Throughout history, different diseases have been studied that have their origin in different birds and, being domestic, can have repercussions on human beings. This extensive list of diseases or infections can be bacterial, viral, fungal, among other forms, which can infect humans. If you want to learn more about Bird Diseases and the dangers that humans run with domestic birds, do not hesitate to continue reading this article.

Bird Diseases
Specifically in the United States, one of the most popular pets are birds, they are in fourth place, after of course dogs, cats and third, fish. This same great popularity means that a very large population of people are exposed to a constant danger of contracting any of these diseases, which, as we mentioned before, can be fungal, viral, bacterial, protozoan, and even parasitic zoonoses.
This entire article focuses exclusively on diseases or infections that are closely related to domestic birds and that can have a detrimental impact on their owners or on humans in general. And these same diseases are not systematically contagious in humans.
It is not necessary to give up birds as pets
Despite the long list of diseases that we humans can contract from these beautiful birds, we should not be discouraged and let this be an impediment to acquiring a bird as a pet. The ability of the microorganisms of these diseases to cause a human being to become infected varies greatly depending on the specific degree of virulence that is being discussed, it also depends on the amount of exposure that this person has and the route by which it has been infected.
Specifically for the owner of the bird, the main preventive measure will always be the most complete hygiene possible, washing hands, sanitation and constant visits to the veterinarian. A large part of these infections or diseases are transmitted by ingesting food or drinks that contain microscopic particles of biological waste from these birds, or by breathing contaminated dust.
For all these reasons, you must follow different steps or precautions to reduce as much as possible the amount of exposure that, as an owner, you have to these harmful diseases. Many biologists and veterinarians strongly advise the use of a mask when cleaning the cage. You should bear in mind that it will always be much better to adopt your bird in a specialized center or hatchery, since in these places the risks of infection are greatly reduced.
All these measures or tips are extremely useful and almost mandatory for all those people who are more prone to contracting these diseases, such as the elderly, children, people with chronic diseases or who have problems with their immune system.
Diseases associated with birds
In the case of human beings, the vast majority of diseases that originate in birds are usually asymptomatic or self-limited, but it should also be taken into account if the owner is presenting some constant symptoms, or unusual symptoms that indicate that they may have an infection; in turn, it should be considered if the bird has died or has become ill in the last days or weeks. In the entire long list of diseases related to domestic birds we can find:
Psittacosis
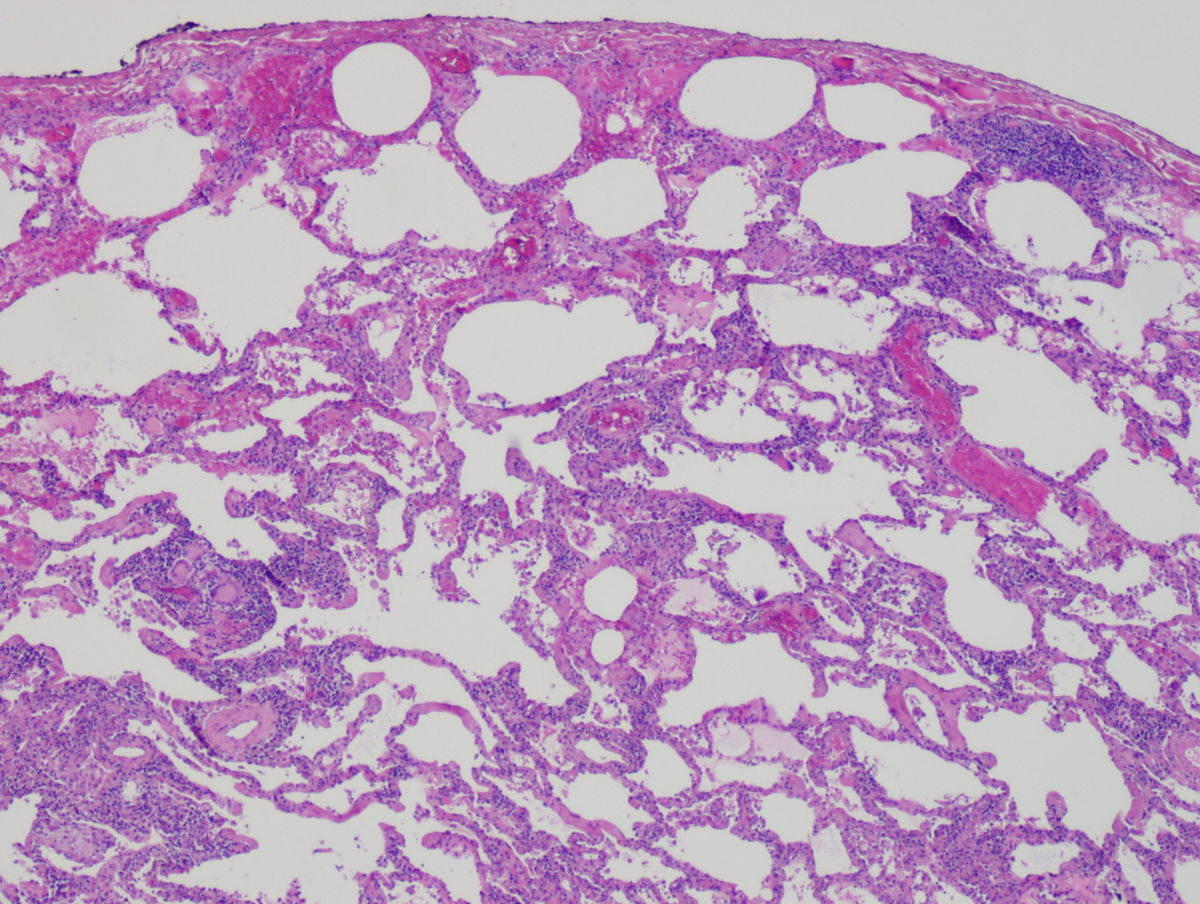
The transmission of this infection called C. psittaci or Psittacosis, is due exclusively to the breathing of different aerosolized particles of excrement, feathers, nasal secretions, or even tissues. Unfortunately it can also be spread between human beings; atypical pneumonia is the most common manifestation of psittacosis in people.
