Biology is divided into five kingdoms, one of them is the animal kingdom, the animal is the one that walks on Planet Earth just as humans walk and can be classified or separated by types of animals, Read on to find out more about them.

The animal kingdom
They are all those beings incapable of synthesizing their own food or of reasoning in difficult situations.
The need to search for food has made the ability to move very important for these organisms, so animals have developed a series of elements designed to facilitate mobility and strength so that their internal and external skeleton serve as a support and mechanism. for hunting and survival.
It has even made these animals evolve over the years and new systems have appeared in them, such as cognitive and sensory. In the animal kingdom it can also be seen how their reproduction in some cases occurs sexually or asexually.
The cells
Cells are the fundamental units of all living beings, as you well know, cells can be eukaryotic or prokaryotic.
The elements of the cell that establish what are the animals are:
- The nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- the plasma membrane
However, there is a very notorious cell in the animal, it is the neuron that specializes solely and exclusively in the nervous system of animals.
animal tissues
The cells to increase their effectiveness meet with each other, giving rise to the tissues, each of these performs a function, coordinated with each of the tissues that make up the animal body. These are distinguished into four types of animal tissues and four derivatives of them, depending on their morphological and physiological characteristics are:
- Nervous tissues: It is made up of cells specialized in the conduction of the nervous impulse, that is, by neurons and by neuroglia, in charge of giving support and nutrition to them, the neurons are formed by a soma, which is the area where the nucleus with dendrite branches that are the ones that carry out the link with the other neurons.
- Epithelial tissue: It is the one that covers the external surface of the body and the internal cavities of multicellular organisms, it is made up of very dense group cells, which can be classified as simple epithelial or stratified epithelial.
- Muscle tissue: It is characterized by the ability to contract, is made up of spindle cells, fibers, formed by proteins with contractile capacity, myosin and actin. These are distinguished into three types of muscle tissues are:
- Skeletal,
- Cardiac
- Smooth
- Conjunctive tissue: This tissue is seen more than anything in vertebrate animals, it is made up of a relatively small number of cells, submerged in an abundant intracellular substance, made up of microscopic cells and surrounded by a matrix.
- Adipose tissue: It is a derivative of connective tissue, made up of cells rich in fat, it is a reserve, support and filling tissue, for example, in the mammary glands.
- Cartilaginous tissue: It is formed by cells that secrete a hard matrix and collagen fibers, it does not have vessels or nerves and it is the support tissue of the embryonic phases of vertebrates.
- Woven bone: It is the main skeletal tissue of vertebrates, the cells of the bone tissue are called osteocytes, this tissue is highly vascularized by numerous blood vessels that irrigate it through some channels.
- Blood tissue: It is made up of blood and plasma, which is found in the suspension of different types of cells such as red and white blood cells, and platelets.
Animal systems and apparatus
Like humans, animals have sense organs that are taste, hearing, smell, sight and touch. The animal system is divided into three, which are formed by the organs, these systems are:
- Skeletal system: This system has been developed over the years, mainly in some species that have been evolving, this serves to provide support and fixation to body tissues.
- Muscular system: Along with the skeleton, it provides support and fixation to the body of animals.
- Nervous system: It is responsible for sending and receiving messages between the different organs of the body, so that they act in a coordinated manner and offer an immediate response to a stimulus.
When all the systems are in good working order, the animals' devices are given a place, among them are:
- Digestive system: It is responsible for breaking down food into simpler components, so that they can be assimilated and conducted to all cells, depending on the type of food, specialized structures may appear in them, for example, crop, gizzard, intestinal ceca, etc. The digestive system of animals requires the help of several organs for its operation.
- Excretory system: It is responsible for eliminating waste from metabolism.
- Respiratory system: Being different in each type of animal, it is the one that carries oxygen to the animal's body and organs, also having the function of expelling it in the form of carbon dioxide. In some animals, breathing can be through the skin, in others it is necessary that they have organs that perform this function, while in aquatic animals it is through gills.
- Circulatory system: It is responsible for distributing the products of digestion and oxygen to all cells, it is made up of veins, arteries, capillaries and the heart.
types and Animal classification
The classification of animals can vary according to their:
- spinal structure: The most used classification.
- Vertebrates
- invertebrates
- Food:
- Herbivores: They feed on plants.
- Carnivores: They eat meat.
- Omnivores: They feed on plants or meat.
- Reproduction:
- Ovoviviparous: Reproduction is through eggs that remain inside the mother's body until they are ready to hatch.
- Oviparous: They lay eggs outside and wait for the birth.
- Viviparous: Animals that are formed in the womb and are born by the mother's reproductive system.
- livelihoods:
- Land
- Aquatic
- Flying
- Natural habits.
As there is a wide variety of animal species on the planet, it is necessary to know that the Taxonomic classification of animals It is the branch of biology that is responsible for giving the name to the species. Like the rest of the organisms, animals are classified according to species and categories.
Animals can be classified according to their vertebral structure in:
- Vertebrates
- invertebrates
Vertebrates
They are the animals that have a backbone, among the kinds of animals Of this classification are the amphibians that were the first vertebrate beings that lived on Planet Earth. Currently, vertebrates only represent a low percentage of the animal kingdom as they grow, their skeleton also develops, their body has an elongated shape and they have a spinal cord and most of the time the brain is protected by the skull.
Vertebrates can be divided into fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- The skeleton of birds is very light and therefore they can fly.
- The fish are more flexible and allows them to move in the water.
- The four-legged vertebrate amphibians breathe through their lungs and through their moist skin, they depend on water at least for reproduction, whereas reptiles lay shell eggs, which allows them to live in completely dry environments.
