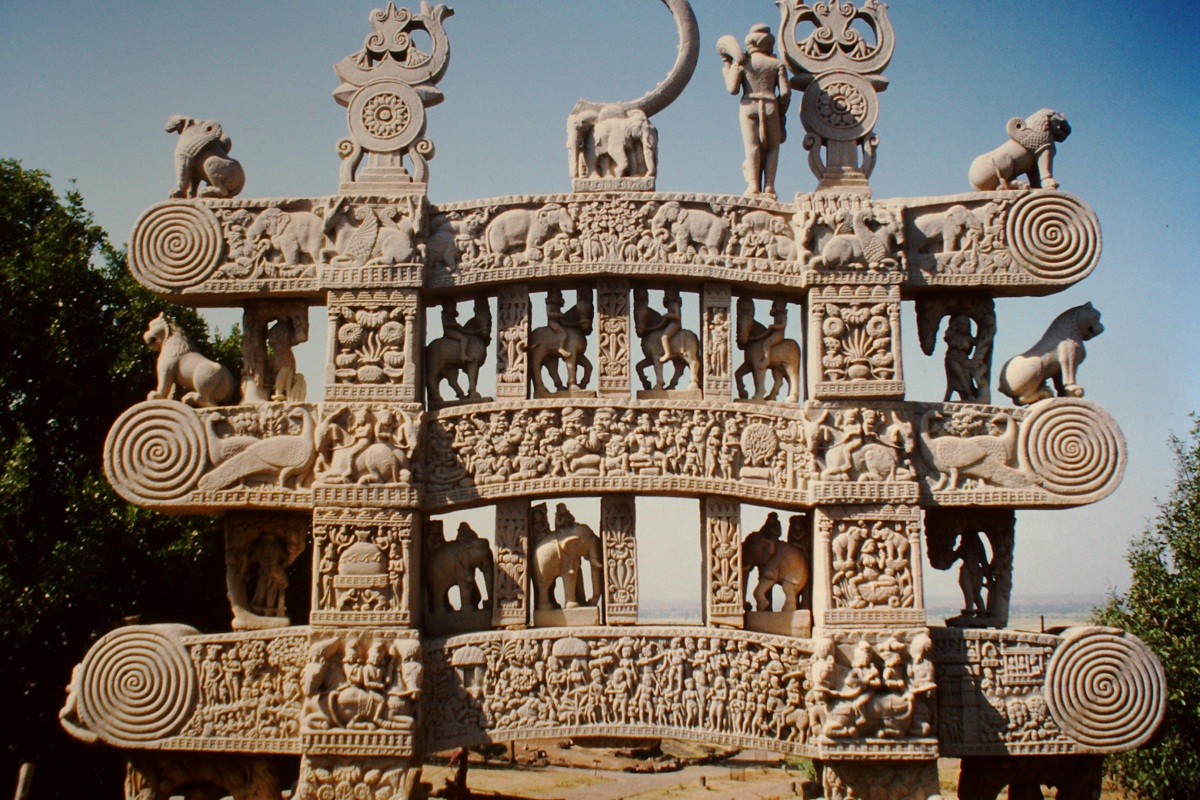
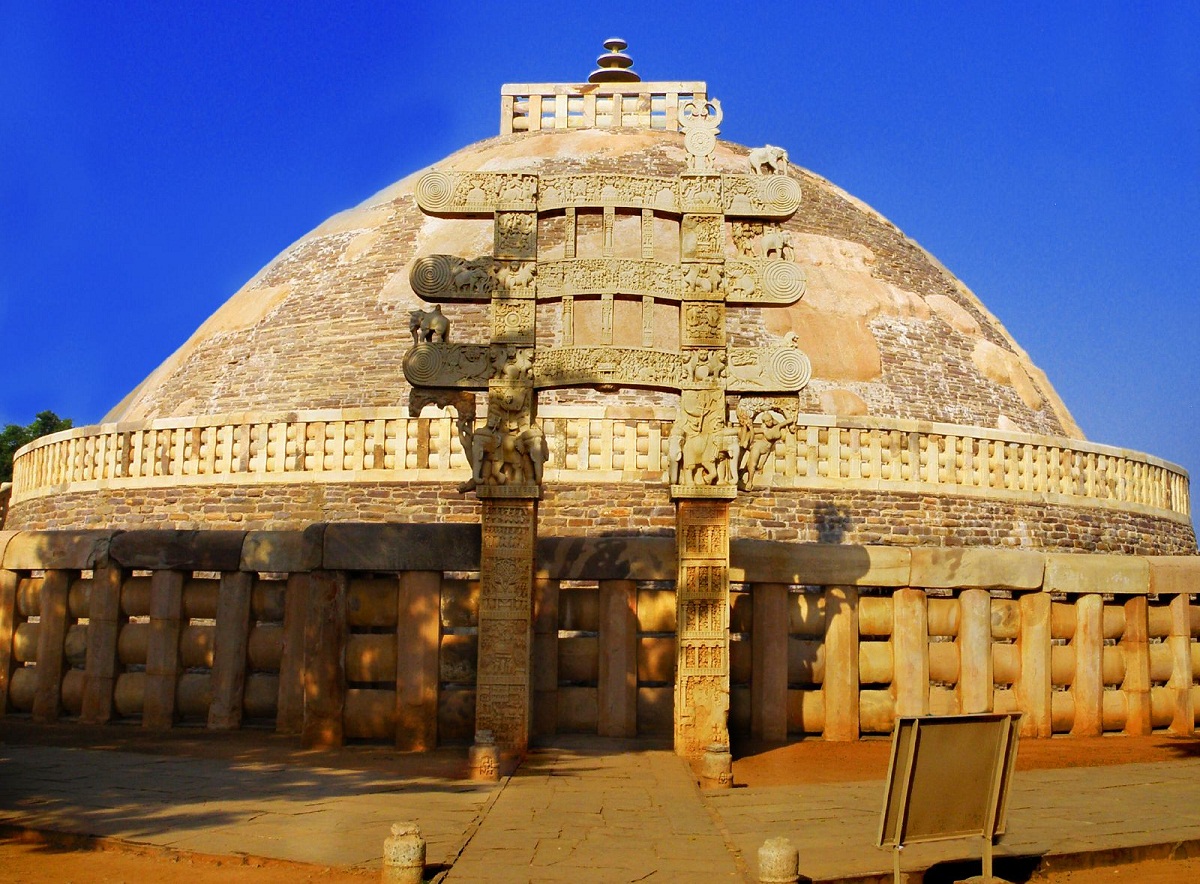
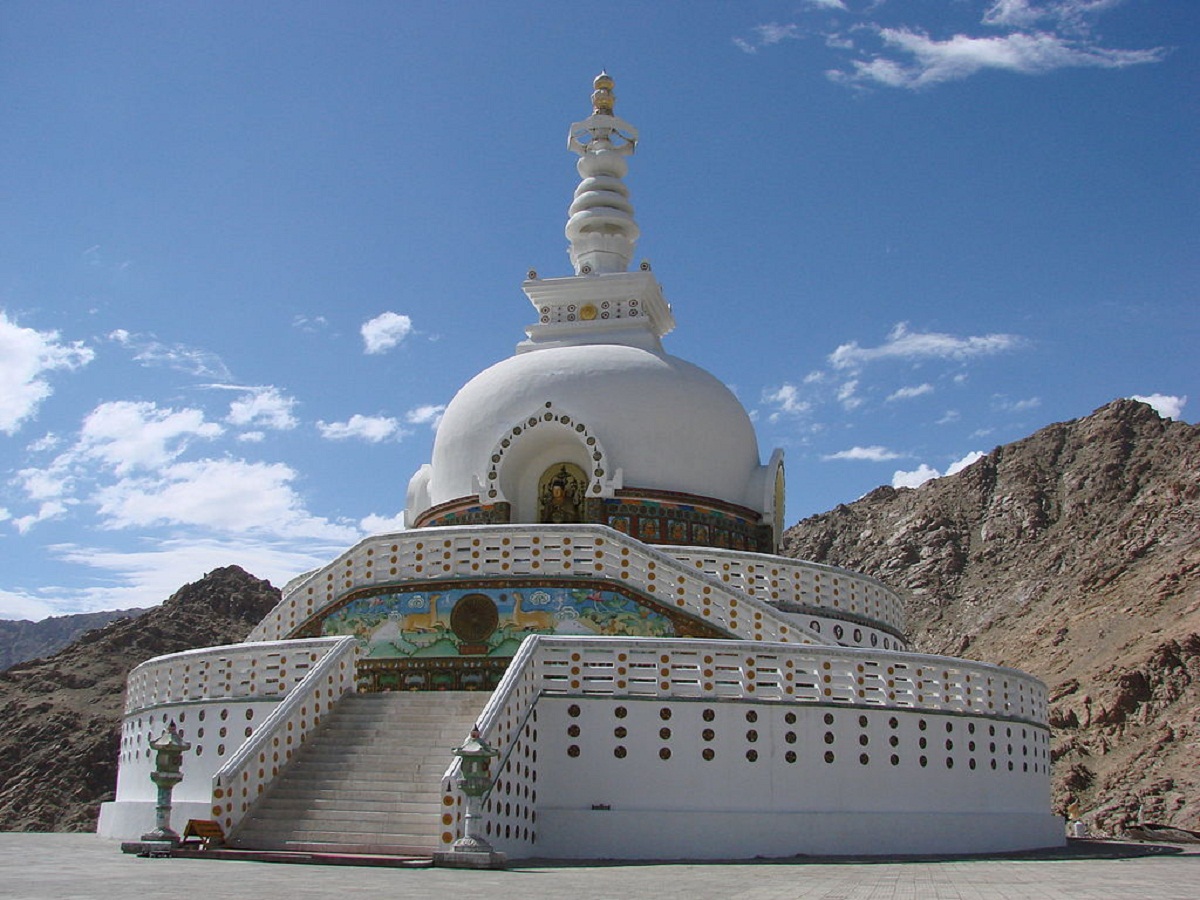
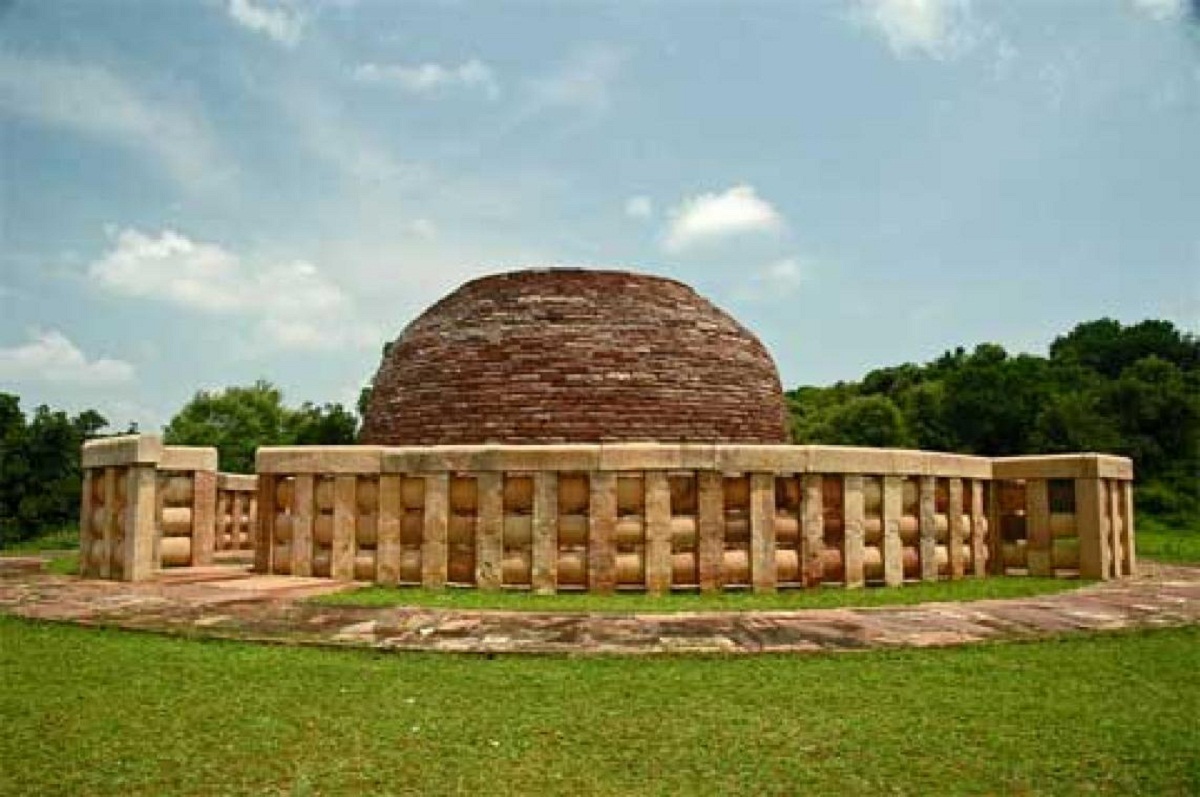
One of the most outstanding monuments of this stage is the stupa, which is a funerary mound that was used as a reliquary. Within it, bodily memories of the Buddha himself were found.
The magnanimous King Asoka was in charge of distributing among the main cities of his vast empire, since he represented the Universe.
Therefore, on a huge structure called maedhi that represented the Earth, a dome was located and its shape was hemispherical, symbolizing the celestial dome.
In the upper part it was flattened and gave rise to a quadrangular palisade plus a mast-shaped structure representing the axis of the world.
Without forgetting three disks in descending representation that simulate an umbrella the three jewels of Buddhism which refer to Buddha, the law and the monks or priests.
Thanks to the circular shape, it allowed the faithful to be able to wander around it as they followed the course of the star king, it was walled with a palisade that contained four doors in relation to the four cardinal points.
They are decorated with reliefs where figures of animals can be seen in addition to the deities and scenes from the life of Buddha.
Where his image did not appear but the same was symbolic for which the lions were used as the representation of the Sakya clan from which Buddha came.
Like the conch that pretended to be the voice of Buddha, in addition to the Buddhi that was the tree of enlightenment, other symbols used were the dharma – chakra.
