The earth, belonging to this vast universe, it also has secrets to unveil and to think that it is not, is a serious mistake. Currently, various aspects of it are still being studied, such as the earth's crust and its behavior.
Understanding the planet in the first place in which the only sign of life in the universe lives, is essential to understand other distant worlds. Sometimes the best can be right in front of your eyes, without having to look further. However, it is still hasty to say that this applies in relation to the universe and what it contains.
You may also be interested in our article: Are there other planets similar to Earth?
If you still don't know what the earth's crust is, keep reading to find out!
Sources: Invdes
During creation and the dawn of time, the planets were created with great precision and with ideal characteristics for each one of them. The composition of the planet Earth is peculiar, since it has various aspects that are widely known today, as well as others that are still under study.
Such aspects are closely related to the natural processes or cycles that take place in the vicinity of the planet. Therefore, understanding what the earth's crust is will contribute to the further understanding of these phenomena, facilitating new scientific results of great help.
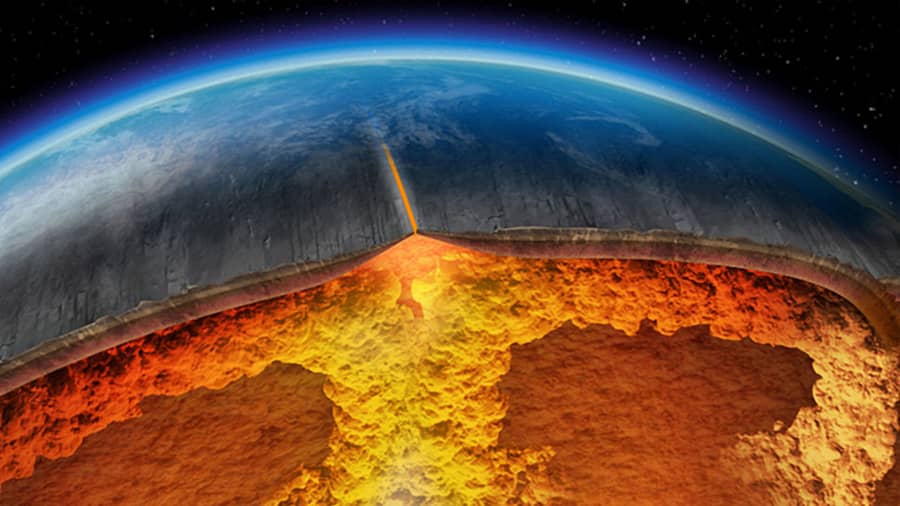
In short, the earth's crust fulfills its role as the outermost layer or if you like, the most superficial on the planet. It is part of the well-known geosphere and, although it sounds hard to believe, its thickness is relatively thin. Even the earth's crust barely holds 1% of the total mass of the Earth's dimensions.
Similarly, the question "what is the earth's crust" has led to the discovery that it is unique among many. What does this mean? Many rocky planets have a compact crust that does not subdivide. In the case of Earth, its crust separates into an oceanic part and a continental part.
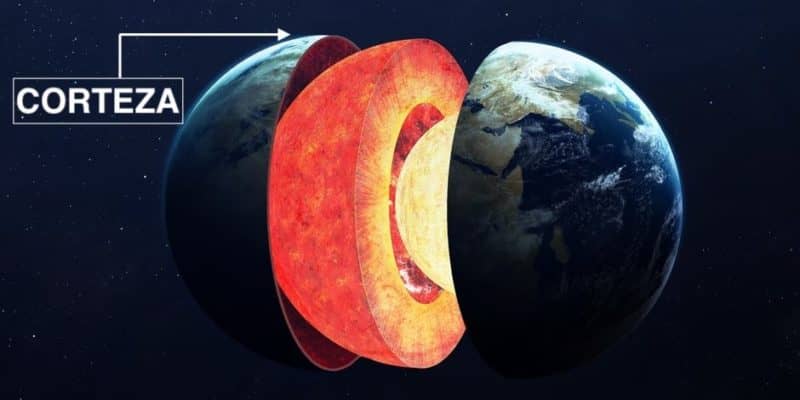
The layers of the earth's crust, key to understanding how it was formed
If you have reached this point, it is because you are interested in finding out more about it. Read on below to learn more about the layers of the Earth's crust and what it's made up of in general.
The sediment, main layer
As its name indicates, this area It is mainly made up of large sedimentary rocks. between the continents and the continental plates. They are a fundamental part and foundations of the mountain ranges as they are known today, as well as of the aforementioned continental plates or platforms.
Internally, the granite layer appears
Being one of the most studied layers of the earth's crust, It is made up almost entirely of granite. An outstanding fact is that, at this point in the crust, lies the famous Conrad discontinuity.
Basically, it is the imaginary line that draws the borders between the granite layer and the next basalt layer at its highest end.
Finally, the powerful basalt layer
It is a continuous area, larger and more extensive compared to their namesakes already named. In addition, as its name indicates, its composition is of the basaltic type in the first instance.
The basaltic layer is in constant relationship with the Earth's mantle, but separated from it due to the Mohorovicic discontinuity. She acts as a separation between one zone and another, delimiting them correctly for future studies.
Now that you know its composition, discover how the earth's crust is divided!
It was previously mentioned that the crust of the planet Earth is practically a rare specimen, based on recent scientific discoveries. She is physiologically divided or fragmented into two crusts, one that is oceanic and the other continental.
On the one hand, the earth's crust in its oceanic part, it is less long-lived than its sister, the continental crust. Likewise, it occupies more than 50% of the earth's surface and lies about 6 miles below the seabed.
All oceanic crust is thinner or finer compared to its namesake, being made up of different elements at the same time. Scientists often coin it with the nickname "Sima", referring to the abundance of silicate and magnesium. It originates from mid-ocean ridges and ends within subduction zones.
On the reverse of the coin, the earth's crust of continental character appears, being opposed to several characteristics presented by Sima. Even this part of the crust is called Sial, by virtue of its best known elements, aluminum and silicate.
With respect to its thickness, it is thicker, boasting more than 40 miles and contrasting with the oceanic crust. In addition to this, their great longevity is based on the fact that they are practically not renewed, since they do not undergo subduction zones. Even the scientific community establishes that they are as old as the planet itself.
This is how it behaves, learn the basics about the dynamics of the earth's crust
Source: Concept
First of all, you must imagine that the elements of the earth's crust, as well as the outermost part of the mantle, are "floating" with respect to each other. All the dynamics of the earth's crust revolves around this premise, an event that generates the so-called tectonic displacement. Thanks to this behavior, the "continental drift" was given rise.
When one zone or plate moves slowly over the other, generates shock, friction and high pressures that modify the terrain. From these events, mountains or tectonic depressions are born to occupy their space in the ecosystem.
Similarly, within the dynamics of the earth's crust there is a process where the plates end up joining one under the other. This effect accumulates pressure and magma until, once the action threshold is exceeded, it releases the contained material. Sound familiar to you? Well this is how volcanoes are formed.
In relation to the same premise, as you already know, these movements are constant, even if they are not felt. Depending on its magnitude or accumulated pressure, cause so-called seismic events, including earthquakes.