- Thanks to their skeleton, mammals walk upright on their legs.
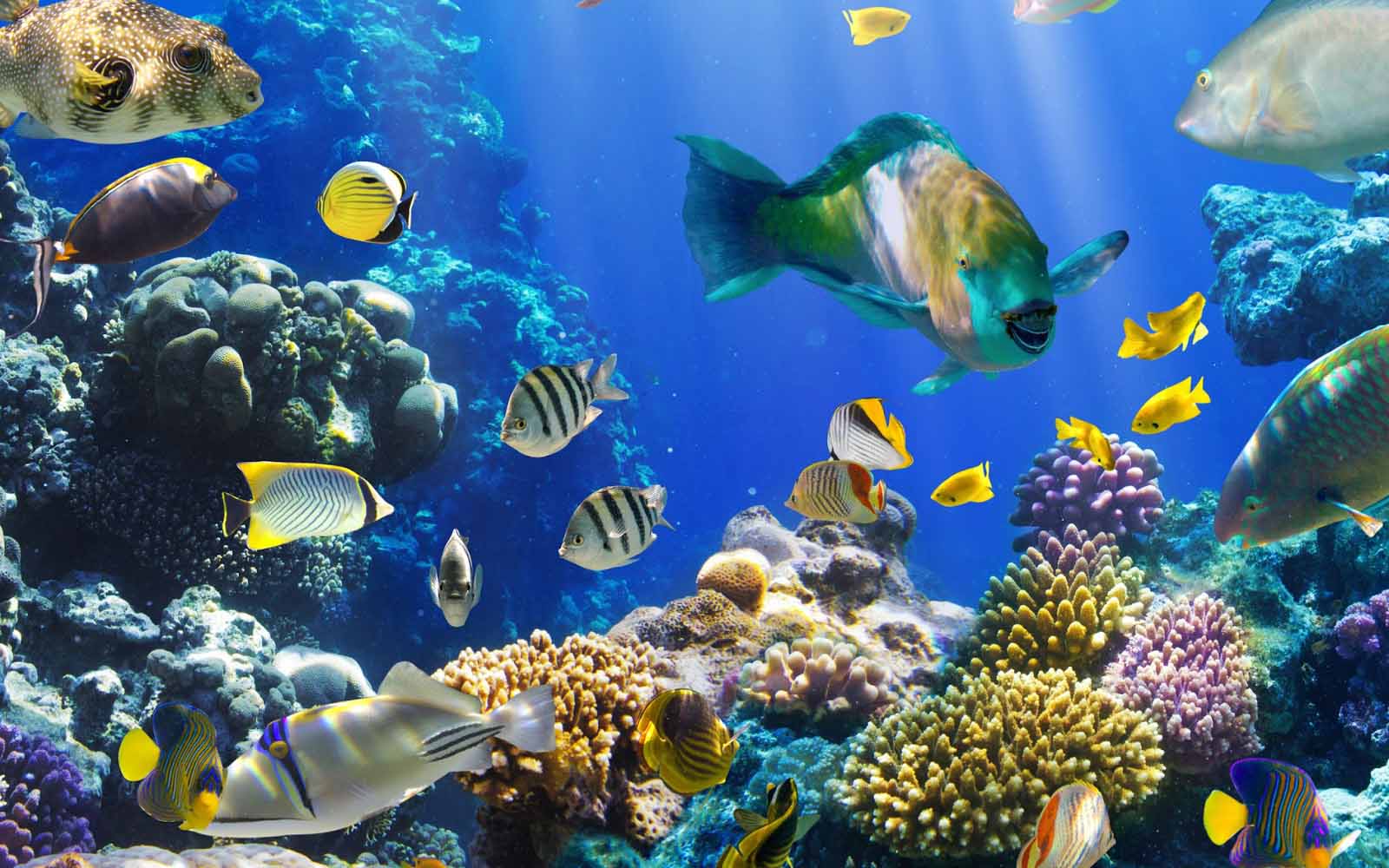
Fish
The name of fish does not refer to any taxonomic category within the animal kingdom, since fish comprise about twenty thousand species that are grouped into, without jaws and with jaws.
Their bodies are covered with scales and they breathe through gills, they have an organ that regulates water pressure and is used to float, submerge, to produce or capture sound, the lateral lines function as a sensory organ for capturing waves and they also have a system to feel, which can be said to be smell.
They move by propelling themselves through undulating movements of the body and helped by the caudal fin, which is the tail, and using the remaining fins to stabilize their swim.
Most kinds of fish are carnivorous, predatory on other fish, birds, and mammals, however, they can also feed on aquatic vegetation or plankton. There are three kinds of fish:
- The cyclostome fish, are jawless fish with a connective and cartilaginous skeleton, for example, lamprey.
- chondrichthyan fish, are fish with a cartilaginous skeleton that never ossifies, there are 600 species that are classified as elasmobranchs that include sharks and rays and chimeras that include another 25 species of fish.
- The osteichthyan fish, are fish with an ossified skeleton, their scales are fused and wrapped in a layer of mucous, they have four or five gills, a highly developed sense of smell, specialized auditory organs and lateral eyes, those that do not have scales, like eels, breathe through their skin , some have functional lungs. This class of fish are oviparous and external fertilization like turtles.
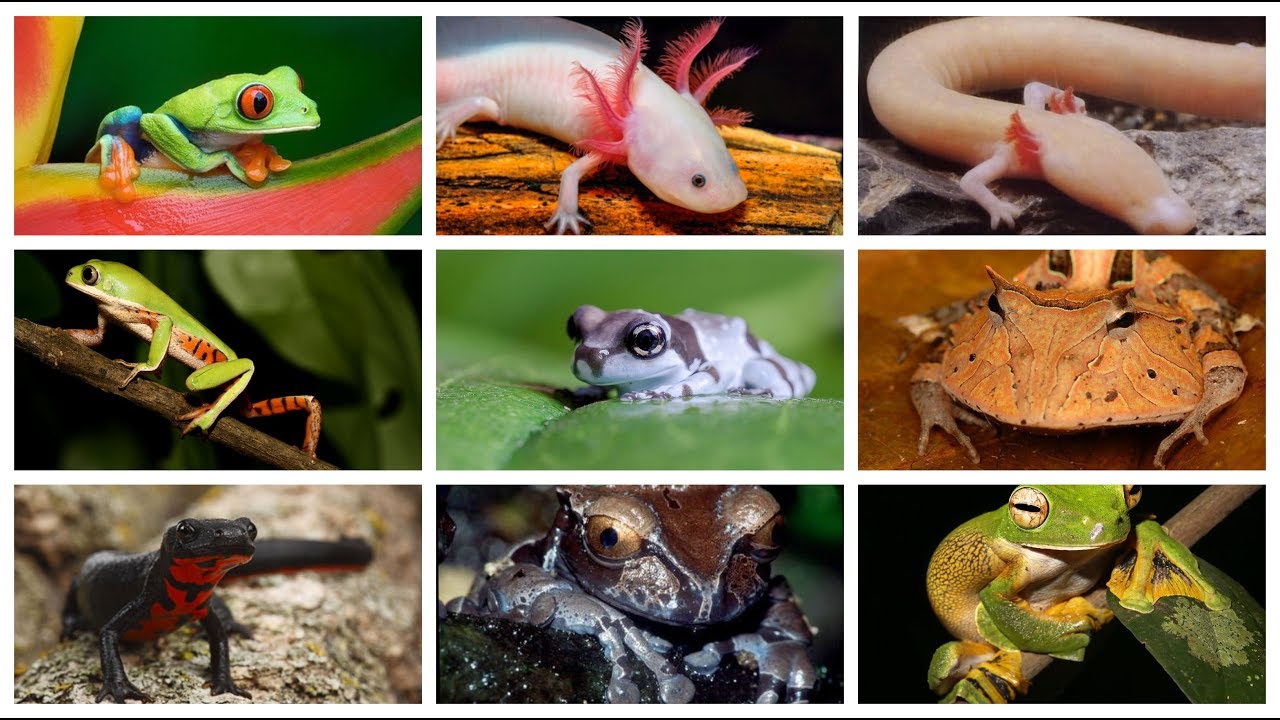
Amphibians
Amphibians ruled the earth for fifty million years, until reptiles came along and displaced them.
Amphibians have a flattened skull that joins the first vertebra of the spinal column, the jaw bones have teeth, they have bare skin without scales, always moist due to the mucous secretions of the epithelial glands, in some species they You can see poisonous glands.
The larval phase takes place in the water while the adults survive both systems, aquatic and terrestrial, this means that when they grow they form lungs or breathe through their skin, their circulatory system is more functional than that of the fish, since they have hearts with two joints and one ventricle.
Amphibians have sensory organs, they are the only animals that still have this characteristic of fish, which is developed by tadpoles, the auditory organ is formed by the inner ear and the middle ear, the eyes are capable of perceiving colors and have well-shaped eyelids developed.
The reproduction of amphibians is always sexual, some species, so that their eggs are safe, have developed special structures to transport them in the mouth, in the belly or in some folds of the skin.
Amphibians are the only animal that so far continues to go through a process of metamorphosis, to become adults, most of these animals are oviparous, they have a defense mechanism depending on the type of species, as well as some have poison, others can change colored, others can shed a part of their body to protect themselves.
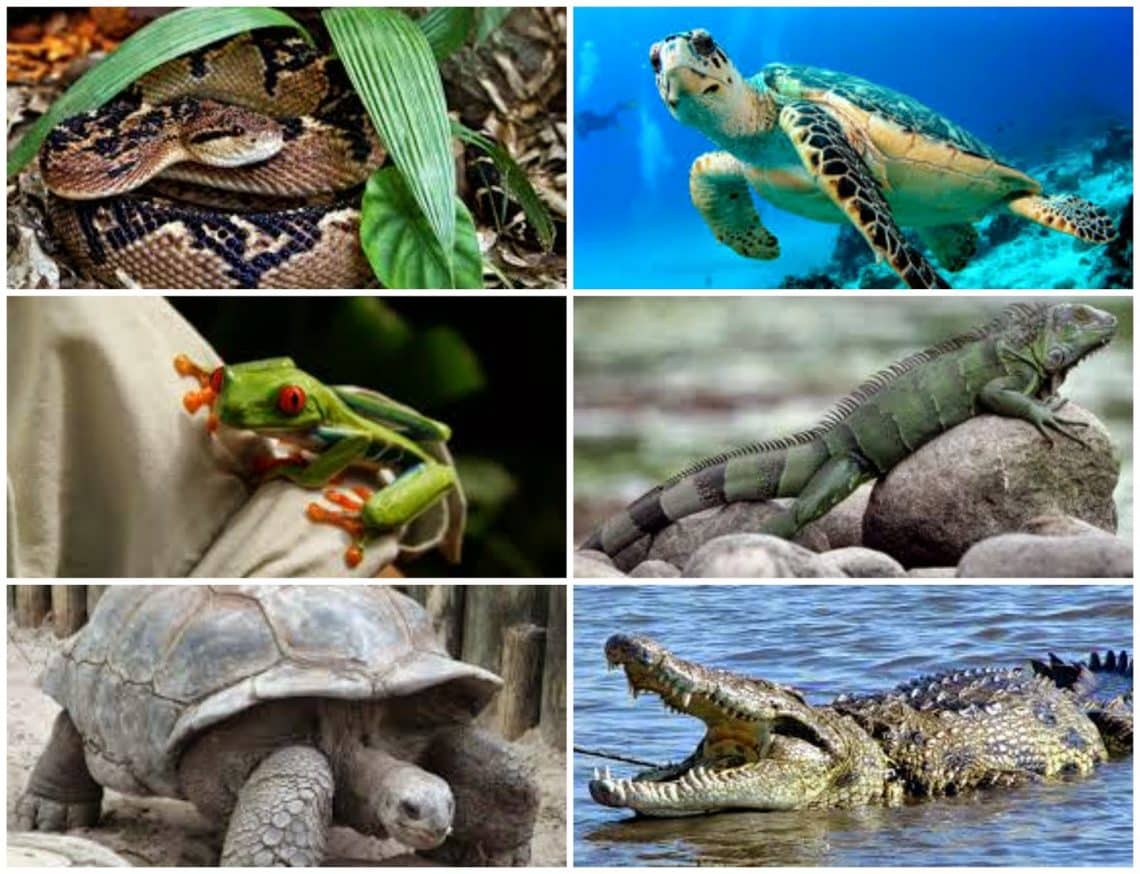
reptiles
They are the first vertebrates completely adapted to terrestrial life, they comprise approximately six thousand species with a fairly wide geographical distribution throughout the planet.
Although the highest concentration is found in the tropics and in cold areas they are scarce, they are divided into three classes:
- The turtles: They are characterized by the shell or shell structure that covers most of their body and protects them.
- The snakes: They are in the scaly group like lizards.
- Crocodiles: Along with the caiman are the group of crocodiles.
The skin of reptiles is dry, it is characterized by the development of horny scales, which are usually very large and marked, as well as the belly of snakes, they constantly change their skin. The mouth is large and the jaws have the same teeth, except in turtles that lack them, their tongue can be agile and forked, almost immobile or long and sticky.
The stomach, the excretory system and the genitals lead to the outside through a common duct, called the cloaca, the heart has two joints and a ventricle, almost separated in two by an incomplete septum. The fertilization of reptiles is internal, these species are oviparous, they lay eggs on the ground and can vary between 6 and 200 eggs per reproductive period.
These animals are known as cold-blooded animals, this is because they do not regulate body temperature through their metabolism, but must always resort to external heat sources, for this reason they also need to live in warm places, where they can regulate your temperature easily. It is common to see them lying down in the sun in order to reserve the energy they use to hunt and digest their prey.
Unlike other reptiles, the snake is the only one that does not have legs and slides along the ground, its movement is undulating when its body is not very heavy. When their body is heavy, they move with an accordion-shaped movement, the snake's speed of movement is thirteen kilometers per hour, it has no ears or eyelids, its body is long and thin, made up of between one hundred and three hundred vertebrae.
It is considered a dangerous species, since one in three species of snake is poisonous and the only way to affect other animals or even man is to bite to inject the venom that has different characteristics depending on the type of snake.
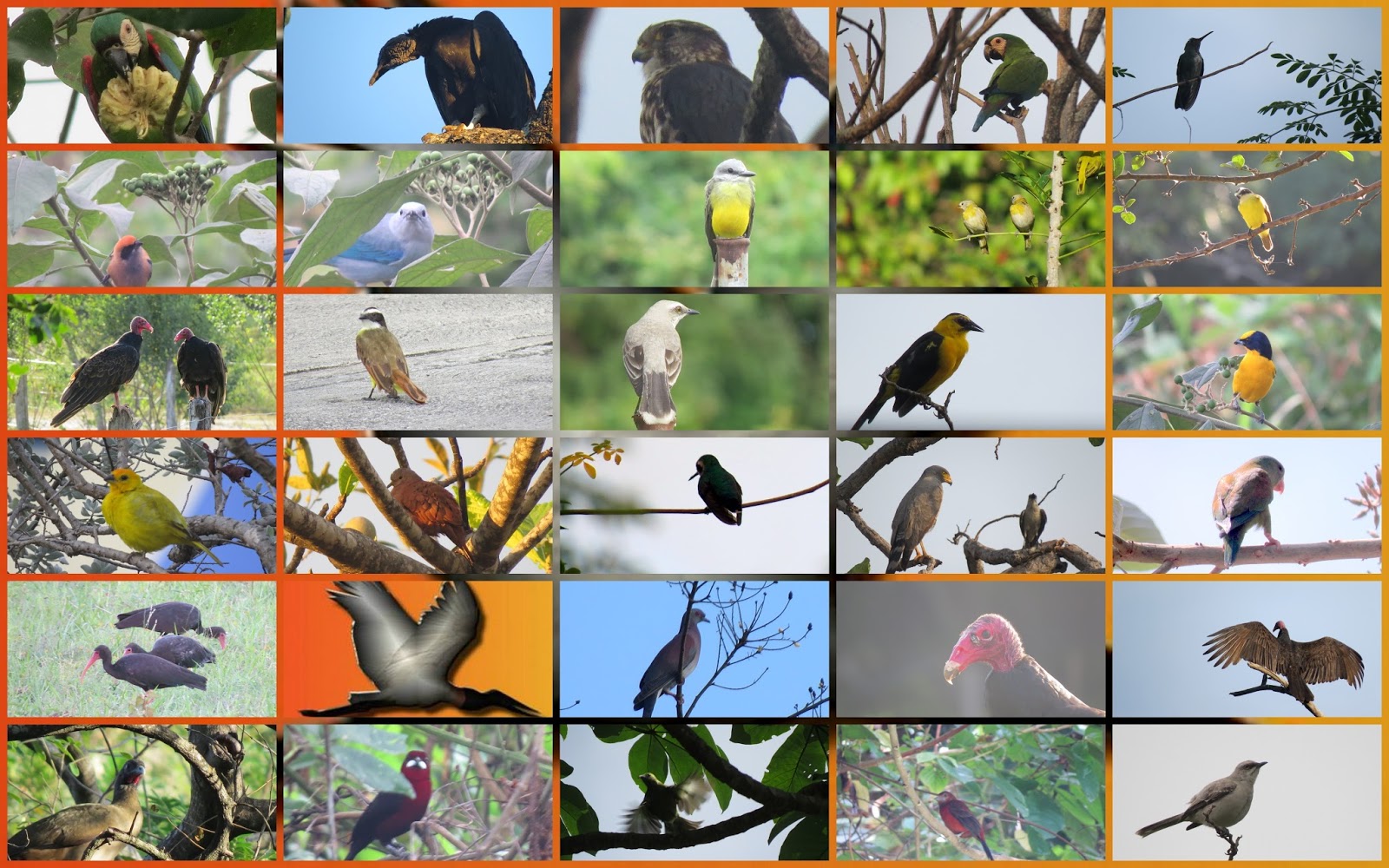
Birds
They are oviparous vertebrates, they are characterized by having the body adapted to flight, to carry out this action their forelimbs have been transformed into wings and the body is covered with feathers.
They maintain a body temperature between forty-one and forty-two centigrade, thanks to their circulatory and respiratory systems they have developed a central nervous system. The feathers and horny beak are its most outstanding features.
The feathers are epidermal formations that consist of a rigid central axis and a standard one, the plumage constantly changes and in the same species can be of a different color, depending on the time of year or the period of reproduction. The beak is made up of two corneas and varies according to the way the bird feeds.
The skeleton of birds is light, compact and rigid, the bones are characterized by not having bone marrow and the spaces where it is found, it is full of air, the sternum is highly developed and forms the front part of the keel, the welded clavicles form the typical V-bone of birds.
The legs are modified for flight since they serve to walk and as landing gear, the musculature of birds is very powerful and tend to concentrate in the center of the body. All birds have a tongue, the esophagus is usually larger and is called a crop to store food.
The stomach consists of a glandular part that digests food and a muscular part that grinds it. The lungs have been reduced while the bronchial network has given rise to air sacs that accumulate air inside when they are flying. The circulatory system consists of a heart with two joints and two ventricles.
The excretory system is made up of kidneys, the brain is larger than that of reptiles, and the centers of vision are larger and more sophisticated. All birds are oviparous and the reproductive apparatus of the males consists of two testicles and the female of two ovaries, fertilization is internal.
There are aquatic birds that spend a good part of their lives in the sea and for this reason their feet are webbed, however, there are birds that cannot fly, such as penguins, which generally live in colonies to protect themselves from predators and any other danger. Said to be seabirds, as they swoop down from great heights and dive to catch food, penguins can dive and dive deep to catch fish they find while underwater.
Mammals
Mammals are a group of vertebrates that have currently achieved greater diversity in forms, this has allowed them to inhabit multiple environments with very different characteristics.
Mammals are classified into two groups, prototheria and theria. animal characteristics Mammals can vary according to the types of animals, the skin is made up of the epidermis which is covered with hair and the dermis.
Another of the formations that mammalian animals have are the cushions of the fingers, the claws, the nails, the hooves and the horns. Its body is divided into three regions: head, trunk and tail, the neck is highly developed except for some animals, four limbs are born from the trunk, generally ending in legs with five fingers.
Although this scheme may vary depending on the movement required by the animal, the common features of mammalian animals is the jaw, which is made up of a single bone. Your hearing apparatus is made up of three cartilages that are responsible for transmitting sounds to the inner ear. The care and feeding of the young through milk produced by mammary glands.
The ability to maintain its body temperature is due to the fact that its body is covered with hair, its reproduction is viviparous, that is, its offspring is born fully formed, through its reproductive system. Mammals have brains.
Its teeth are made up of teeth of various sizes and shapes, the tongue has a very complex musculature that gives it great mobility, the stomach presents in most of them a single cavity, the intestine varies in length, depending on the type of food, the respiratory system consists of several systems that reach the lungs where they branch into bronchioles.
They have two circuits of blood circulation and the heart is shared in two joints and two ventricles, they have two kidneys that through them pass urine to the bladder and out through the urethra. It has a highly developed and highly complex brain that continues in the spinal cord.
They have cerebral cortex which is in charge of sensory and motor functions, in which the highest mental faculties of mammals are located. The reproductive system of males is made up of two testicles, females have two ovaries, which discharge the ovules through ducts, fertilization is always internal and sexual intercourse takes place, the female is only sexually receptive during the period of heat that she produces. ovulation.
examples of vertebrate animals
- FishPairing: Seahorse, anchovies, eel, catfish, herring, others.
- Birds: Ostrich, rhea, partridges, penguins, pelicans, gannets, other ducks
- reptiles: Lizards, iguanas, chameleons, snakes, lizards, crocodiles, alligators, others.
- Mammals: Platypuses, marsupials, anteaters, horses, mice, Rabbit, lemur, others.
- Amphibians: Frogs, salamander, toads, midwife toad, others.
invertebrates
They are all animals that do not have a backbone, they are classified into:
- Arthropods
- non arthropods
Although many are microscopic, some can reach a large size, as is the case of the giant squid, which can reach almost twenty meters in length, although it may not seem so at first glance.
Invertebrates also have eyes, heads, legs and tails, they are advanced invertebrates, however simple invertebrates such as sponges do not comply with this rule, they have a simple body both externally and internally.
Types of non-arthropod animals
They are called non-arthropod invertebrates, about six types whose main common characteristic is to differentiate from arthropods, these animals are:
- Sponges
- Cnidarians
- Platelmintos
- Molluscs
- annelids
- Echinoderms
Sponges
They are marine invertebrates considered to have the simplest organization, despite being true multicellular organisms, they do not have differentiated and specialized organs. The body of the sponges is organized in a system of channels and internal chambers, they feed by filtering the food particles that the water transports.
The choanocytes are flagellated cells inside the sponge that create and maintain a constant flow of water through the body, thanks to the movement developed by their flagella, the water enters through the multiple pores and circulates through the system of channels and chambers, until reach the central cavity and finally exit through the osculum.
They are also responsible for incorporating the particles found in the water, we can say that these particles are bacteria, algae and some organic waste, which pass into a specialized cell where they are digested and then the digestion products are released into the Exterior.
Sponges can reproduce asexually by budding and sexually by eggs, they are classified into three groups:
- calcareous
- hexactinellides
- demosponges
They generally live in coastal and benthic areas, some can be found at great depths, the existence of sponges has been unknown since ancient times, Aristotle speaks of sponges around the year 350 BC, defining them as marine animals endowed with a great capacity for regeneration .
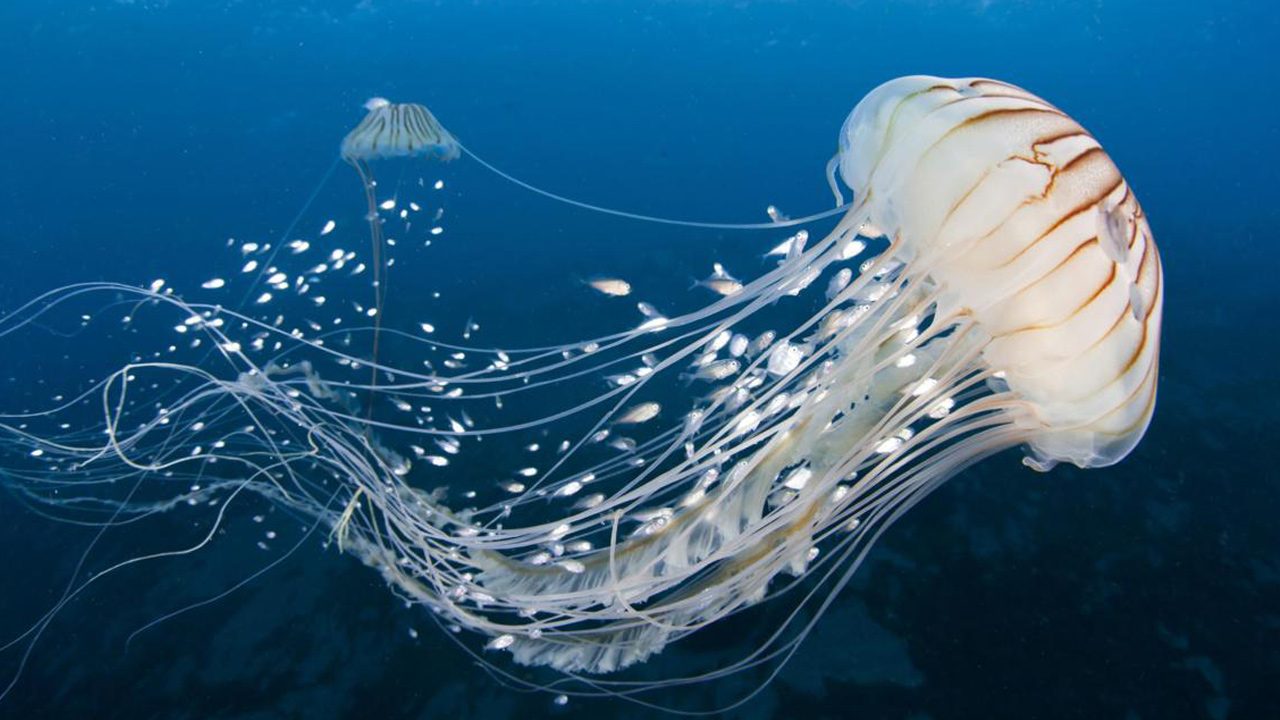
Cnidarians
They are aquatic organisms that have several equal planes of symmetry, have organs that are assembled into systems, and come in two forms: polyps and jellyfish.
A typical polyp is fixed to the substrate by a base or foot, in the back center of the crown is the mouth, surrounded by numerous tentacles, which in turn are covered with stinging cells. Polyps normally form colonies by a type of asexual reproduction called budding.
Jellyfish are free forms, swimmers, mobile and solitary individuals, inhabitants of water masses, they are bell-shaped and have the same elements as polyps but placed upside down, the external surface is called an umbrella.
Both the body of polyps and jellyfish have a central cavity called the gastrovascular cavity, connected to the outside by a single opening, which serves as both mouth and anus.
The body wall that limits this central cavity is made up of three layers, the epidermis, below it a layer of connective tissue and the mesoglea lining the gastrovascular cavity, there is an epithelial tissue called the gastrodermis below the epidermis. These animals have nerve and muscle cells that allow contractions and movement.
They can be classified into three groups:
- Hydrozoa
- scyphozoa
- Anthozoans
They can also be seen in fresh water, such as the hydra, which has the ability to secrete from the cells of the epidermis, a membrane called perisarch which acts extraskeletally.
Jellyfish can occur under two degrees of complexity, the simplest are the hydromedusae, which are usually small in size and have a non-accepted gastrovascular cavity, whereas the scyphomedusae medusa have a septate cavity.
Molluscs
The body of molluscs is covered by a special layer called the mantle, which forms two lateral folds that surround and enclose the body in the parallel cavity. Most molluscs breathe through gills, but some, like land snails, have lungs. The pharynx has a scraping organ called the radula.
The nervous system is highly developed and reaches the greatest complexity of all invertebrates in cephalopods, the circulatory system is open and its blood contains hemocyanin that can be defined as a respiratory pigment.
Molluscs are classified into seven groups according to the characteristics of the foot and the shell and according to the development of the nervous system, the most important are:
- Gastropods with highly developed heads and feet and a spiral-shaped visceral mass are terrestrial and aquatic.
- Bivalves with a shell formed by two articulated valves and an atrophied head, these are aquatic.
Cephalopods with the foot transformed into several arms that surround the head, the shell may be atrophied, they are aquatic.
Molluscs have a soft, non-segmented body in which three parts can be distinguished, the more or less differentiated head, a visceral mass in which most of the organs are found, and a muscular foot.
They have adapted to almost all living conditions, they live in land areas, in fresh waters and in marine waters, their size varies from a few millimeters to several meters, most of them have their bodies protected by a shell, although sometimes this can be internal, there are two types of molluscs:
- The monoplacóforos are the most primitive molluscs and have the shell formed by a single piece.
- Polyplacophores have a shell made up of eight articulated plates, which covers the entire body.
The snails have a soft body and in the face of any threat they retract inside their shell, where they are safe, the shell of the snail is a calcareous exoskeleton that in addition to serving as protection also serves as a support, as the snail grows its shell grows with it.
In octopuses, the arms are full of suckers, which they use mainly to capture their prey, they also find it very useful to adhere to rocks and move along the seabed. To attract the attention of females, males of some species position themselves in such a way that the larger suckers at the base of the tentacles are exposed.
Types of arthropod animals
Arthropods are the most abundant type of organisms in the animal kingdom, with more than 80% of all known species, current arthropods are divided into three types, all of them have a union in each part of their body, thanks to which they are Easily identifiable, together with the annelids they are the only animals that have a segmented body and articulated appendages.
Their great capacity to adapt to the environment has allowed them to occupy all the habitats on the planet. The types of arthropods are:
- The insects
- crustaceans
- the arachnids
The body of arthropods is made up of interconnected segments and are grouped into three regions or parts:
- Head
- Chest
- Abdomen
In each segment there is a pair of appendages, in addition to a pair of ganglia of the nervous system, arthropods have well-developed organic systems, the digestive system is complex and three zones can be distinguished in it:
- Previous
- Intermedia
- Posterior
The blood system is open, that is, blood and plasma fluids mix and give rise to hemolymph, respiration can be cutaneous, branchial or tracheal, the nervous system is hyponeuric, that is, it is located ventral to the digestive tract , is made up of as many pairs of ganglia as there are segments.
Arthropods have receptive, tactile, visual, chemical and acoustic organisms. As for their reproduction, they are unisexual, sometimes the difference between the male and the female are very noticeable, fertilization is usually internal and to achieve this they are provided with different types of appendages related to copulation.
Embryonic development is complex, the individual just hatched from the egg has to go through several phases before acquiring the appearance of the adult, in some cases the changes are continuous, in others they are sudden and profound, this can be called metamorphosis .
Insects
The classes of insects constitute the largest and most varied group of the animal kingdom and include the only invertebrates capable of flight, more than a million species of insects are known and there are still many to be discovered.
They have adapted to all terrestrial and freshwater environments, they can live under extreme conditions, which other types of animals would not tolerate, they are absent in the marine ecosystem, the great diversity of insects is due to their great adaptability and the conquest of the aerial medium, thanks to the wings that allow it to fly.
In the body of insects three parts are differentiated:
- The cabeza
- The thorax
- The abdomen
As for reproduction, they have sex separately and sexual dimorphism between males and females is frequent, fertilization is internal through a dome. These types of animals have characteristics such as:
- On the head it has a pair of antennae, a mouth and a chewing apparatus, as visual organs they usually have three ocelli or two compound eyes.
- The thorax is made up of three segments and they have three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings on the sides.
- The abdomen is divided into eleven segments and a final segment called the telsón, breathes through tracheae and excretes through the digestive tubes.
Reproduction is sexual and in some cases asexual, the types of development from the egg to the adult are:
- ametabolusmetamorphosis does not occur.
- heterometabolus, is when there is an intermediate phase between the egg, the adult and the oil.
- MetabolusThis is when metamorphosis occurs.
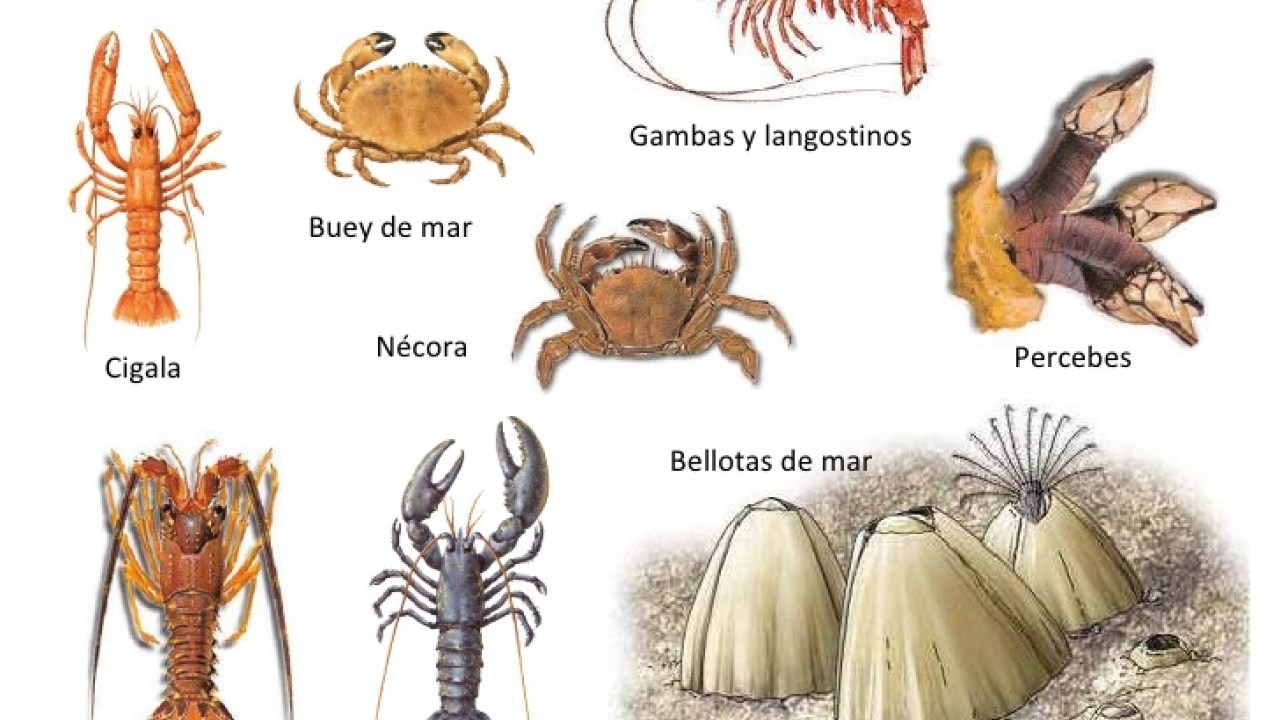
Seafood
Crustaceans are characterized by having two pairs of antennae, there are about thirty thousand species, most of them aquatic, although some have adapted to life on land, three different regions can be seen in their body:
- cephalic
- Thoracic
- Abdominal
The first two are often united and form a cephalothorax, covered by a shell, they have specialized appendages: chewing, respiratory, reproductive, among others.
The class of crustaceans is divided into four main groups:
- copepods: They are small crustaceans that are very important in the marine world, there are also many species that are parasitic on fish.
- barnacles: They live attached to rocks, wood or other surfaces.
- amphipods: They measure a few millimeters and abound among the algae and the soft depths of the ocean.
- decapods: They are the most evolved crustaceans and the most numerous, they have five pairs of walking legs, the group includes prawns, crayfish, lobster and crabs.
Arachnids
Its main characteristic is the presence of pincer-shaped appendages or hooks located in the mouth, called chelicerae, the body is divided into two parts, cephalothorax and abdomen, in some cases a third segment can be seen, which would be the tail, this only in the case of scorpions.
The arachnids have a total of six pairs of appendages, of which four are locomotors, one pair are chelicerae and one pair have tactile functions, almost all of them are predators capable of capturing and immobilizing their prey, which they crush and absorb their liquids . They breathe through gills or lungs, others through a trachea similar to that of insects.
The excretion is carried out through the digestion tubes, they present sexual dimorphism and most are oviparous, scorpions constitute the most archaic arachnid order, the body is covered by a shell, the pedipalps are highly developed and have pincers at the end. The tail is thin and narrow and at the end of it is a poisonous stinger, which they use to hunt.
Pseudo-scorpions look like miniature scorpions, no larger than a centimeter, although they lack a tail and a stinger. Solífugos or spiders of the sun have a body covered with hair, they have eight legs and pincers that come out of their face.
The araneids comprise the spiders, they usually have between six and eight eyes, formed by two pieces and with the capacity to inoculate poison, the abdomen has silk-producing glands, the mites, finally, are small and with an unsegmented body, some are living libre and many others are parasites like ticks. They are terrestrial animals and their body is covered by an exoskeleton, they are generally carnivorous.
The arachnids originated more than 500 million years ago and were aquatic, they stood out for their large size among the fossil species, there are specimens of more than three meters in length, without a doubt the largest arthropods that have ever existed.
examples of invertebrate animals
- Sponges: Calciesponges, vitreous, bath, coralline.
- Cnidarians: Lion's Mane Jellyfish, corals, box jellyfish, gorgonians.
- Platelmintos: I had it
- MolluscsPairing: Snails, clams, oysters, squid, octopus.
- annelids: Marine worms, earthworm, leech.
- EchinodermsPairing: starfish, sea cucumbers, sea urchins.