Referring to the wheel of the law as well as Buddha Pada, which is the footprint of Buddha and the symbol of purity represented by the lotus flower, highlighting the stupas for their quality.
Therefore, you can see that the architecture was linked with nature in relation to the Chaitva sanctuaries and monasteries.
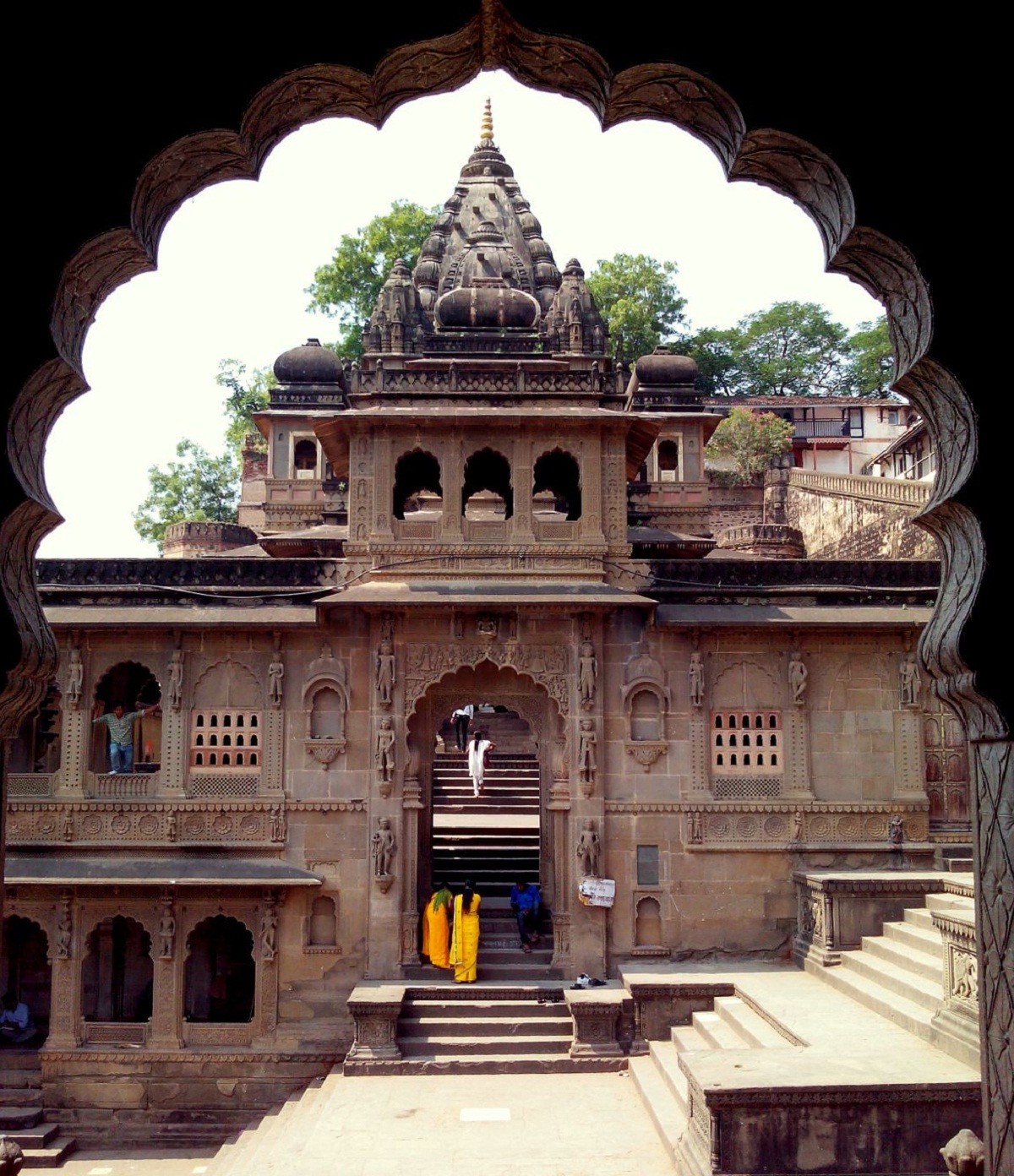
Known as Vihara, generally in Hindu Art, the elaboration of cave sanctuaries is evidenced, which were excavated in the stone and on the slopes of the mountains.
Architecture had a great role in Hindu Art, since the chaitva was made up of an apsidal floor plan which was made up of three naves plus the barrel vault made up of a series of arches called kudu.
These arches were typical of Hindu Art and stand out for their slightly pointed shape which was supported by the pillars while the vihara was a meeting place.
Its square-shaped floor plan and on its sides were the rooms of the monks, connected by a lintel system that formed a flat roof.
Among the structures of this historical moment, the Karli chaitya stands out, which was excavated in the stone and has a facade where the ogee arch is evident.
Inside it presents a nave with multiple corridors plus a large number of bell-shaped columns and reliefs of human images and animals such as elephants and a small stupa inside as a hemicycle.
It is in this stage where the sculpture of the Hindu Art was developed based on the elaboration of the capitals thanks to the Persian influence including the representation of animals presenting a balance in the forms to be represented.
