La biosphere it is where life occurs on planet earth, that is, the most important part of the planet since without it life could not be maintained on the planet as we now know it, we invite you to continue reading to understand a little more about the value of this layer of the Earth.

The biosphere
The name of this layer of the earth was given by the geologist Suess, it is located on the lithosphere, including the hydrosphere and the lower part of the atmosphere, in which the phenomenon of life is manifested.
However, many will wonder if in all branches of study biosphere means the same thing, a very common question is what is biosphere in ecology, It is one of the layers of the earth where the Kingdoms of Living Beings, that is, it is the one that maintains life on the planet.
Our planet
Earth is one of the new planets in the solar system, so named because it is made up of celestial bodies that revolve around the sun. Science does not yet know what the real age of the Earth is. Just like other celestial bodies, the earth would have been formed from the agglomeration of gases and dust that revolved around the sun.
The particles grouped in this way began to release energy, which was then transformed into heat. Over time, the action of the intense heat caused the function of the different elements. Very slowly, the earth cooled. This is how the different levels or layers that we know today, such as the layers of the biosphere or earth, originated.
Origin of the Earth
The appearance of the earth has undergone many significant variations. The relief or external appearance of the earth's surface is the product of the action of lifting, crashing and sinking of the plates that support the continents, through millions of years. It is also due to external factors, such as rain or wind and living organisms.
Our planet shows very defined zones: the hydrosphere and the continental mass. The hydrosphere is the sum of liquid water and solid water (ice) and corresponds to 70% of the earth's surface. Therefore, more than half of the earth's surface is occupied by water, which is why it is called the biosphere.
The continental mass presents different reliefs called mountains, valleys and volcanoes, the same thing happens at the bottom of the sea. The atmosphere, which covers the earth's surface, is made up of different gases, but above all oxygen and nitrogen.
The biosphere is composed of a series of chemical elements that are part of living beings.
- The most abundant bioelements are: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen.
- Those of lower concentration are: Sulphur, phosphorus and calcium.
- Trace elements are found in living beings in small concentrations, but they must not be forgotten as their absence can cause significant deficiencies. The most important are: fluorine, iron, zinc and copper.
- Some of the bioelements are found in living beings in an ionic form, such as sodium, potassium, calcium, chlorine and magnesium, and they have important functions in the regulation of osmotic processes.
Life began in the water
The water was the scene of the first signs of life. The first living beings, which were composed of a single cell, originated in the various chemical reactions that operated on rocks and minerals, these beings were unicellular organisms.
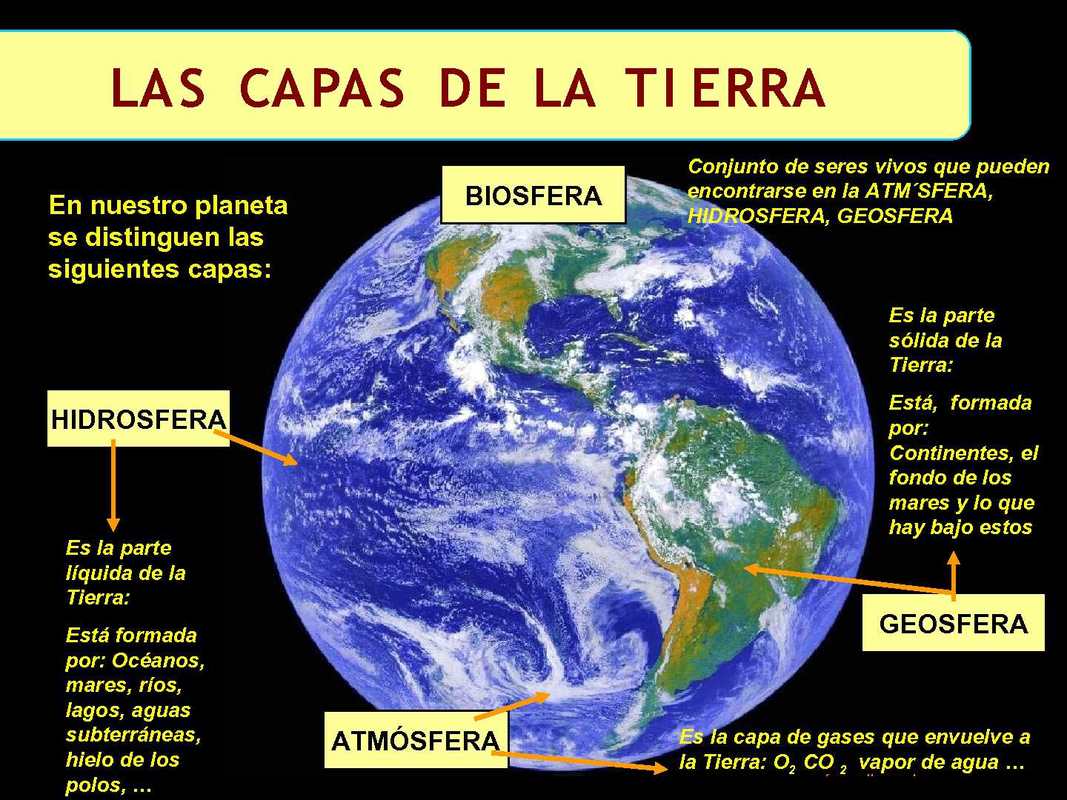
The first thing that can be seen, almost with the naked eye, is that the earth has three layers, a solid, a liquid and a gaseous, respectively called the solid sphere, the hydrosphere and the atmosphere. The solid sphere is made up of the compact mass that forms the continents and the solid layers that exist under the oceans and that reach the center of the planet.
The hydrosphere is the liquid layer of the earth's surface, it is made up of the oceans and seas and also by inland or continental waters such as lakes, rivers and underground deposits, this layer did not exist when the earth was formed and did not appear until the cooling of the planet caused the condensation of the water vapor that was in the primitive atmosphere.
The atmosphere is the gaseous layer that surrounds the earth, as with the hydrosphere, its existence is essential for the development of life, the atmosphere protects the earth from radiation that is harmful to life and acts as a thermal regulator avoiding excessive heating or cooling of the earth's surface.
The phenomena that give rise to winds and rains are produced in it, which is why its participation in the climate is essential.
structure of the biosphere
The earth is made up of concentric layers, the crust, the mantle, and the core, from shallowest to deepest. The separation between these three layers has been established thanks to the propagation of seismic waves, since between the crust and the mantle there is a zone of discontinuity called the Mohorovicic discontinuity, in which the propagation speed of P waves increases and S, this discontinuity is located about thirty kilometers deep and was discovered in 1910.
Also the separation between the mantle and the core is given by a zone of discontinuity called the Gutenberg discontinuity, this zone that was discovered in 1906 is characterized by a notable decrease in speed in the P waves and by the disappearance of the S waves, not spreads deeper.
According to these data we know that the earth's crust is the area between the surface and the Mohorovicic discontinuity, its average thickness is thirty kilometers, but it decreases significantly under the oceans, where it varies between five and ten kilometers and can increase up to seventy kilometers below the great mountain systems.
It is generally accepted that the crust is divided into two layers, an upper one in which granite predominates and a lower one in which basalt predominates. The mantle, the second layer of the earth's structure, is formed mainly by silicates and extends from the crust to the core, it is divided into two parts, the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
The first reaches up to seven hundred kilometers of depression and the second up to two thousand nine hundred kilometers where the Gutenberg intermittence is, within the mantle above a depression between fifty and two hundred kilometers, there is an area where the speed of diffusion of the seismic loops decreases considerably, this zone is known as the asthenosphere or zone of reduced velocity and it is here that most earthquakes originate.
Scientists explain that this decrease in the speed of seismic waves is due to the existence of molten or semi-molten rock, which is also responsible for the existence of convection currents in the asthenosphere.
The set formed by the crust and the mantle up to the asthenosphere is called the lithosphere, it is an area structured by spherical caps called plates that have great rigidity, its study has given rise to a theory on the formation of continents, which is currently the most widely accepted.
Below the crust and the mantle is the core, which is the central element of the earth, the core extends from two thousand nine hundred kilometers, that is, from the Gutenberg discontinuity, the fact that in this area stop propagating S waves indicates that the materials found here are in a fluid state.
This sector, which reaches depths of up to five thousand one hundred kilometers, is called the outer core. After five thousand one hundred kilometers there is an increase in the propagation speed of the P waves, which indicates the passage to an area where the materials are found. again in a solid state, it is the inner core that reaches up to six thousand seven hundred and thirty kilometers deep.
That is to say, up to the center of the planet, as a whole the nucleus is constituted fundamentally by iron and a certain proportion of nickel, apparently in the fluid part of the nucleus there is a series of currents that could be the origin of the earth's magnetic field. .
Characteristics of the biosphere
Studies of the structure of the earth have given us some of its characteristics, such as its temperature and density due to the activity of volcanoes, men will be able to verify early on that the rocks that make up the interior of the terrestrial globe are found at very high temperatures.
In effect, the fact that the lava is propelled with force to the outside and at temperatures that can exceed a thousand centigrade clearly shows that in the heart of the earth there are great pressures and temperatures infinitely higher than those recorded in the Earth. surface.
As if this were not enough, when deep mines began to be excavated for the extraction of minerals, it was found that the same rocks could be found at temperatures of more than fifty centigrade. These and other direct experiences have made it possible to determine that the temperature increases inside the globe at a rate of one degree centigrade for every hundred meters of depth.
This increase in temperatures that socially affects the outer layers of our planet is known as the geothermal gradient. At greater depths, the temperature increases to a lesser extent than if this gradient remained constant in the center of the earth, it would be reached in the two hundred thousand degrees centigrade, when the reality is that they do not exceed four thousand five hundred degrees centigrade.
Thanks to some astronomical calculations, it is known that the average density of the earth is 5,5 grams per cubic centimeter, however, and as it happens with temperature, the density varies considerably from the surface to the center of the earth, so while the rocks on the surface have a density of 2,8 grams per cubic centimeter, those in the interior can exceed seven grams per cubic centimeter.
The existence of different layers with different densities inside the terrestrial globe can be explained by the increase in temperature and also by the natural radioactivity released by the rocks.
The atmosphere
There are several compartments of the atmosphere that, depending on the characteristics that serve as the basis for establishing their stratification in homogeneous layers. The atmosphere is made up of four layers:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
The structure of the atmosphere can also be analyzed based on its chemical composition. In this case, three different layers are distinguished: the homosphere, the heterosphere and the exosphere.
The homosphere that is calculated up to fifteen meters high, is basically composed of nitrogen and oxygen, in the same way it has tiny portions of other chemical compounds a little more harmful to humans, however, essential for its existence, one of the problems currently facing humanity is precisely the excessive increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
This increase in the content of carbon dioxide brings as a consequence, among other causes, gaseous emissions from industry or the combustion of internal combustion engines that can give rise to the so-called greenhouse effect, which occurs when the excess of CO2 does not allow the energy that the earth returns to the transformed atmosphere, in fact the greatest danger of the greenhouse effect, as its name indicates, is that it could lead to global warming of our planet that would end up making life in the biosphere impossible.
Some scientists maintain that the excess carbon dioxide will be absorbed from the plant mass, particularly by large tropical forests, but others believe that this will not be the case and that in about 50 years the temperature will already have increased two and a half centigrade on average. , while rainfall will have decreased by 10%.
The homosphere encompasses almost all of a third of the thermal levels of the atmosphere, the troposphere, the stratosphere and the mesosphere in which the chemical structure is what is visible to the naked eye, except in the final division of the stratosphere where in its totality ozone is the component that exists.
It is the denomination ozonesphere or ozone layer that sucks a part of the sun's ultraviolet radiation preventing these rays so harmful to human existence from reaching the surface of our home that is known as Earth or biosphere, ozone is a gas whose corpuscle It is made up of three oxygen particles, that is, O3, which forms and decomposes in the atmosphere by absorbing ultraviolet rays from the sun.
This process, which has taken place unalterably for thousands of years, has been affected in recent times by certain polluting emissions that have produced a hole in the ozone layer, that is, ozone has stopped forming as before and as a result of this a part of our planet has been left without its benefactor protection and causing Diseases Caused by Pollution.
According to scientists, the causes of this alteration of the ozone layer are certain gases derived from chlorine called chlorofluorocarbons, these gases used in refrigerator aerosols and refrigeration systems have been restricted by many governments as a result of the alarm voice launched by scientists. and environmentalists.
The products of these investigations bore fruit in the year 1996, when geologists finally gave the valuable information that the hole in the ozone layer was beginning to close in the lower part of the homosphere, that is, in the troposphere and especially in the first three kilometers, the air contains some impurities such as water vapor, dust, salt crystals, sulfur gases, among others.
Of all these impurities, the most important is the water vapor that produces the evaporation of surface waters and the transpiration of plants, water vapor is very happy, it has a great importance in human life since it is the cause of essential phenomena of the weather, such as humidity, clouds, rain, dew, among others.
The heterosphere that covers between a hundred and a thousand kilometers, is composed of different light gases, which were divided into four microlayers:
- the first molecular nitrogen
- the second atomic oxygen
- the third and fourth of atomic hydrogen