We can find that the symptoms begin to appear between the first seven or fourteen days after exposure to the bacteria, the person in question will begin to suffer from fever, chills, will be bothered by light, very intense headaches, and also a constant and annoying cough. It is well known that between 10 and 70% of those affected by this disease present hepatosplenomegaly, which is a condition where there is a regrowth of the spleen and liver, this is because the liver cannot process the correct form of glucocerebroside.
Other manifestations of psittacosis but very rare are: Myocarditis, endocarditis with a negative bacterial culture, pericarditis, thrombophlebitis, and even different mental disorders. At the time when pneumonitis is combined and this hepatosplenomegaly is suspected, and any disease other than Psittacosis is almost ruled out.
Influenza
Any of the subtypes of influenza A viruses can spread in birds, unlike influenza type B. Despite this, there are many important genetic differences in all subtypes of influenza type A that usually affect humans and birds alike. The bird flu virus such as H5N1, H9N2, H7N7, among others, is a zoonosis, which clearly indicates that it affects humans and birds.
Although these are its official names, it is colloquially called bird flu or avian influenza; this disease and its variations emerged in approximately 1997 and was extremely associated with poultry. In the case of H5N1, which is highly virulent, has killed millions and millions of birds around the world, and in turn has infected several hundred people regardless of the region of the world, it should be noted that half of the infected humans have unfortunately died.
Various variations of this bird flu that can seriously affect humans have been totally isolated from different species of birds that are usually only seen in captivity, among these we can find the canary, poultry, parrots, and also different birds. aquatic and migratory. According to many studies and different scientists, it is well known that domestic birds have not been completely implicated in the transmission of this flu, but, nevertheless, they are potential threats if they have had any type of contact with other birds that may be infected. .
The form of contagion between birds and humans is usually by breathing droplets or any type of fluid from an infected bird; also, less frequently, transmission can originate from contaminated environmental sources. According to different Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or CDC, around the United States, the presence of H5N1 has been evidenced in various family groups, however, human-to-human transmission is very rare, very limited and also fickle.
The symptoms of this dangerous avian flu may become completely absent, or they may respond to an infection in the entire respiratory system, the number of eggs laid begins to decrease markedly, constant illness, and finally death. For humans, you should suspect avian flu in anyone with flu symptoms who has also recently been in contact with birds, specifically poultry or any infected wild birds; also if you have gone to endemic regions or had some kind of contact with people infected or suspected of having contracted avian flu.
The WHO, or World Health Organization, using its Epidemic and Pandemic Alert Office, has information about the different regions of the world where avian influenza is endemic, or in any case that may appear due to outbreaks.