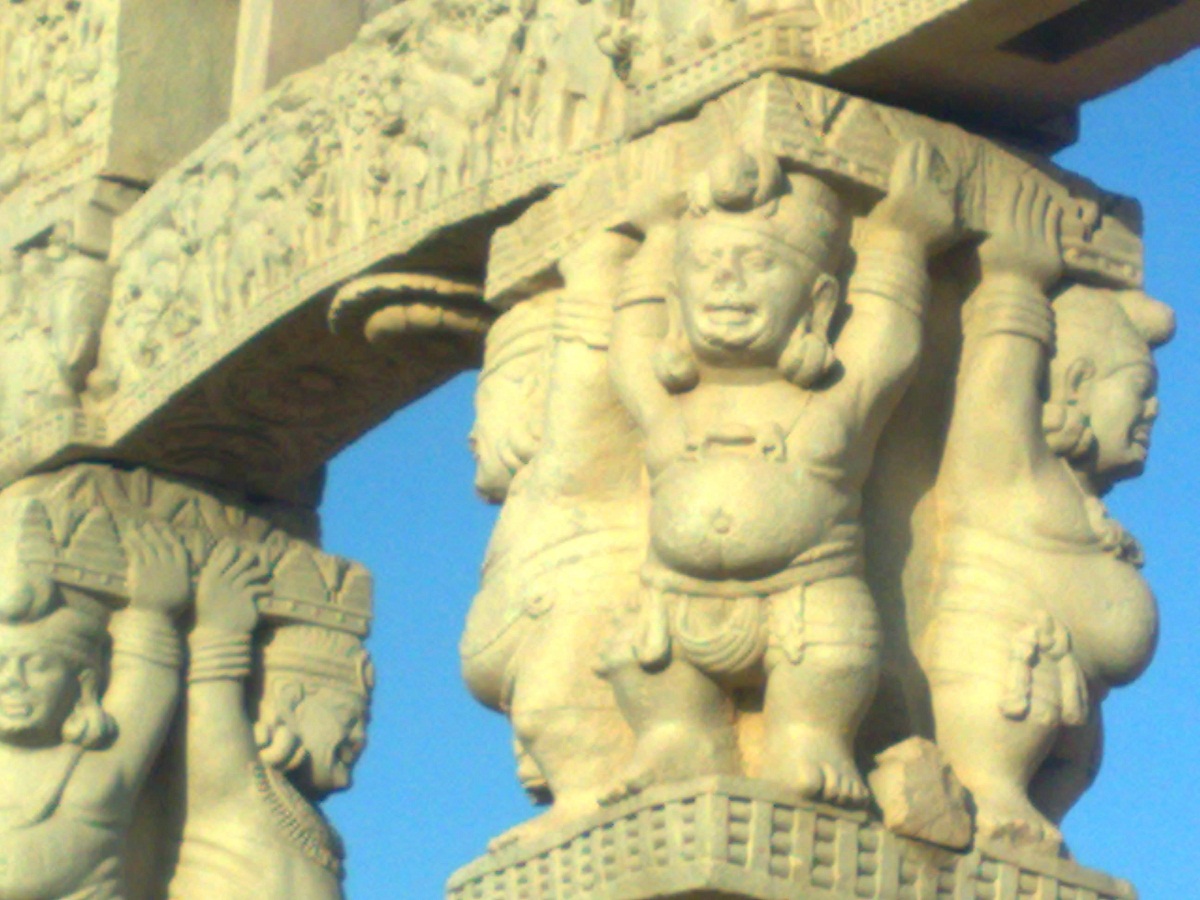
Regarding the high-relief, it was static while the low-relief narrated the scenes, the railings known in this region as védika were also decorated, without forgetting the doors of the stupas.
In this period the first versions of the iconography of Hindu Art appear through the representation of the vaksis that are the spirits of nature.
Remember this art is related to the sacred and was symbolized through naked women who were simply adorned through the use of jewelry.
An example of this can be seen in the east door of the Sanchi stupa and they were made thanks to the triple bending that showed a movement thanks to the three curves very common in this period of Hindu Art.
With this, erotic scenes that were part of the prayer began to be performed in Hindu Art and spirituality coupled with sensuality was planned in them.
the art of gandhara
In relation to the first centuries before the Christian era and the first century after Christ, when the Maurya dynasty died out, what is known as India.
It began to divide into small kingdoms where Hindus were found as well as Indo-Greeks belonging to the Andhra and Sunga dynasties.
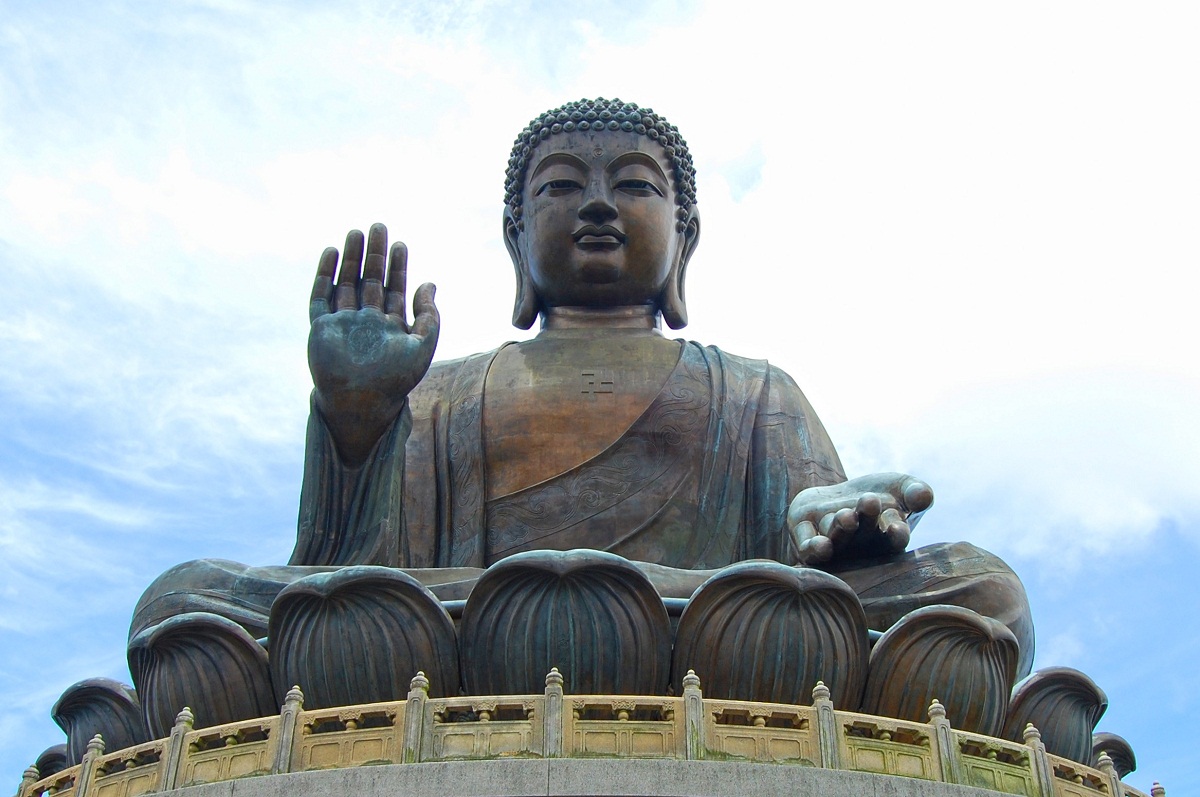
Other kingdoms belonged to the Indo-Scythian, which was the Kusana dynasty, and thanks to the Indo-Greek art, the art of Gandhara was developed with a great Greco-Buddhist tradition, where the direct representation of the image of Buddha began, unlike the other stages where it was only symbolized.
This transformation is promoted thanks to Mahayana Buddhism that began the veneration of Buddha as a deity and his figure entered the pantheon of bodhisattvas who decided to renounce nirvana in order to enlighten men on how to wash their souls.
With this, a new iconography related to Buddha called lakshana begins in Hindu Art, which was symbolized by a mandala that referred to a halo or a glow that demonstrated his holiness.
In addition, the ushnisha is a bow or a protuberance of the skull to demonstrate superior knowledge about this image compared to humans and the urn is placed between the eyebrows, which represents the illumination of this deity.
Regarding the lobes of the ears of this deity, it is observed that they are elongated, which represents wisdom and the folds that are observed in the neck of this image represent happiness, in addition, the mantle symbolizes austerity and through his right hand he grants Blessings to all watchers.
In order to create these images in Hindu Art, it was required to be inspired by other cultures such as the Greek as well as the Roman, using a delicate counterpoint and peace and calm are observed on its face, alluding to the deity Apollo of the Roman civilization. .
Regarding architecture in this context of Hindu Art, the construction of the monasteries was made up of sanctuaries, rooms and meeting rooms.
As is the case of the vihara in the Takht-i-Bahi region, very close to Peshawar, where the evolution of the stupas can be seen, so the dome is placed on a tall cylinder-shaped drum.
That was superimposed on a base in the form of a square, being the most outstanding of them the Kaniska in the Peshawar region, the excellent mercantile work is observed in this period thanks to the silk route.
Something of great value such as spices was exported from India since at that time there were no refrigeration methods in addition to the trade related to precious stones and metals.
Silk, unknown articles and jade were exported from the Chinese nation, as can be seen in the Kapisa archaeological center north of the town of Kabul.
Where the city was located to spend the summer of the Kusana dynasty, ivories carved in India were found. Like lacquers of Chinese origin and bronzes from Rome, even the glass that demonstrates the great commercial relations between these cultures.
Mathura Art
This style of Hindu art was generated between the XNUMXst and XNUMXth centuries of the Christian era and it was located in the town of Ganges between the territories of Agra and Delhi, which was the main city and capital of the Kusana dynasty.
There is evidence of a great artistic school that would spread throughout the land of India, including Gupta art, but thanks to the invasion of the Islamic civilization there are few representations due to their destruction.
But according to the investigations carried out, this type of art made the fusion of traditional elements of India with those of the Greco-Roman civilizations.
Among them stands out the collection and ivories of the trousseau of a princess found in the town of Begram with respect to the image of Buddha.
She was in a sitting position with her legs crossed, very similar to a yoga posture, and wheels were observed on both her hands and her feet.
If the Buddha was placed next to other figures, the size of this was much larger in relation to the others, demonstrating in Hindu Art the degree of hierarchy between the deities.
The Art of Amaravati
Between the XNUMXnd and XNUMXrd centuries of the Christian era, the city of Amaravati was located in a valley near the Krishna river, it has a style similar to that of Mathura.
Regarding the Greco-Roman influence thanks to the findings that were observed in the ruins of Virapatnam very close to Pondicherry.
As in the previous stages, its most prominent constructions are the stupas and the monasteries, one of them stands out for its height of 30 meters.
Being that of Amaravati and in relation to Hindu Art, sculpture stands out where centralized compositions are made where the group is fundamental in the scenes to be sculpted.
All these characters show a special smile, mainly the female ones, and use previous styles forming an eclectic representation.
Well, Buddha is symbolized as a human being and in other scenes as a superior being that requires other representations to know him.
Well, it was frequent to symbolize Buddha by means of the wheel which made a similarity with the Star King and the figure of a horse was also used.
That he used when he decided to get away from worldly life and even in a fig tree, a tree that represents wisdom, because under this tree he was in charge of preaching the word.
The Gupta Art
This art originated between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries of the Christian era and is one of the most typical arches of Hindu art, being a classical era where Buddhism spread. Throughout all the regions of Asia allowing the creation of the philosophy called Vedanta, besides the dramatic literature flourishes.
Hindu Art evolves thanks to formal purism and harmony between the figures created demonstrating an idealization of the human figure and the stupas are placed vertically denoting greater relevance in the ornament of sculpture.
Which has been made in bas-relief with the use of stone and stucco coatings are made among them, those of Rayagrija, Nalanda and Sarnath stand out.
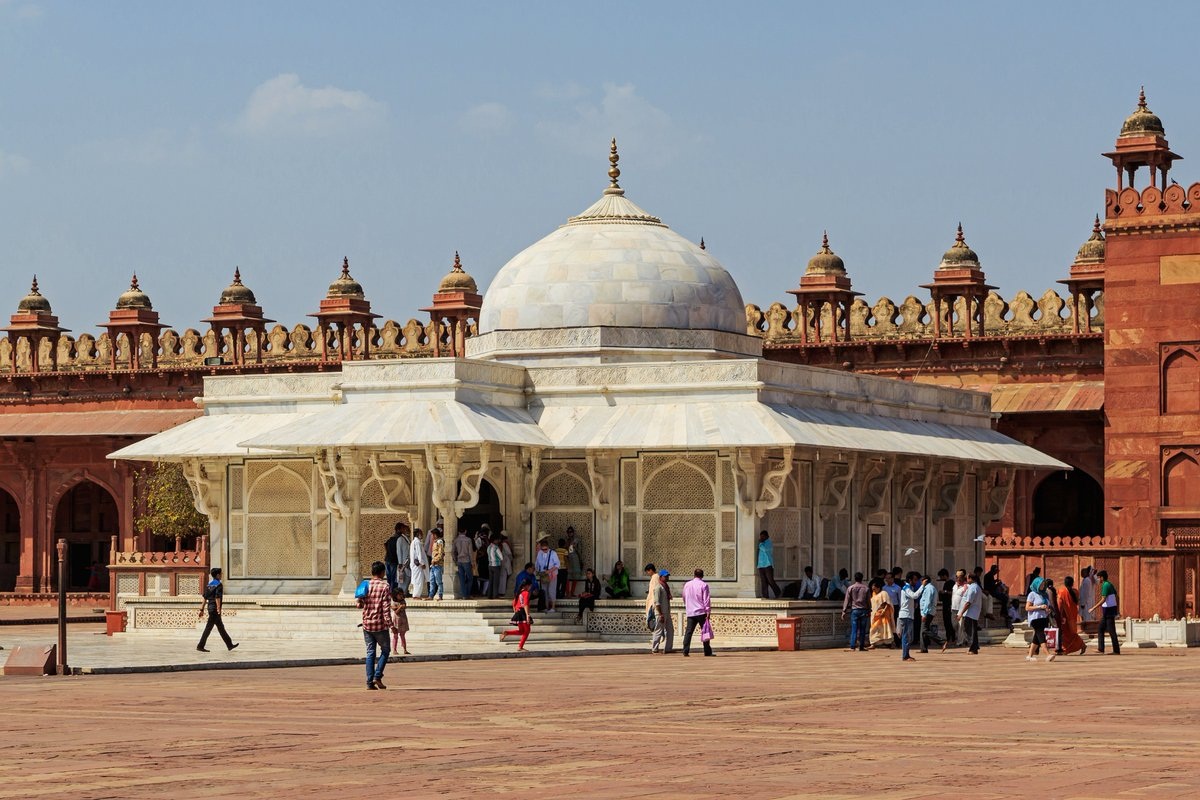
The greatest architectural works that were carried out in this period of Hindu Art are the cave sanctuaries or also known as vihara.
Among them Aurangabad, Elephanta, Ajanta and Ellora. Regarding the temples built in the open air, Bhitargaon, Bodh Gaya, Sanchi, Deogarh Sirpur and Chezarla stand out.
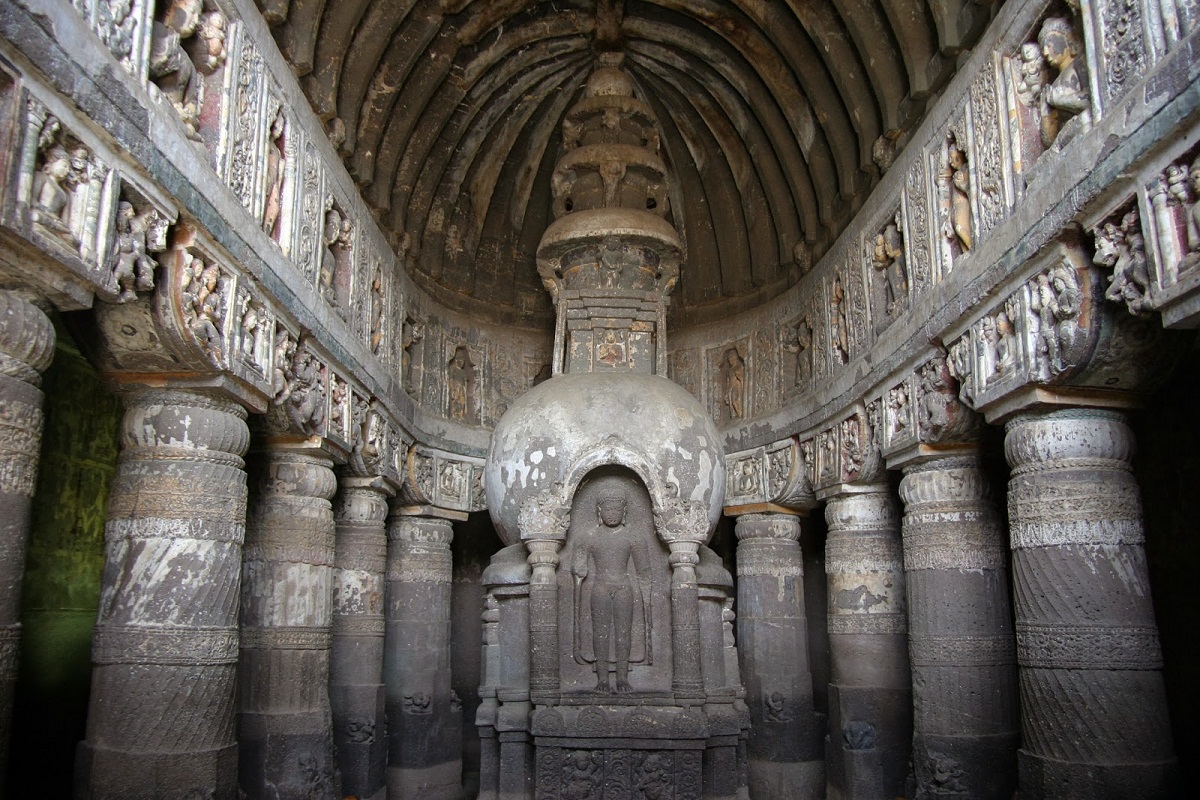
One of the temples or sanctuaries that stands out in Hindu Art is the Ajanta made between the XNUMXnd and XNUMXth centuries of the Christian era, it is made up of thirty caves.
Which were excavated in the rock specifically in the volcanic basalt and in them sanctuaries, rooms for the monks and meeting rooms were elaborated, they house all the manifestations of Hindu Art such as sculpture, architecture and painting.
Sixteen of these caves are decorated with amazing murals where a large number of pigments of plant and mineral origin were used on a layer of clay fused with straw and then lime was added.
The referent topic of these images is Buddha and the scenes correspond to the popular Buddhist tales known as jataka and even scenes of the usual order and of the nature so essential in Hindu Art can be evidenced.
These frescoes from the Ajanta sanctuaries present the naturalism and mythology of Mahayana Buddhism where the Bodhisattva of the blue lotus is observed where it is given a large size and a large number of animals surround it without order or perspective.
The posture is double flexion and the ideal of beauty of this time is evident in her features and the shape of her eyes very similar to a lotus flower petal and her eyebrows denote a curve very similar to the Indian arch.
Another of the temples where Hindu Art is evident in all its splendor is Ellora between the years 750 and 850. It is dedicated to Sivá. It was made of volcanic rock and has a large patio that ranges around one hundred meters long.
The structure is made up of two two-story buildings and has huge columns, both its exterior and its interior are adorned by human figures in multiple positions and in various attitudes.
Sexual practices, fights, meditation, dances, human images that simulate flying are observed, as well as life-size elephants adorning the walls of the temple.
With respect to the main scene, which is about four meters high, the gods Sivá and Parvati are presented at the top of the mountain and at the top of it, the demon with multiple arms and heads called Ravana is observed.
The main temple is made in honor of lingam and is in the center of the sanctuary in this sacred place inhabited by Buddhist monks and Hindu Brahmins demonstrating tolerance and peaceful coexistence between both religions.
With respect to the Elephanta temple, it is located on an island in Bombay Bay, when accessing the temple, a huge elephant sculpture is observed, hence the name given by the Portuguese in the year 1712.
It stands out for its surprising high-reliefs, among them the bust of Sivá Majadeva made in the XNUMXth century. This bust is six meters high and is represented by three heads, one male, one female and one hermaphrodite.
Which represent the principles referring to the constructive and destructive duality in addition to the divine essence demonstrated in the whole.
Regarding the main chapel of this temple, it is again dedicated to the lingam male organ, which is the main attribute of Sivá and is symbolized by a monolithic cylinder.
One of the qualities of the Hindu Art of this period is the serenity and balance which is represented in the image of Buddha where he is ideally symbolized and presents a sweetness and spirituality that are typical of the Mathura style.
The main sculpture that is made is of Buddha sitting on his throne as if he were meditating, his legs are crossed similar to the yoga position and his hands are in various positions according to the mudra he is performing, which is part of an esoteric language.
Another example of Hindu Art is the Master Buddha that comes from Samath in the XNUMXth century where the smoothness in the lines created is observed.
A great perfection is shown in the realization of the face demonstrating an ideal beauty but at the same time mythical with a smooth movement that denotes sensuality and spirituality very typical of Hindu Art.
Likewise, the torso of the Bodhisattva stands out, which comes from the Sanchi region, which dates back to the XNUMXth century, and has a soft skin in addition to the clothes it wears and the jewels that adorn it.
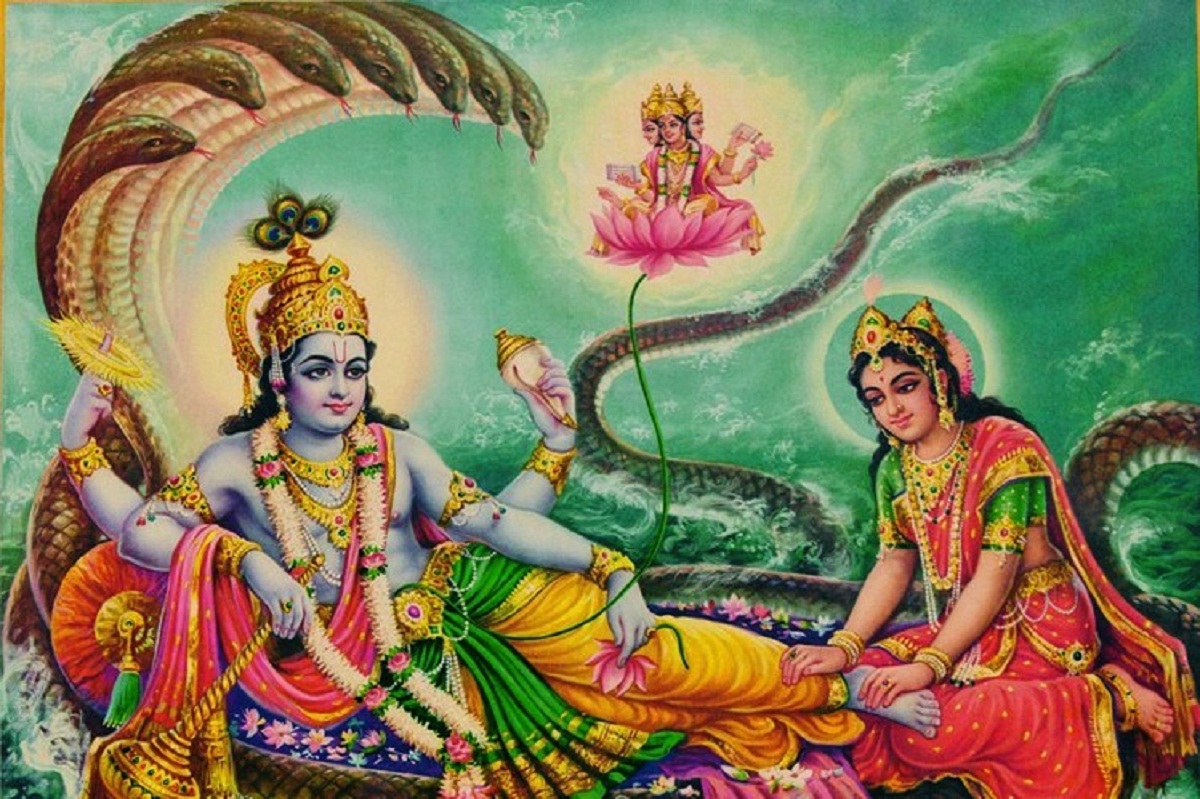
It also highlights a relief of Vishnu where he is sleeping on the snake named Ananta next to other Hindu deities.
This Gupta art spread throughout the Deccan region, fostering a diversity of styles that are known as post-Gupta and, as there were several kingdoms in the region of India, each town used it in its best way among those that stand out.
The architectural and sculptural complex of the city of Mahabalipuran that since 1984 is a World Heritage Site.
A beautiful relief called the Descent of the Ganges is evidenced and it has a length of twenty-seven meters and in relation to the height of this temple it is nine meters, it is built with granite.
Inside there are more than one hundred figures between Hindu deities, humans as well as animals as evidenced by the elephants that are made on a natural scale in the surroundings three huge rocks were carved giving them the shape of a lion, elephant and bull respectively.
Likewise, five monolithic granite sanctuaries can be seen, which are shaped like cars and have reliefs where guamna figures and animals can be seen.
In the Bengal region, the Pala and Sena dynasties also distinguished themselves from the Gupta style, showing greater magnanimity.
And Impersonal Expressions The Pala dynasty style stupa with a bulb-like dome was transmitted to the locality of Nepal and Southeast Asia specifically in regions such as Burma, Thailand and Cambodia.
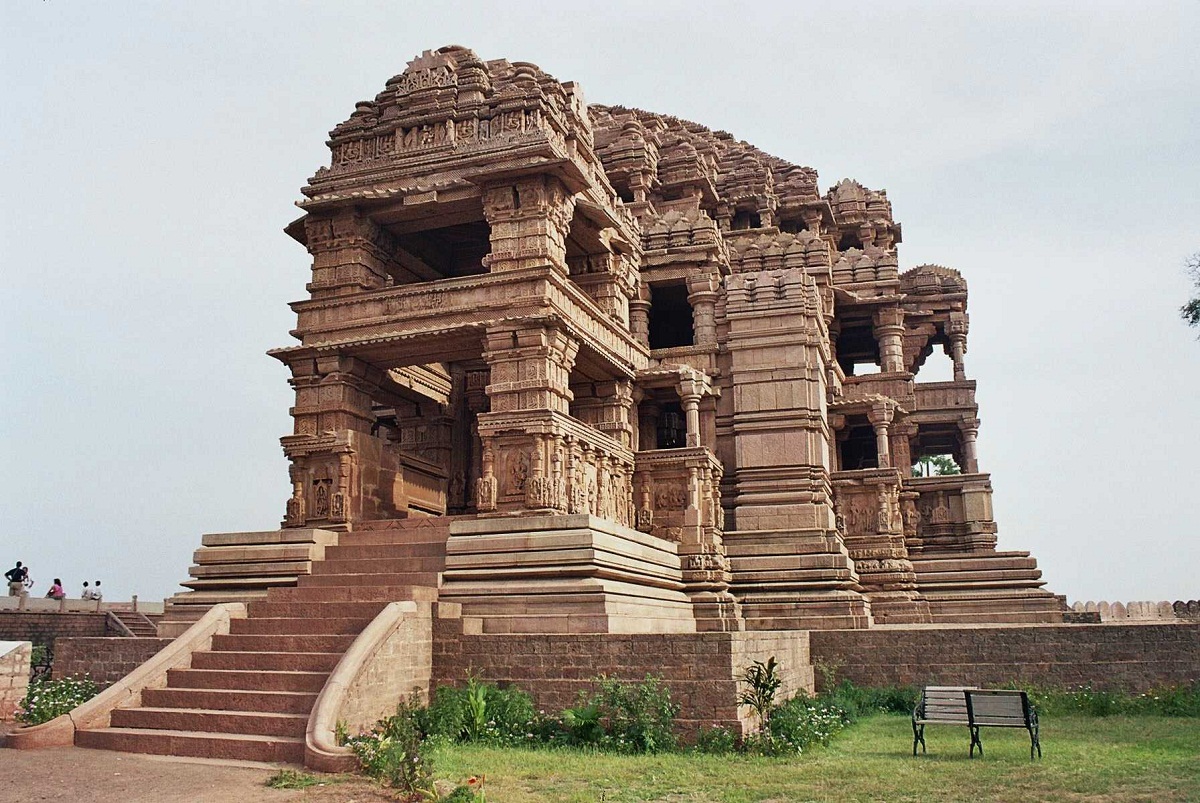
Hindu art between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries
After the invasion of the White Huns, the region of India was again formed into small kingdoms that faced each other.
For power in regard to the north and west of India was occupied by the raiput known as King's Son were warrior clans.
These were in charge of forming multiple dynasties such as the Solanki, Rastrakuta, Chandella and Pratihara which in turn formed new artistic styles that further evolved Hindu Art until the time of the invasions of the Mongol nation.
Regarding the religion of Buddhism, it lost part of its power against Hinduism, which became the national religion.
A large number of religious sanctuaries were built thanks to the contributions of the landowners who owned extensive territories, which allowed the feudal system.
Regarding the architecture of this period of Hindu Art, two modalities are observed, as is the case of the covered building and the other structure was the pyramid, very typical of Dravidian art.
Hindu temples called nagara were built around the ancient sanctuaries where the images of the deities were kept.
Regarding fertility, as is the case with the lingam and the ioni, circular designs were made to protect these ancient buildings.
Therefore, in front of the structure, a terrace was created where various rooms were observed inside the tower and the building was projected upwards as the masculine element on a structure that referred to the feminine element ioni.
The plan of the structure was carried out in an east-west direction following the Star King, so its design was suitable for astrological studies.
To make the measurements, a rigorous scale was used to make the appropriate proportions with the intention of making a similarity of the Universe.
For this they used the lintel system and although they knew the dome and the arches, they did not think it necessary to use them. They are used when the Muslims arrive.
The decoration that was used in the Hindu Art of this time was on the outside of the temple to avoid distraction inside which had to be dark with the intention of being able to perform the sacred cult.
With respect to the nagara in this stage of Hindu Art, four styles were created, such as the one from Orissa designed through the use of red sandstone.
In these buildings, the use of superimposed volumes is observed, which are connected by a tight passageway, as can be seen in the Lingaraja temple in the town of Bhubaneswar.
Hindu Art between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries manifested a new style called Khajuraho in the religious capital of the Chandella, another of the dynasties that held power in a territory of India between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries.
Demonstrating a great majesty in the elaboration of their temples and in the sculptures that were in charge of adorning them.
It is said that at this stage around eighty temples were built, of which only twenty-two remain in an excellent state of conservation. It is said that the area occupied ranges from twenty-one square kilometers.
Among these temples, Khandariya Majadeva stands out, created around the year 1000. It was made on a platform where the sanctuary is at the bottom of the structure and the sculptures are of great quality.
Where the scenes demonstrate mythological, erotic tantric and legendary topics which are evidenced on the walls of the building and since 1986 this site was declared a World Heritage Site.
The Lingaraja temple located in the Bhuvaneswari region in the year 1100 is created in honor of the deity Sivá. It is a set of buildings and among them the sikara stands out as a tower which curves as the height advances and as the end is a stone disc called amalaka.
The exterior walls of this religious sanctuary are adorned with sculptures, while inside there is a lingam in the form of a granite block on the respective ioni as a tribute to fertility.
One of the attributes of this temple is that the exterior walls are ornamented with small-scale designs from the temple itself, demonstrating their fascination with the multiplication of objects and their number.
Another of the temples of great artistic significance is the one built in honor of the Sun God in the Konarak region between 1240 and 1258, being a great example of the architecture of this period of Hindu Art.
But only of this structure remains the mandapa in the shape of a chariot with its finely sculpted horses as well as wheels at the base of the building. This building was declared a World Heritage Site in 1984.
We can also tell you about the Kesava temple located in the Somnathpur region, built in 1268, which stands out among the other constructions for its horizontal design and is made up of three star-shaped sanctuaries as well as a rectangular mandapa.
It shows a large number of decorative sculptures typical of Hindu Art, there are also the enormous living temples located in the Chola region, which were built between the years XI and XII.
Regarding the sculpture of Hindu Art, reliefs are still made in the various sanctuaries as well as isolated figures and scenes that show us a narrative fact specifically about the Hindu cycle related to mythology.
Many of the explicit scenes of the tantras demonstrate how through sex one can reach the spiritual elevation of human beings.
The sculptures are now made using another material such as bronze, widely used in the region of Bengal and Bihar related to Buddhist topics.
Likewise, bronze was used to create sculptures from Tamil Nadu, a theme of the Hindu religion and other deities, such as Sivá Nataraja, who was the king of dance.
In the Chola dynasty Tamil Nadu is represented with four arms in addition to long hair and in one of his hands a drum to demonstrate the sound through the ingenuity of Hindu Art.
It can be seen in other of his hands a flame is observed that is fire as an element of destruction this image is surrounded by a ring in flames that represents the cyclical process of the Universe.
The same stands out in this period of Hindu Art the statue of Gomatesvara made in the year 978 and 993 which measures about seventeen meters high which represents the Jaini master named Bahubali.
Islamic art period
This originates between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries when the Muslim invasion arose, which brought a stir in Hindu Art as they were in charge of destroying a large number of temples and thereby eradicating Buddhism in the nation of India.
After a great succession of dynasties in this period, such as the Guríes, Gaznawies, Tugluquies, Khilji dynasty and the slave dynasty, the Mongol Empire was later formed, which was in charge of uniting all the regions of this nation in a single territory.
Therefore, Hindu art was enriched with elements of Islamic culture, specifically with regard to architecture, elements such as the arch, the vault, the dome were used, in addition to the use of lime mortar.
New buildings were even built for the Hindu culture, such as mosques, and in relation to ornament, they learned to decorate with mosaics and to use calligraphy, as well as the technique of embedding objects and tesserae for decorations.
Through the Islamic influence, Hindu art acquired a new conception of the line and the use of space of already known elements such as white marble and red sandstone.
Therefore, Hindu mosques were built which are made up of three naves which are made specifically for prayer and the wall is oriented towards Mecca where the mihrab and minbar are located.
With respect to the central nave, it is made up of three to five vaults which are placed longitudinally and in their ornament they use a design of stalactites called murkana.
It is equipped with a large patio and a basin for lavatories, often porticoed to be used as a pardon. In the corners, the minarets were placed, as well as a room for the priests.
Among the most outstanding of these mosques in Hindu Art we can point out the Sultanate of Delhi created in the year 1210 and the Oila – i – Kohna Masjid.
Located in the Purana Qila of the Humayun region in the year 1541 and in the provincial sultanates, the Atala Masjid stands out in the town of Jaunpur created in the year 1408.
In the region of Dehli, the Tower of Victory stands out, it is the tallest minaret in the world, its height is seventy-two meters, it was built between 1194 and 1199 under the command of Outb ad-Din Avbak who founded the slave dynasty.
This building has a frustoconical design and the plant was created in an undulating poly shape with various lines, it is made up of five floors.
Each one has terraces folding the muqarnas, the initial three made with red sandstone and the rest in white marble plus an epigraphic ornament made in stripes.
The whole of this structure is made up of a pillar made of iron measuring approximately seven meters and it was forged during the reign of Chandragupta II who lived between the years 375 and 413.
One of the singularities of this building is that despite the date of construction it does not present any type of corrosion and in 1993 it was part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Mughal architecture
It was one of the most fruitful and presented great splendor in Islamic art in India. Among its first manifestations is the Babri Masjid mosque ordered to be built by the first Mughal sovereign named Babur.
With respect to Fatehpur Sikri, unlike the other buildings that had a religious connotation, this was a palace that was built between 1571 and 1585 near the town of Agra under the command of Emperor Akbar to be the seat of the court.
It is a structure that is walled and measures approximately six kilometers in space, several structures were built. Based on red sandstone, among them stands out Diwan - i-khas, which was a cube-shaped building where the emperor received visitors.
It also contained a pond named Anup Talao and gardens influenced by Persian Art which was fourfold and within them was the house of prayer called Ibadat Khana without forgetting the harem area.
Where several buildings were designed, such as the Panch Mahal, which was a recreation pavilion, the Birbal Mahal, which was the Queen's duplex room.
The palace of the winds and the pavilion of the queen mother as well as a mosque that stands out because its mausoleum was made with openwork white marble and stone inlays.
The Mausoleum of the town of Agra named Itimad-Ud-Daulah created between 1622 and 1628 shows the transformation of the initial Mughal architecture where red sandstone was used as raw material and later white marble was used.
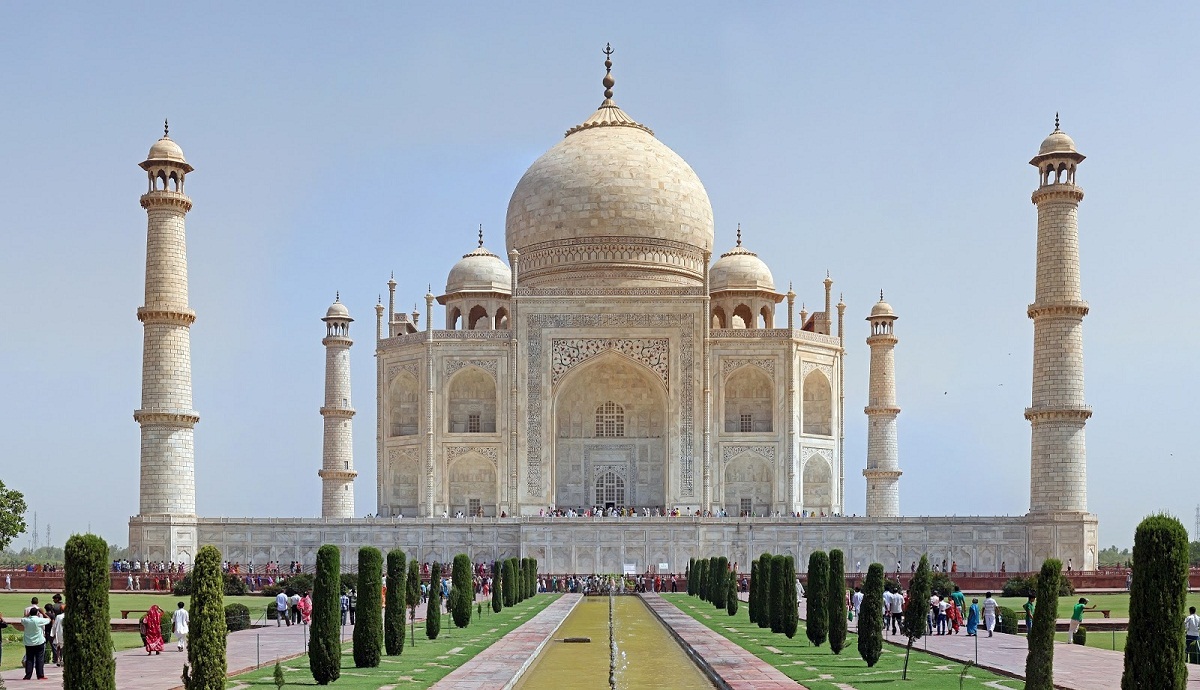
Among them, the Tai Mahal stands out. It was built under the orders of Nur Jahan, wife of Jahangir, to bury her father named Mirza Ghiyas Beg, who obtained the title of Itimad-ud-Daulá, which means pillar of the state.
The walls of this building were made of white marble inlaid with precious stones such as onyx, lapis lazuli and topaz.
Regarding the drawings, the Persian influence is observed and is symbolized by geometric figures and vases of flowers or plants with ornamental motifs.
So the Tai Mahal is the work endowed with beauty that was carried out in Mughal Art between the years 1632 and 1654 that the emperor Sah Yahan ordered to be built.
In honor of his late wife Mumtaz Mahal is a mausoleum made of white marble, the construction platform swings seven meters flanked by four towers.
The facade of this structure has a Persian iwan-type arch with other smaller ones on the sides. The interior room is octagonal in shape and rises with a large dome, which is also flanked by two other small bulb-shaped domes.
Being one of the best known structures in the world today thanks to the harmony of its proportions and the delicate decoration where inlays with floral inspirations and geometric shapes are evident.
In addition, in front of this majestic building there is a beautiful Persian garden that is surrounded by four water channels which intersect.
They allude to the four rivers of Paradise where water, wine, milk and honey flow. It was declared one of the Seven Wonders of the Modern World in 2007.
Traditional Hindu Art
It is important to note that traditional Hindu Art was still manifested in the southern region of the Deccan locality specifically in the Vijayanagar kingdom between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries.
Where the Tiruvengalanatha sanctuary stands out made in the year 1534 which was made in honor of the deity Vishnu as well as the Lotus Palace.
The doors of these buildings were made with lobed arches, demonstrating a fusion between traditional Hindu and Islamic forms.
Therefore, the use of elements such as vaults, arches and domes, without forgetting columns and balconies, was used in Hindu art.
The religious buildings of this region were large and complex where a large number of entrance towers can be seen, which were tall and had a pyramid shape.
Which represented Mount Meru, which is the Hindu Olympus where superimposed friezes and decorations of sculptures made of stucco and brilliantly colored are observed.
Another of the sanctuary cities that is important to highlight in this article on Hindu Art corresponds to Madurai, created in the Nayvak dynasty in the XNUMXth century.
This shrine is consecrated in honor of Minaksi the goddess who has fish-shaped eyes and Sivá Sundaresvara who is the Beautiful Lord.
It contains polychrome statues of Hindu deities and the sanctuary is surrounded by a series of corridors and hypostyle halls that have finely carved columns.
Among which stands out the hall of the thousand columns decorated with images of monstrous animals, today it is a museum where a collection of bronze from Chola and Vijayanagar is housed.
With regard to painting in Hindu Art, it was perfected in the field of miniature, a genre that was adopted from Islamic art, specifically in chromatism.
In terms of perspective, beginning in the fifteenth century, clear but not varied colors were used in figures without relief and in stylized faces with striking eyes.
Two main schools were created in this area, being Rajasthani the one that developed in the regions of Malwa, Mewar, Jaipur, Kishangarh and Bundi where landscape qualities, static composition and drawn characters are presented frontally.
The other school is the Pahari which originated in the eighteenth century in the town of Panvab in the small kingdoms of Guler and Kangra. The style is very sensitive and colorful in courtly and chivalrous scenes, specifically in the myth of Krishna.
It is at this stage that textile art prospers in materials such as silk and cotton, managing to work in one hundred and fifty different types of cotton.
Where multiple modalities are observed according to the region, such is the case of the painted fabric of the Deccan as well as the fabric mixed with cotton made in Gujarat.
These fabrics were painted, printed, dyed and embroidered with multiple applications, demonstrating the skill of their creators.
Even Jain art was developed in great harmony, which was a style of great interest in the Western world that was reflected in the temples and sculptures created with white marble.
Where inlays of precious stones of different colors were made and allowing a great ornament in the sanctuaries among them, the Ranakpur temple stands out as well as the Neminath temple on Mount Abu.
Miniature art also stands out, as is the case with the illustrations of the Kalpa-sutra, which is the sacred Jaini text that narrates the actions of Mahavira, who was the founder of this religious sect.
This text was in a horizontal format made with palm leaves in which two main colors were used, such as red and indigo, as well as static figures with a rigid frontality.
In addition, at this stage the main works of the Sikh warrior people were developed and their religion was founded in 1469 by the patriarch Nanak, based on the belief in a God who could not be named and on worshiping his sacred book.
Called Guru Granth Sahib among the largest monuments of this sculpture are in the city of Amritsar in the town of Pavab that was built in 1574 where the Golden Temple called Gurdwara Har Mandir stands out.
Colonial Art
This was done between the 1757th and XNUMXth centuries when Great Britain defeated France and occupied the nation of India in the year XNUMX called the Seven Years' War.
When the occupation of the English arose, a colonial style spread that contributed to the Hindu Art the languages related to the European style.
It should be noted that during this confrontation between the French and English soldiers, the inhabitants appropriated both artistic styles, as can be seen in French-style regions such as Baroda, Hiderabad and Nagpur.
Likewise, the Portuguese architectural style of baroque forms was observed in Hindu art that was whipped with the Hindu arts and they stand out in the Cathedral of Goa created between the years 1562 and 1619.
As well as in the Basilica of the Good Jesus of Goa that was built between 1594 and 1605 where the remains of the tomb of San Francisco Javier are housed.
Such is the interest of these Portuguese constructions with Hindu Art that they have been part of the World Heritage Site since 1986.
With the conquest by the English, a neoclassical style was created that was very similar to the one that was being carried out in the United States simultaneously.
Such is the case of the Fort of Saint George in Madras, which was built between 1644 and 1714, as well as the Cathedral of Saint Thomas in Bombay, which was built in 1718.
It should be noted that in 1690 the city of Calcutta was founded, where the headquarters of the British East India Company was established.
Therefore, since the XNUMXth century it has been the seat of the administration of the English nation in the Hindu region and among the first military constructions that it carried out.
Fort Williams is located between the years 1700 and 1716 after this, a religious temple as is the case of the Cathedral of San Juan built in 1787.
In addition to the seat of the viceroyalty, the Raj Bhayan Palace was built between 1798 and 1805, creating a city with large spaces with gardens, such as the Maidan Park, the Government Plaze, the Zoo, the Botanical Garden and Dalhousie Square.
In the XNUMXth century, the Victorian neo-Gothic style was used specifically in the official buildings of the English invasion and one of the cities that showed splendor in this style was Bombay, where great architectural constructions were carried out.
Among them is the Town Hall in the year 1855 as well as a religious temple such as the Afghan Memorial Church in the year 1857.
The Crawford Market in the year 1867 then the Rajabai Tower in the year 1874 and to move the Victoria Terminus Station between the years 1840 and 1847.
In the city of Calcutta, the hospital was built in 1835, as well as a religious temple, St. Paul's Cathedral between 1840 and 1847. In addition, the University was created in 1857, the Madrasa in 1871 and in the year 1875 the Indian Museum.
Mid-nineteenth century
Traditional Hindu art stood out in the city of Jaipur, the capital of Ravastan, in 1728 and was called the pink city because of the use of terracotta.
To paint the buildings among this architectural complex, the Maharaja Palace from the year 1728 stands out, then the Ishvarlat Tower that was created in the year 1743.
In addition to the Palace of the Winds from the year 1799, it has a beautiful façade built with stone shutters where the colors pink and white were used. It was used as a lookout point by the women of the harem.
Another of the works that stands out is the Jantar Mnatar created in 1728, as well as an astronomical observatory made of marble and sandstone, it has sundials, astrolabes and chandeliers.
Due to the British East India Company, which is responsible for the export of agricultural products such as tea, spices, rice, coffee and sugar, as well as products from the textile area, it allowed an artistic exchange.
The English Company was interested in carrying out studies related to the cartography and ethnography of the region. For this, they were in charge of bringing artists of European origin.
With the intention of being able to document the main monuments of Hindu Art and the beautiful landscapes of the Hindu region. Thanks to Western art, transformations were made in Hindu Art as they learned the technique of oil painting as well as the use of perspective and chiaroscuro.
Creating a style known as the art of the company where the western technique was used in representations of Hindu Art mainly in picturesque scenes very striking for the English bourgeoisie.
Simultaneously, thanks to the fusion of English art with Hindu art, a style called Kalighat pat was created in Calcutta, which was responsible for mixing Hindu roots with the realism denoted by Western art.
The Contemporary Art
After great mobilizations, India achieved its independence in 1947 and new constructions were carried out thanks to the mediation of foreign architects.
Such is the case of Le Corbusier in the town of Chandigarh, this city was created by the architect of Swiss origin in 1953 by the new government thanks to the independence movement.
This architect was in charge of designing the urban plan of the city in addition to constructing multiple official buildings such as the Parliament, the Ministries, the Courts and the Government Palace.
Where the use of geometric volumes in a pure way is observed in addition to the use of new materials and techniques such as concrete and glass.
In addition, another architect of western origin worked, such as Otto Königsberger, and in 1939 he was appointed head of the state of Mysore.
In this region the Hindu Institute of Science was built between 1943 and 1944 as well as the Victoria Hall in 1946 in the city of Bangalore without forgetting the plan of the city of Bhubanesvara.
For the XNUMXth century, the city of Calcutta was the center of Hindu Art in India, creating the Bengal school, which allowed the revival of traditional Hindu art to prosper through the sponsorship of the Tagore family.
Specifically Rabindranath Tagore who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1913 and among his qualities stood out that of being an expressionist painter of a dark color.
In 1920, he founded the Faculty of Fine Arts of Santiniketan, very close to the city of Calcutta. It is important to highlight the influence of this family in the development of Hindu art.
It should be noted that the Tagore family received the Japanese philosopher and artist Okakura Kakuzö in India in 1902, so this family was impregnated with a large number of intellectuals and artists.
After the independence of this nation, Hindu Art has been impregnated with various Western techniques thanks to globalization.
As can be seen, in 1946 Francis Newton Souza founded a group called Bombay Progressives who, in addition to having strong leftist ideas, were in favor of Hindu Art.
Between the years 1050 and 1970, neotantrism originates, an artistic movement that reflects Hindu art from a modern perspective from the abstract point of view, then cubism appears.
Today Hindu Art is found in the field of contemporary plastic arts and by 2007 there were about 500 Hindus among the lists of the most sought-after artists in the world.
We tell you in this article about Hindu Art that currently the most sought-after artist in terms of sculptures is Anish Kapoor, who has managed to sell 24 lots for an amount of 6.440.150 euros.
Other artistic expressions of this culture
Other manifestations of the fine arts in the Hindu culture are observed, demonstrating its great variety thanks to the influences of the diverse cultures that dominated the Hindu territory.
In the literature
In the field of literature, this begins in the year 1500 before the Christian era through a Sanskrit text that was transmitted orally by its inhabitants.
Already in medieval times, thanks to the influences of other civilizations, writing had been introduced in this region and several modalities are observed, among them the drama stands out, which refers to the mythological epics where the imaginative character is glimpsed.
Among these texts stands out Bhavabhuti who was the author of Malatimadhaya a love story similar to that of Romeo and Juliet.
With respect to the epic poem, the most appropriate is the Ramayana, which comes from a new genre with the name of mahakavva referring to mythological and historical topics.
Lyrical poetry is represented in a text known as Sataka elaborated by Bhartrihari on the daily life of Hindus and the way of seeing life with respect to poems related to the theme of love is Gitagovinda created by Javadeva.
The fables where short stories with a great reflection are observed and are typical of Hindu folklore demonstrating their educational character among the authors who stand out in this topic are Naravana and Sivadasa.
Another famous book of Hindu Art literature is the Kamasutra dating from the XNUMXth century written by Vatsyavana where a large number of precepts and advice related to love are observed, since in Hindu culture sex is a form of prayer that allows you to reach enlightenment. .
Thanks to the invasion of Islamic culture, a flourishing of regional languages is observed in the region of India, which is why a large amount of literature is created in Hindi, Tamil, Bangali, Mahratta, Ravastani, Girati and Telugu.
The dramatic genre showed great progress and spread throughout the Hindu region, one of the most prominent being Ananda Raya Makhin.
Who was the author of the work Yiva-nandana, it was elaborated in the year 1700 where the drama of the human soul of a king imprisoned in his palace, which is the body itself, is discussed.
Likewise, the contemporary literature of Hindu Art is influenced by international currents thanks to globalization, among which the English domain stands out.
There are many Hindu figures in the literary world such as Madhusudan Datta, Sri Aurobindo, Rabindranath Tagore, Bankim Chandra Chattopadhvav, Jaishankar Prasad, Munshi Premchand, Mirza Galib among other great scholars of this noble region.
In the field of Music
It is important to note that thanks to the various cultures that were integrated into Hindu Art, music shows an eclectic stamp from the beginning of the Aryan culture that had melodies made up of only two musical notes.
While the Dravidians had much more elaborate music, as well as the dances of this ethnic group that are ascendants of the inhabitants of India, they were mainly related to fertility.
As for the proto-Mediterraneans, they allowed us to discover new musical instruments such as the magudhi and well known throughout the world because snakes are enchanted with this flute.
In medieval times music was vocalized and accompanied by musical instruments such as Greek zithers and harps. It is imperative to highlight the musical treatises that were made, such as the Brijad-deshi written by Matamga in the XNUMXth century.
In addition to Narada's Naradiva-siksa in the XNUMXth century and not forgetting the Samgita-Ratnakara of Sarnga Deva in the XNUMXth century. The musical notes were made up of seven being sa, ri, ga, ma, pa, dha, and ni.
To make the melodies, they were made with various structures of tonal cycles with multiple ornaments that were coupled with a specific measure of time that allowed marking the slow, medium or fast rhythm.
Later the music received the Islamic influence causing the division of two traditions in music known as the northern one that maintained the Islamic influence being romantic, decorative and the southern one more conservative to the Hindu Art proving to be austere and intellectual.
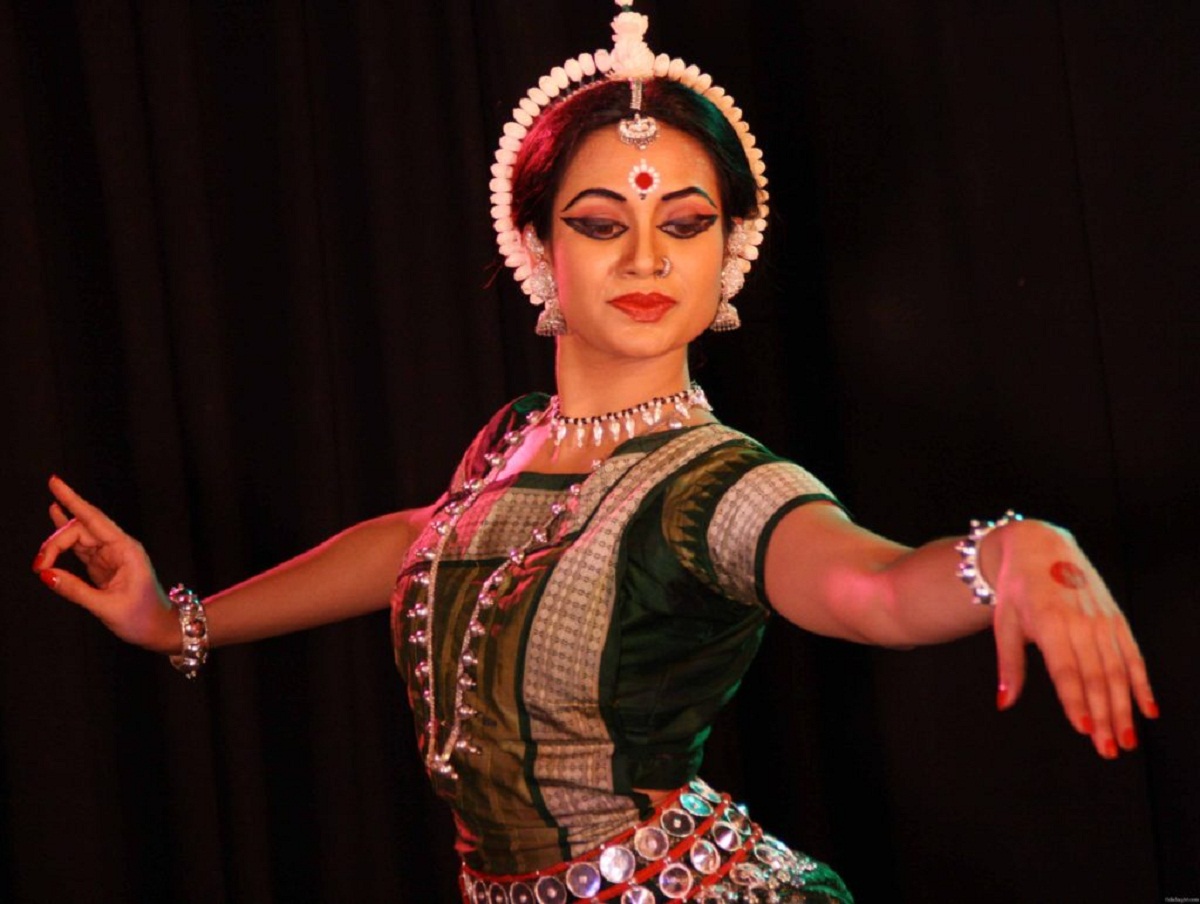
Performing Arts
The Hindu Art was benefited by the theater, the song, the dance and the mimicry and it was oriented towards mythological themes of the Hindu deities and the heroes of this nation.
Only the costumes and makeup of each of the actors on stage stood out and it was performed in modalities being the following: seven acts that correspond to the term Sakuntala and that of ten acts to Mricchakatika.
With regard to medieval times, the mahanataka stands out, which was a great show referring to the Hindu epics, the dutangada where an actor recites the text and other actors are in charge of staging the plot and the dance.
Then another modality called kathakali appears where the emphasis of gestures accompanied by music is evident. The dance is part of the theater and in it the corporal expression and the gestures are observed to the movement of the music.
The Indian Cinema
Thanks to technology in this nation, a large film manufacturing similar to that of the United States has been generated, but they call it Bollywood because it was built in the city of Bombay, the topics that are mostly used are of a mythological nature, in addition to traditional dances.
One of the aspects to take into account is that Hindu society is the population that most preferentially attends cinemas and the record exceeds one billion users in just three months.
As historical data, the cinematographer of the Lumiere brothers arrived in this nation in 1896 and in 1913 the first vernacular film of this region called Harishandra by Dadeseheb Phalke was made.
Regarding the first title that included audio, it was Alam Ara in the year 1931 produced by Ardeshir Irani by that time they had already made a hundred films per year specifically in Hindi, Bengali and Tamil.
Already in the 1940s and 1950s, a new way of making films emerged from the social point of view, showing the Hindu society in a realistic way.
Among the directors that stand out are the following: Mehboob Khan, Bimal Roy, Pather Panchali, Farah Khan, Satvajit Ray, among other great filmmakers.
If you found this article interesting, I invite you to visit the following links: