Therapeutic cloning consists of the creation of a cloned embryo from the pluripotent cells of a patient with the aim of obtaining stem cells and using them for the treatment of diseases without immunological rejection.
That is to say, is a genetic manipulation technique that uses embryos for therapeutic purposes and this has generated great controversy worldwide raising bioethical issues such as the dignity of the embryo, the beginning of life or the individuality of the human being. In this post we will talk about the practical advantages of therapeutic cloning as well as the bioethical problems it poses. Stay with us to learn more about the therapeutic cloning: a biomedical revolution?
What is therapeutic cloning?
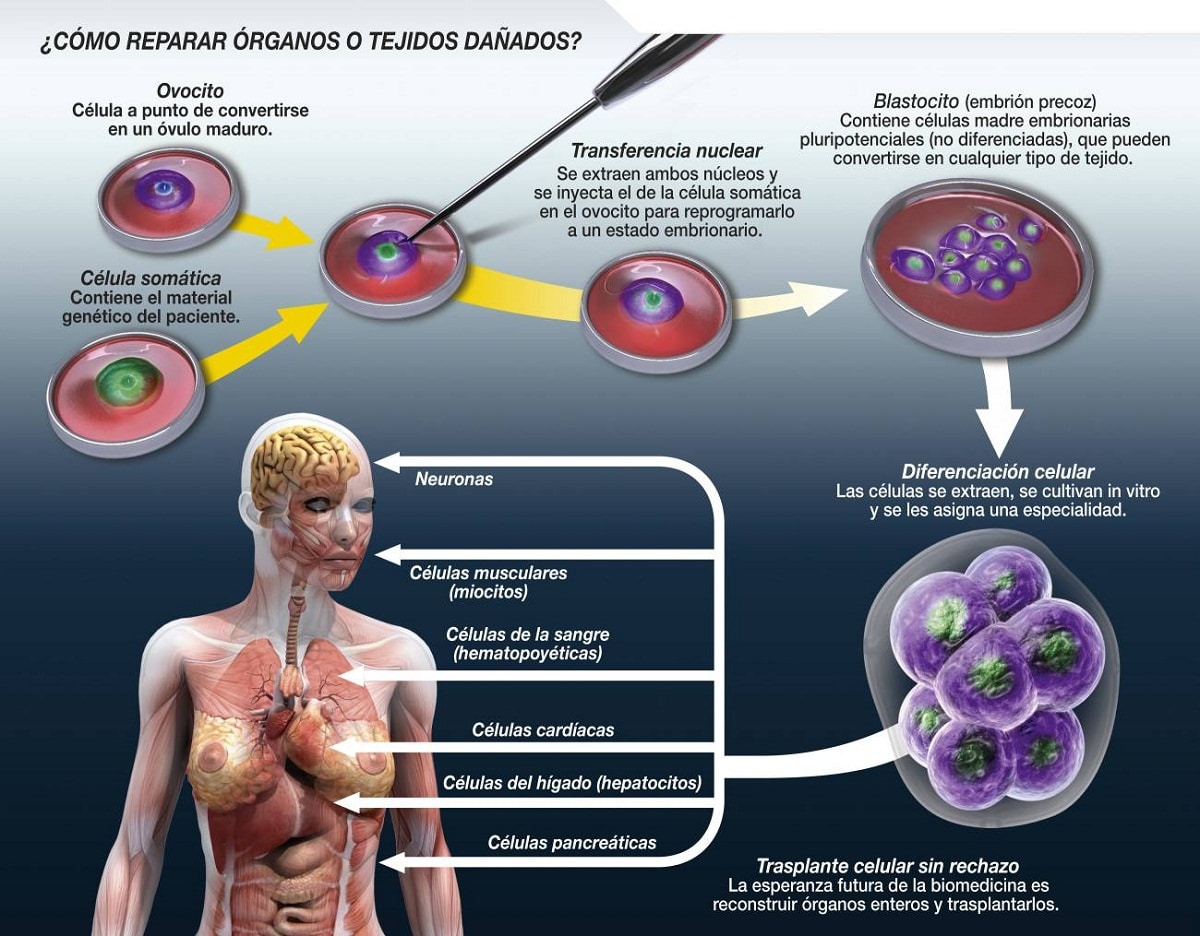
The therapeutic cloning process consists of nuclear transfer from a donor somatic cell to a previously enucleated recipient reproductive cell, the ovum. This involves removing the nucleus from a somatic (non-reproductive) cell from a donor and inserting it into an enucleated (no nucleus) ovum, the recipient cell.
The egg cell is then stimulated to divide so that it begins to multiply and form an early embryo (the blastula). This embryo is cultured for a few days to obtain pluripotent stem cells, which are cells with the capacity or potential to become any type of cell in the human body, also known as embryonic stem cells.
Practical applications of therapeutic cloning
Embryonic stem cells have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the human body, making them a promising source for regenerative medicine.
These cells could be used to replace damaged or diseased cells in patients, offering the possibility of treat disease and injury without risk of immune rejection. For example, they could be used to generate heart tissue for patients with heart disease, neurons to treat neurological diseases, or pancreatic cells to treat diabetes.
Advantages of therapeutic cloning
One of the main benefits attributed to therapeutic cloning is the possibility of obtaining autologous stem cells. These cells receive this name because they are obtained from the individual (the patient) and are used for their own benefit, since they have the advantage that they do not pose immunological rejection problems, thus avoiding the need to use immunosuppressants after tissue transplantation or organs (obtained by therapeutic cloning) in the patient.
Therefore therapeutic cloning opens the possibility of obtaining fully personalized cell therapies without risk of rejection.
In addition, therapeutic cloning could offer a method for the mass production of stem cells, which would allow lower costs and improve accessibility to this type of treatment. This can also have a huge economic impact on the biomedical industry.
bioethical problems

However, the massive production of embryos for their subsequent destruction for therapeutic purposes opens up a controversial and sensitive debate about life as a concept: ethical and moral debates appear about the dignity of the embryo whose existence would be relegated to a practical utilitarianism “ripping away the right” to be what he is destined to be: an adult individual.
Questions of all kinds appear, such as: Do humans really have the power to decide the future of a life (that of the embryo)? This question would lead to the following: when does life begin? In the zygote? In the embryo? And if, by consensus, some believe that it is in the embryo, at what stage of its development? In the blastula stage or early embryo (the one used in therapeutic cloning)? Later? These are the same issues that arise in other sensitive issues such as abortion. And it is that it is extremely complex to define the limits of life and the rights of the embryo, despite the fact that this technique was born with a positive therapeutic purpose.
Embryo manipulation has generated strong criticism, especially from religious groups and defenders of life, who argue that all human life has the right to be protected from its beginning, including embryos. For this reason, therapeutic cloning has been strongly criticized by these groups and its viability is subject to strong judgment.
Another concern with therapeutic cloning is that cloned human cells could be used for non-therapeutic purposes., such as clandestine reproductive cloning, since it is absolutely legally prohibited throughout the world.
Therapeutic cloning vs reproductive cloning

It is important to note that reproductive and therapeutic cloning are two different concepts. Reproductive cloning is aimed at generating a complete individual, while therapeutic cloning aims to generate a tissue, maximum a complete organ, with the purpose of treating a disease. (i.e. for therapeutic purposes). Therefore, the treatment of the cloned embryo obtained in both cases is different, although equally controversial.
Reproductive cloning in humans is absolutely prohibited worldwide., as we anticipated a few lines ago, and therapeutic cloning has a feasibility closely limited by legislation, although it may well vary according to the jurisprudence of each country.
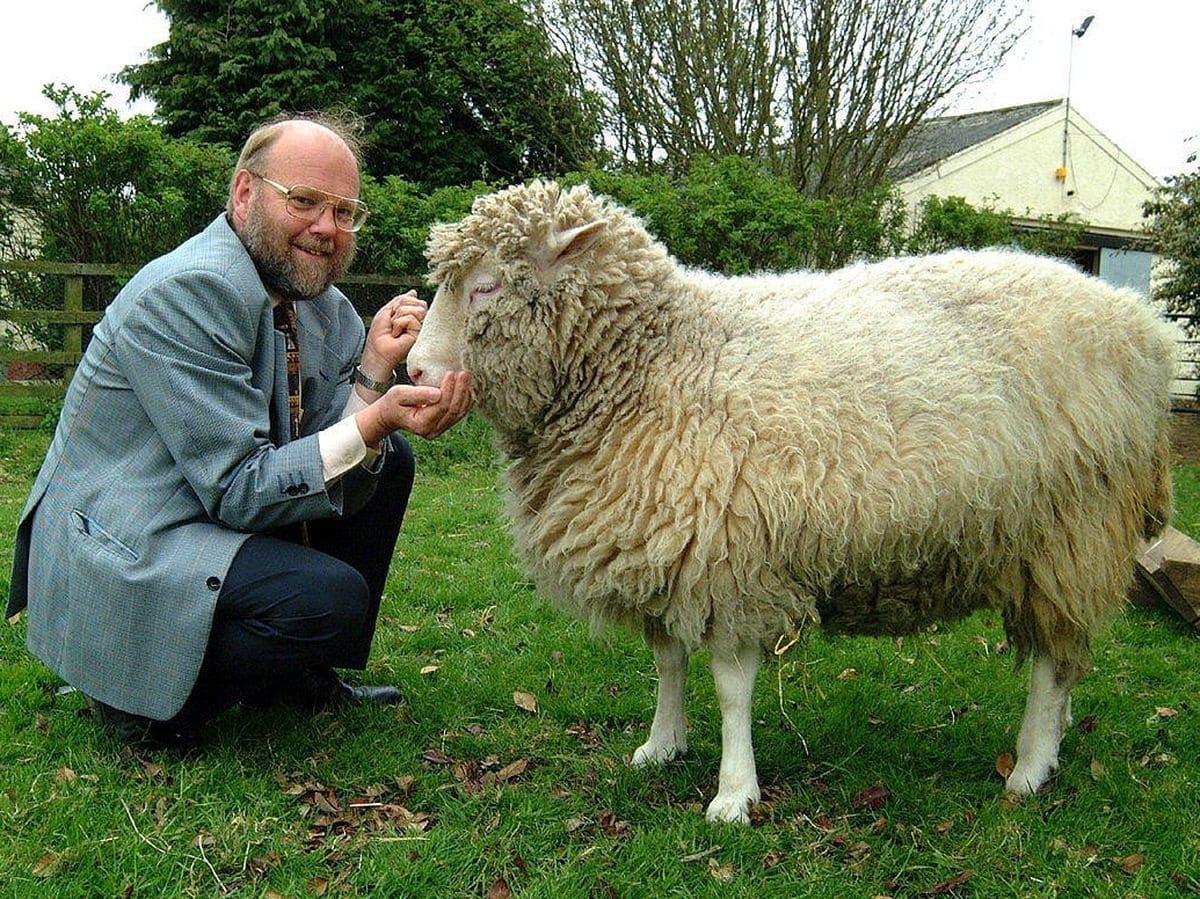
As we all know, reproductive cloning has only been carried out in animals and under experimental regulation, we are talking about dolly the famous sheep, who came into the world in 1996 to bring about a revolutionary change in science.
Since then, different investigations have been generated around therapeutic cloning, in order to obtain stem cells identical to those of the patient to treat different diseases.
Alternatives to therapeutic cloning
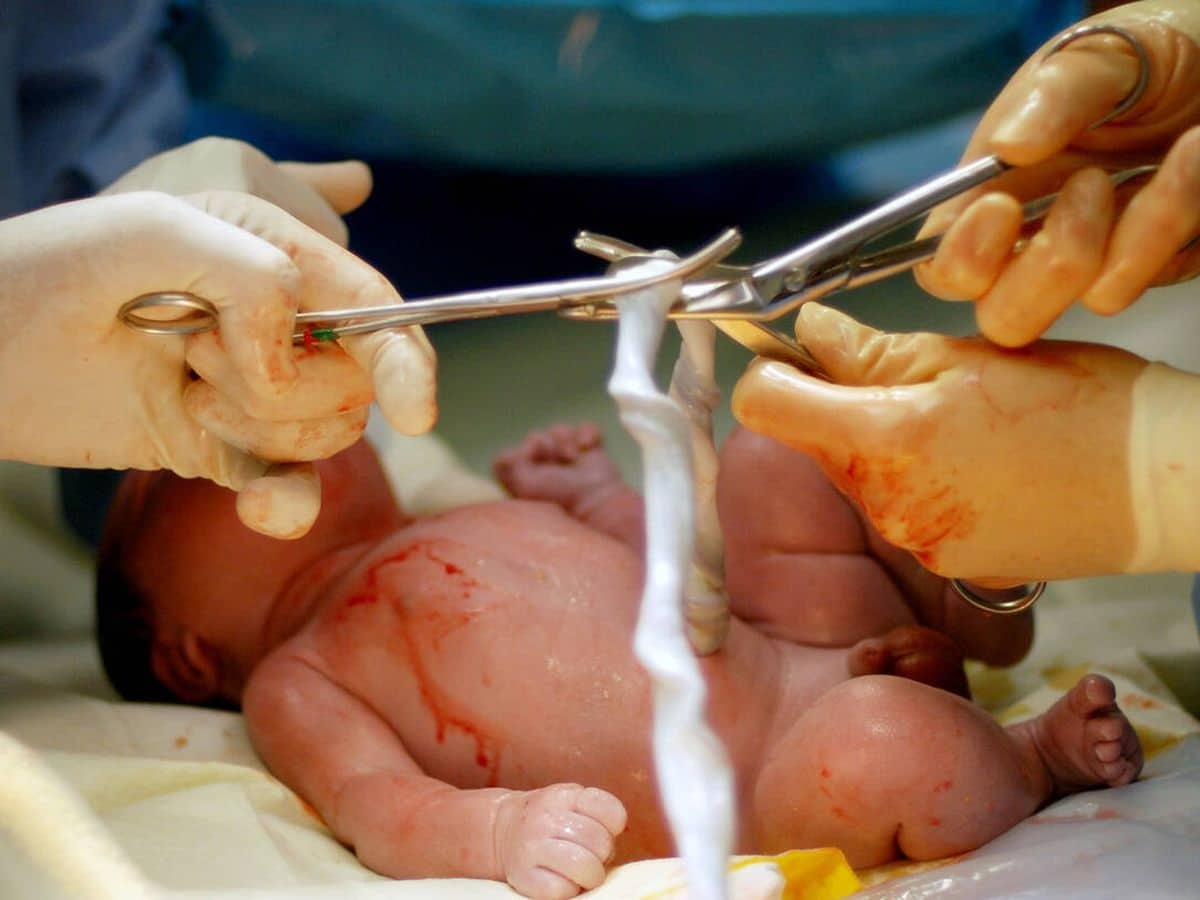
Due to the controversial debate that this technique entails, science raises interesting alternatives to therapeutic cloning that also make it possible to obtain stem cells.
One of them is the cell reprogramming, also known as iPS. This technique consists of taking adult cells and reprogramming them to behave like embryonic stem cells, and it has been used successfully to treat diseases such as Parkinson's or diabetes.
There is also the option of Obtaining stem cells from extraembryonic attachments, such as the umbilical cord: Stem cells can be extracted from it at the moment of delivery that would be stored in stem cell banks for later use. This type of stem cells also have the advantage that they do not generate rejection in the patient, since they are not foreign cells, but their own.
The debate is still open: is therapeutic cloning a biomedical revolution?
Therapeutic cloning may appear to be a promising option for the treatment of diseases by creating autologous stem cells from the patient. However, its feasibility and ethics remain the subject of debate. In addition, there are other alternatives available that can provide stem cells ethically and safely.
It is important to continue researching and developing all these techniques to advance in the treatment of diseases and improve the quality of life of patients.