All the symptoms or signs of avian influenza in humans are: infection of the entire upper respiratory tract, very high fever, constant cough, and gastrointestinal problems. Highly virulent subtypes such as H5N1 can cause a disease that progresses by leaps and bounds until finally reaching death. On the other hand, we can highlight other less virulent subtypes such as H9N2, which causes much milder symptoms compared to the aforementioned.
histoplasmosis
This fungus called Histoplasma capsulatum, causes a disease which is based on colonizing the entire gastrointestinal tract of birds, and in turn, also contaminates the soil through the droppings of birds, and also bats. Among the most endemic areas in the world we can highlight all the valleys of Ohio and the surroundings of the Mississippi River. It is worth mentioning that parrots and canaries are not at all susceptible to symptomatically suffering from this fungus, unlike pigeons, which are often treated as pets for those who love birds, which can become infected if they come into contact with the mushroom.
In the case of human beings, the most regular is contagion by breathing toxins from the soil that is completely contaminated by this fungus. To this day, no case of human-to-human transmission has ever been seen. In humans, the severity of this disease depends entirely on the size of the inoculum, and in turn, on the immunity of the infected person. According to many studies, in more than 90% of all human cases, the primary infection has extremely mild symptoms and tends to go completely unnoticed
Incubation of this infection usually takes approximately 7 to 21 days; once it appears, the symptoms can be: chills, very dry cough, headaches, high fever, and even adenopathy with pain in the chest area. In the case of disseminated disease, it is much more common in people who have chronic diseases or with difficulties in the immune system, the symptoms are usually weight loss, fever, pancytopenia, and even hepatosplenomegaly, as in the case of avian influenza.
Newcastle disease
Newcastle disease, or avian pneumoencephalitis, is a virus which is called paramyxovirus 1, it can infect different animals such as birds and reptiles, but unfortunately it can also seriously infect humans. This disease tends to be much more common in wild birds, however, parrots specifically are extremely susceptible to this virus, in addition to this, parrots are often natural reservoirs that can continue to harbor and spread the virus for up to 12 months after they are infected. symptoms are gone.
Parrots brought to the United States illegally from the Amazon are the largest single source of infection for all citizens of this country. This virus is transmitted through the feces of any bird that is infected, and also any type of fluid or secretion of oral, ocular or nasal origin, these same secretions can be on clothing, footwear or belongings.
Many of the birds that are infected do not present any type of symptom; however, many others tend to have green diarrhea, respiratory abnormalities, muscle tremor, circling, paralysis, or periorbital and neck edema. Unfortunately the mortality rate in the case of birds is 100%. In the case of humans, the infection initially manifests itself with conjunctivitis, on this occasion chills, lethargy and fever are extremely rare.
This is due to the fact that it is in poultry where this virus prevails, and the keepers of these are the most exposed to contagion. However, recovery in humans tends to be extremely rapid. It must be taken into account that anyone who is infected with Newcastle disease or avian pneumoencephalitis must avoid any type of contact with any bird at all costs.
Q fever
This serious disease is caused by a bacterium called Coxiella burneii, which is a gram-negative pleomorphic rod. All ticks and various vertebrates such as sheep, goats and, less frequently, birds; are natural reservoirs of this bacterium. In the specific case of human beings, contagion originates through direct contact with infected animals, or when breathing dust contaminated with placental tissue or infected feces. While birds can get this infection through experimental or natural means.
In humans the symptoms are: very intense headaches, pneumonia, photophobia and high fever. In the most serious cases, meningitis, thrombosis, and even hepatitis can manifest. It is important to note that if the infection is acquired during pregnancy, it can cause serious consequences such as prematurity, stillbirth, and abortion.
West Nile Fever
Where this virus is most abundant is usually in different wild birds, such as crows or birds of prey, however, it can also be present in pet birds. The main route of contagion of this disease from birds to humans is the bite of a mosquito to an infected bird and then to a human being. It is important to note that direct contagion from the bird to the human being has not been discovered, nor vice versa. Birds that are infected can be completely asymptomatic, sick, or reluctant to fly, in turn they die from disseminated infection.
In the case of human beings, the incubation stage of this disease is approximately 3 to 14 days, after this incubation a sudden and intense fever begins, nausea, vomiting, malaise, lymphadenopathy, retroorbital pain, and also rash. The neurological manifestation is presented by ataxia, extrapyramidalism, myelitis, alteration in the nerves found in the skull, optic neuritis, and even seizures; however, all of this is quite unusual and is more common in the elderly, or patients with immune system problems.
In less than 1% of all those infected, the disease is much more serious, bringing with it symptoms such as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis, Guillain-Barre syndrome.
allergic alveolitis
Allergic alveolitis has a wide variety of names, among which we can find hypersensitivity pneumonitis, pneumoconiosis caused by dandruff from Australian parrots, ornithologists' disease, pigeon breeder's lung, or also, pigeon lung disease; It is not a simple zoonosis, the term illustrates the disease or diffuse infection of the parenchyma, which is caused by constant exposure to inhaled allergen. Despite this, you should be suspicious in any patient who has any type of pulmonary symptom and who has also had recent exposure to birds.
Avian proteins are a well-known great trigger. This acute allergic alveolitis is medically indistinguishable from a simple respiratory infection. This is mainly characterized by the appearance of a very intense cough, feeling of chest pressure, fever, chills, dyspnea, malaise, and finally myalgia. All these symptoms tend to improve enormously after 24 or 48 hours if there is no type of exposure to the antigen, however, they are repeated when there is constant exposure.
In the case of this subacute disease, it manifests quite similar symptoms, symptoms which gradually worsen over months or weeks, and in turn can become indiscernible from the signs of some interstitial lung disease. In the majority of patients with this chronic alveolitis, tuberculous or fungal pneumonia is diagnosed or initially suspected, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is also regularly diagnosed.
As long as those affected do not have any type of contact with this allergen, they will have an extremely favorable evolution, otherwise, if this exposure is constant, the patient could develop pulmonary fibrosis that will be irreversible.
Diseases with gastrointestinal symptoms
In this extensive list of diseases, which are associated with all types of domestic birds, we can find serious diseases that are primarily characterized by manifesting themselves with different gastrointestinal problems, among all of these we can find the following:
Salmonellosis
Salmonella species that are not typhoid take over the entire gastrointestinal tract of a wide variety of animals, including birds. It is well known that approximately 80% of chicken eggs are contaminated by these gram negative bacteria.
The spread of this disease, non-typhoid Salmonella, to humans is much more common from all poultry, farm products, pet birds and reptiles, and even chickens and ducks have become spread this horrible infection to humans. Birds that are infected can become asymptomatic and transmit this infection while they are completely healthy; On the other hand, in birds, the infection can also grow and become enteritis, or a hemorrhagic hepatosplenic disease and lead to painful death.
In humans, gastroenteritis caused by non-typhoidal salmonella begins approximately 18 hours after digestion; This manifests itself by causing fevers, vomiting, intense nausea, and even severe non-bloody diarrhea in the patient. It should be noted that most gastroenteric infections are self-limited, that is, they tend to end in approximately four or ten days.
In the case of the most serious infection, or that progresses systemically, which requires treatment, it is much more common in patients who present some type of complication or weakness in their immune system, in patients who previously present gastric hypoacidity, or that the moment arrives where all the integrity of the gastrointestinal mucous membranes has been lost, in turn also occurs in children under three months, and in patients with chronic gastrointestinal diseases, or even an HIV infection.
Despite all this, the infection caused by non-typhoidal salmonella can be resolved without too many complications. This can also infect structurally abnormal places such as previous fractures, abnormal lung tissues, very serious degenerative arthropathy or also lithiasis. In humans at increased risk, such as the elderly, with chest, abdominal or back pain, with previous gastroenteritis, arteritis of the large vessels due to non-typhoidal salmonella should be suspected.
Campylobacteriosis
Campylobacteriosis is based on a disease that is caused by a bacterium called Campylobacter jejuni, the largest reservoirs of this bacterium tend to be wild birds and also poultry, however, this bacterium can be found in other types of animals and also many other pets. The most exposed and affected by this disease are the parrots, or psittaciforms, and also the sparrows and canaries that are passerines.
This microorganism takes over the entire small intestine and colon of birds, and unfortunately it can infect humans when they have any with the feces or skeletons of these infected birds. Birds that present campylobacteriosis can present different symptoms among which we can find loss of appetite, lethargy, along with this loss of appetite also comes weight loss, yellow diarrhea, and even hepatitis; the vast majority of all infected birds tend to die from all of this.
In the case of human beings, the most common form of infection of all is through the consumption or handling of infected chickens; In turn, it can also be due to the consumption of milk, or other different products that are contaminated with the feces of carrier animals. Despite this, according to different studies, 24% of cases occur from totally unknown sources.
In a vulgar way, the disease that occurs due to Campylobacter jejuni causes an acute gastrointestinal condition, which is self-limited and is characterized primarily by symptoms such as diarrhea, intestinal pain and also fever. This same diarrhea is usually quite watery or even bloody, it can cause eight or ten bowel movements a day at the height of the disease. In the case of fever, it usually lasts approximately up to a week.
This disease in the vast majority of cases is usually cured in no more than seven days, however, there are a number of patients who could have a relapse where they will have diarrhea lasting a few weeks. According to various studies, approximately 20-40% of Guillain-Barre syndrome cases are preceded by this disease caused by Campylobacter jejuni.
giardiasis
This is an intestinal infection, which is caused by a protozoan of the Giardia species, mainly Giardia lamblia; which affects both humans and different mammals. The place where this parasite occurs is in the droppings of birds, however, the real role that birds play in terms of transmission to humans is not yet known. The infection is regularly spread by the consumption or use of water that has been on a surface that is contaminated, although it has also been proven that there is human-to-human contagion.
Domestic birds that are infected suffer symptoms of gastroenteritis and can be treated without many complications, however, it is very common that they can become infected again. As a general rule, most Giardiasis infections that occur in humans are completely asymptomatic, however, approximately 50% of those affected by this protozoan may present with abdominal pain, flatulence, intense diarrhea, nausea, belching, and also vomiting, all this within the first three days or three weeks after the parasite has entered your body.
A fairly important clinical finding may be lactose intolerance at the beginning of this infection. All of these symptoms can resolve in about a week; in the case of prolonged infection it usually occurs in only 20% of those affected. All patients who suffer from hypochlorhydria or hypogammaglobulinemia, children, and different travelers to endemic areas are those who are at greatest risk of suffering from this horrible parasite.
Diseases with skin symptoms
Like the aforementioned diseases, there is another diverse group of infections or diseases that can cause skin symptoms in humans, and also in different animals, among all this variety we can find:
pasteurellosis
This disease is caused by a gram negative bacterium which is called Pasteurella multocida, this same bacterium is the cause of avian cholera and is also an inhabitant of a healthy nasopharynx in some birds. A large part of the domestic birds that are infected with pasteurellosis by the bite of a cat, unfortunately usually die of avian cholera. Pasteurella bacteria can be spread to humans through the scratches or bites of domestic birds.
The lesions in humans that are infected by this bacterium are erythematous and slightly painful, but in semiology, the seriousness of this infection can be greatly underestimated. Contagion by droplets in the air is usually quite rare and huge, however, in these cases it usually causes symptoms such as pneumonia, acute or subacute bronchitis, and even septicemia.
erysipeloid
This disease originates from a bacterium called Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae, this same bacterium is contagious to humans through direct contact with poultry or domestic birds. In the case of domestic birds, this infection can lead to sepsis, however, its manifestation in veterinary practice is very rare.
In the case of human beings, this infection directly affects the skin with continuity solution, which causes a localized infection, considerably painful and can also present itching; at first this is a pale red and then turns to a red blue. This same infection can affect the different nearby joints; septicemia or endocarditis are quite rare conditions to see in the case of humans.
Cryptococcosis
This disease originates from a capsulated yeast called Cryptococcus neoformans, this same disease is usually found in domestic birds and is completely asymptomatic and is also contagious. This microorganism can be regularly found in soil that is completely contaminated by the feces of infected birds.
In general, the most common symptoms of this cryptococcal disease are meningeal and also pulmonary. Although the usual contagion is through broken skin, cutaneous cryptococcosis can be found in different skin lesions such as cellulitis, herpes, molluscum and also pseudonodules similar to Kaposi's sarcoma. In the specific case of people with immune system problems, this infection can be present in the lungs and central nervous system.
Avian mite dermatitis
Many birds can become carriers of different kinds of mites, these can become mites in their feathers, or "alarm" mites, which indicates that they cannot infect humans. However, despite this, there are different mites that can be harmful to humans, such as Ornithonyssus sylviarum, which is found in poultry that live in the north; and also Dermanyssus gallinae, which is better known as the chicken or poultry mite.
These two mites can be found without much complication immersed in the entire food industry that includes poultry, however, on many occasions it can also be found in different domestic birds.
Non-tuberculous mycobacteriosis
Nontuberculous mycobacteriosis is caused by an organism of the Mycobacterium species, which can be fortuitum, abscessus, avium, ulcerans, marinum, kansasii, and chelonae. These are ubiquitous in the environment and can infect different animals; An example is the case of M. avium subsp avium, which is the cause of avian tuberculosis.
All birds can become carriers of these mycobacteria, they can be found in their claws, legs and also their beak, which greatly facilitates infection to humans. In the specific case of asymptomatic infections, the place where the mycobacteria is inoculated is the place where the symptoms are determined. This non-tuberculous mycobacteriosis can be suspected when the pulmonary or skin infection does not respond satisfactorily with empirical treatment.
Different patients with previous pulmonary conditions or with problems in their immune system, suffer from a much higher risk of suffering from pulmonary or disseminated disease.
If you want to know more about birds and other animals, do not hesitate for a moment to continue reading these other articles: