In this article we bring you important information about the egyptian Religion, one of the most complex religions that have existed throughout the history of the world, since it was one of the most powerful and believing societies that have existed, being a polytheistic religion many of its resources were destined to make offerings to the different gods Egyptians Find out everything!

egyptian religion
It was a civilization that was formed around the year 4000 BC. After the writing arose. The Egyptian civilization was one of the most powerful and iconic societies of all time. This civilization was established on the banks of the Nile River. Located north of the African continent. This river has been of great importance to the Egyptian civilization since when it grows. The Egyptians could supply themselves with abundant water and use it in agriculture and irrigation of the fields.
While the Egyptian civilization was engaged in all their daily work they also had a great religious life and full of many beliefs. That is why it should be noted that the Egyptian religion was practiced for a long time, it is estimated that it lasted more than three thousand years.
In this way, the Egyptian civilization had adopted a very complex belief system, religious dogmas had already been integrated into their daily work, giving an Egyptian religion full of various gods. Where the Egyptians believed that these divine beings could dominate natural phenomena through their power.
That is why in the Egyptian religion it was widely practiced by the Egyptians since these people, by providing the gods with food and offerings, could gain their favor. That is why the Egyptians focused on practicing the Egyptian religion with the Pharaoh who was the closest person to the Egyptian gods. So was a figure known as the king of Egypt.
Many Egyptians came to believe, thanks to the Egyptian religion, that the pharaohs had divine power because of their position in society. That is why he was also adored and paid tribute to what he represented. In turn, the pharaoh was able to perform offerings and rites to each Egyptian god in order to keep the Egyptian civilization free from any calamity or disaster that might occur. By not paying some tribute to the different Egyptian gods, natural catastrophes could happen.
That is why the system of government of the Egyptians used came to monopolize large amounts of tributes and resources to build and build temples and sanctuaries for the different Egyptian gods that were destined to pay tribute since the Egyptians were very faithful to the Egyptian religion .
Many Egyptians tried to communicate with the different gods in order to satisfy their own needs. They did it through prayer, prayers or using black magic that was already being used at that time. Although there were many different practices used in order to engage in conversation with the Egyptian gods, a very important feature in Egyptian religion.
It is important to note that the Egyptian religion grew very rapidly and prominently throughout the course of Egyptian history. While the figure of the pharaoh was declining with the passage of time. Another characteristic to mention about the Egyptian religion was the funerary practices that they carried out.
Since the Egyptians made great efforts to ensure their soul in the afterlife, after they died, they designed tombs, furniture and various offerings to preserve the lifeless body. To be able to use it as well as the soul.
History of the Egyptian Religion
During the Egyptian religion that manifested itself in the Egyptian predynastic period, the Egyptian civilization dedicated itself to deifying all the natural phenomena that were taking place over time, since these phenomena were disconcerting the Egyptians and instilling fear in the population. . Because they found no reason for this to happen.
That is why the civilization was creating its Egyptian religion associating certain gods with the characteristics of the different animals and they were representing the Egyptian gods with an amorphous body because it consisted of a human body with the head of the animal they believed to be the Egyptian god. .
For example, an Egyptian God to whom many offerings and rituals were rendered was the God Horus who was made up of a human body with the head of a falcon and was known in Egyptian religion as the master of the heavens or the elevated one.
Another Egyptian god created in the Egyptian religion by this civilization was the god Anubis or the so-called Crocodile God, a very feared god since he was always an eminent danger for each person who entered the waters of the Nile River without precaution. But at the same time this god Anubis was highly revered by the Egyptian civilization. In the same way, this god was created a triad which was made up of his wife and his son.
Many gods were also infused with human passions for which many rituals and offerings were performed in the different sanctuaries and temples that were built for the favors received by the Egyptians.
Although it should be noted that the Egyptian people were divided into two sectors which were known as Upper and Lower Egypt. Each of these regions maintained their Egyptian religion by creating their gods and their rituals and cults. Which resulted in the worship of many Egyptian gods at once.
These gods were acquiring an important relevance according to the city where they were worshiped. For example, in the city of Thebes, the most worshiped Egyptian god was Amun. While in Heliopolis he was the god Ra. But in the city of Memphis there were two gods to which to offer offerings which were the goddess Hathor and the God Ptah.
In order to bring order to the set of Egyptian gods and the Egyptian religion to be understood by civilization, the priests who were the main head of the temples and sanctuaries began to organize the large number of Egyptian gods and explain each of their characteristics. As well as the relationship they had between them.
Many characteristics that were taken to carry out the organization was the creation of the world and the flood of the Nile river. All the characteristics of the Egyptian religion were devised and systematized by the different beliefs that the Egyptians had. In the different cities such as Heliopolis and Thebes. All these writings were reflected in the well-known texts of the pyramids and the book of the dead, as well as many similar redactions that existed.
In the Egyptian religion, it was based on the priests offering the population that Egypt was a country with a lot of fertile land since it was next to the Nile River and was surrounded by a great desert. Therefore in their religious beliefs they divided the world into three parts which were:
Heaven: known as Num and it was the place where the gods lived since the so-called Celestial goddess Nut "The greatest goddess and who gave birth to the other Egyptian gods" the Egyptians represented her with the body of a woman and this covered the entire Earth.
The earth: It was the home destined for men and women. It was known as the house of Geb who was the creator God and was represented as a man who was under the Goddess Nut.
The beyond: It was also known as Duat or the kingdom of the dead, it was first ruled by the God Osiris and then the God Horus was in charge of this kingdom. But the one who crossed it in his solar boat during the night was the God Ra. The spirits of the dead roamed there avoiding all dangers in order to return again to earthly life.
Egyptian deities
In the Egyptian religion, the Egyptians were very believers that the natural phenomena that were occurring were divine forces of the gods. That is why the Egyptians over time designed a pantheon of Egyptian gods to which they gave each god divine forces and powers as well as related it to an animal.
In this way, the religious practices carried out by the Egyptians were with the intention of appeasing the natural phenomena that brought misfortune to their communities. But offerings and ceremonies were also made to the different gods to thank them for the favors they received.
That is why the Egyptian religion was based on a complex polytheistic system since the Egyptians were very sure that the gods could manifest themselves in different natural phenomena. But at the same time they had several mythological roles. For example, the sun in the Egyptian religion was related to multiple deities since it contains many natural forces.
That is why the Egyptian pantheon was very organized because the Egyptian gods had various roles in the Egyptian religion. Since they ranged from the gods that fulfilled vital functions in the universe to the so-called minor gods that were well recognized in the cities and some regions that fulfilled some purposes of the Egyptian population.
The Egyptians also adopted foreign gods and sometimes added to the Egyptian religion people who were pharaohs who died and were considered divine beings by the Egyptian civilization. But there were some commoners who were deified by the Egyptian religion, such as Imhotep, who in life served as a wise man, inventor, doctor, astronomer, and the first known architect and engineer in Egyptian history.
In the Egyptian religion, the different gods that formed the Egyptian pantheon were not given a literal representation of their appearance since it was believed that there was not a single representation for the Egyptian gods since their nature was mysterious. That is why the Egyptians made various forms to be able to recognize the different Egyptian gods. In addition to abstract figures to be able to indicate the role that each god had in the Egyptian religion.
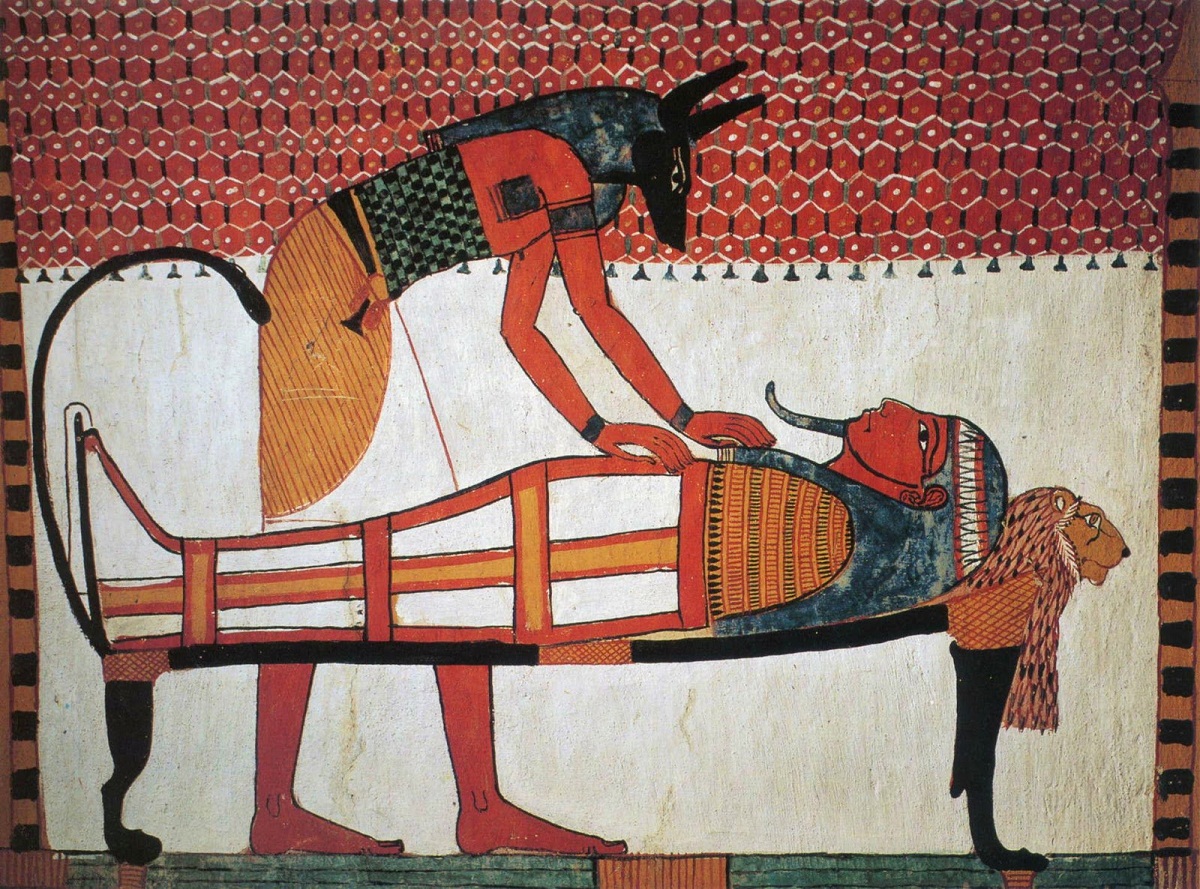
We can denote a very clear example of what the Egyptians did with the god Anubis, who represented him with a human body with the head of a jackal. Since this animal has scavenging habits and destroys the lifeless body. But to counteract this threat they used it in order to preserve the body of the deceased.
It is also noted that the animal's black skin was related to the color of the dead person's flesh once it was mummified. Likewise, the Egyptians agreed that the black ground was a symbol of resurrection. That is why when making the iconography of the gods they were represented in different ways.
The Egyptians associated the gods with particular cities and regions and worshiped them, but over time they changed places and the Egyptian God who was worshiped in a city did not have to be from that place or have been originated his cult in that city. An example of this was the Egyptian god Monthu who was known as the chief god of the city of Thebes.
But that was in the period of the Ancient Kingdom of Egypt, but over the years this Egyptian God was replaced by the God Amun. Who could have emerged in another city but became so popular among the Egyptians that offerings and ceremonies began to be made in the city of Thebes.
Associations of Egyptian Gods
In the Egyptian civilization with the passage of time they were relating the different gods for what they represented in the Egyptian religion and the forces and power they were obtaining, in this way the Egyptians were placing the different gods in groups in order to reflect relationships .
For which some groups of gods had an indeterminate size of gods and determined them by the functions that they fulfilled in the Egyptian religion. Many of these groups were made up of minor Egyptian gods who had little identity.
While combinations of Egyptian gods were made based on their mythology and the symbology of their numbers. Therefore, they united a pair of Egyptian gods that almost always represented the duality of opposite phenomena. A combination of Gods widely used in Egyptian religion is the well-known family triad.
In this family triad they joined the Egyptian gods as a family formed by a father, a mother and a son. Where the Egyptian civilization paid tributes and ceremonies to the entire triad in the different Egyptian temples and sanctuaries. Many groups of gods were very important for the Egyptian civilization, among which the well-known Ennead stands out, which constituted a set of nine Egyptian gods.
This group of Egyptian gods was made up of the gods Atum, Shu, Tefnut, Nut, Geb, Isis, Osiris, Nephthys, and Seth. Tribute and offerings were paid to them in the city of Heliopolis. In this system of nine gods it was known as the theological system where many areas of the Egyptian religion were involved which were the creation of the world, the kingdom on earth and life after death.
Also the relationship that occurred between the different Egyptian gods was expressed in a process known as syncretism where two or more Egyptian gods were related to form a new composite God. This process occurred on several occasions in the Egyptian religion and was based on the recognition of an Egyptian God within the body of another God.
Although these links between the Egyptian gods were known as fluid links, they were not intended for permanence, since the fusion of two Egyptian gods into one could develop multiplex syncretic connections.
For which the syncretism used in the best way combined many Egyptian gods that had similar characteristics. While in other events the Egyptian gods were related by their different nature.
In another example of these relationships, that of the God Amun stands out, who is known in Egyptian religion as the God of hidden power and was related to the Egyptian God Ra. Where this caused the power that was behind all things to become a great visible power in nature.
The Genesis in the Egyptian Religion
While the groups of gods were being formed by the Egyptians, they were losing influence in civilization since the beliefs that people had regarding the gods were very dominant and in the groups of gods those beliefs were transforming, combining and syncretizing. For example, the group of gods formed by the God Ra together with the God Aton was renamed Aton-Ra, and the characteristics of the God Ra were more dominant.
Then as time passed the God Ra was absorbed by the Egyptian God Horus. And this group was known by the name of Ra-Horajti. In the same way it happened with the Egyptian God Ptah who became Ptah-Seker, since he was assimilated by the God Osiris, this group of gods was known as Ptah-Seker-Osiris.
It is necessary to emphasize that one of the most worshiped goddesses in the Egyptian religion is the Egyptian Goddess Hathor. These goddesses due to the fame that she had in the Egyptian religion and in civilization over time, divine powers of other gods were added to her. But in the end she was assimilated by the Egyptian goddess Isis.
In the Egyptian civilization there were many good and bad gods, but these gods that had a reputation for being evil were combined with other Egyptian gods with the same fame. As was done with the God Seth, who was known as a hero God. This gave him many characteristics of the gods that were evil.
According to what is told in history, he had this recognition by the Egyptian civilization because the Hisco civilization took this God as its protector and the Egyptians condemned the God Seth as an evil God against the Egyptian civilization.
When was the influence of the Greeks in the Egyptian civilization. In addition, what had greater importance in the Egyptian religion was the group of Gods that became known as the triad which was composed of the God Horus, the God Osiris and his wife the Goddess Isis. While his great enemy was the Egyptian God Seth.
All this is well known in the Egyptian religion through the different stories that have been told over time, such as the myth of the "Legend of Osiris and Isis". This group of gods was also known as the triad as they assimilated a great cult of gods and many characteristics of gods before them.
Although each god of the triad was worshiped in his Egyptian temple or sanctuary. Since the God Horus was worshiped in the city of Edfu, the Goddess Isis was paid tributes in the city of Dendera and finally the God Osiri was offered offerings in the city of Abydos. Although there were many stages in the Egyptian religion to worship these gods since at one time the God Osiris had an aspect very similar to that of the God Horus.
These ways of making the gods equal had the purpose of leading the Egyptian religion towards monotheism. But this form of Egyptian religion already had a history but very small in the fourteenth century BC. This happened in the stage of Pharaoh Akhenaten who only wants to worship the Egyptian God Aten.
That is why Pharaoh Akhenaten transformed the God Aton into a sun disk, but this was a nice aspect for the Egyptian religion that was violently rejected by the priests and later by the entire Egyptian people.
But there are historical documents such as the Royal Canon of Turin where it is written in hieroglyphics that several Egyptian gods in various stages were the governors of Egypt, among which Ptah, Ra, Shu, Geb, Osiris, Seth, Thot, Maat and Horus stand out;
Each God had a great time as governed. After that stage they had the so-called Shemsu Hor who were known as the followers of the God Horus. This stage lasted at least 13.420 years. Before the first dynasty of pharaohs was born. Then the so-called Menes took possession of the throne of Egypt and remained in power for at least 36.620 years.
Egyptian Religion and Ma'at
The Egyptian religion was centered on the concept of the word Ma'at, which translated into Spanish means that it had to do with justice, order and truth. Since these were the laws of the universe and should be governed by human society. This word has existed since the creation of the universe and without these words the world would have no order or cohesion.
However, in the Egyptian religion it was believed that the Ma'at was always under an imminent threat that caused it to go out of order. For which he needed Egyptian society to keep him in his state of order and justice. This at the human level means that all the people who are part of society should help and coexist.
By doing this, the cosmic level rose and all the forces of nature, that is, the force of the Egyptian gods, came together to give a balance to the earth. That is why it was a main purpose in the Egyptian religion.
That is why the Egyptian civilization had the intention of keeping the Ma'at in the cosmos and to the gods a series of offerings and ceremonies should be made to remove lies and disorder in the Egyptian population and always follow the path of truth.
A very important point in the Egyptian religion is that the civilization had a conception of time which was very focused on keeping the Ma'at going. That is why whenever Egyptian religion is studied in a timeline, a cyclical pattern that always repeats itself stands out since the Ma'at was renewed during periodic events in the original creation, one of these events was known as the flood of the Nile river that was produced every year.
Another important event was to be able to renew the Ma'at in the Egyptian religion when a new pharaoh was elected. But the event that was most important in the Egyptian religion to renew the Ma'at was the journey that the God Ra made daily through the so-called twelve gates.
Having an idea about the cosmos, the Egyptian civilization had a flat vision of the earth. Where they personified the God Geb and the goddess Nut arched over this God. But both Egyptian gods were separated by the God Shu.
Who was known as the God of the air and under all the earth was the underworld and above in the sky the underheaven was located as parallel extensions and further away was the infinite expansion of Nu that was known as the chaos that existed before the creation of the world.
Although many Egyptians also believed in a site that was known as the Duat. A mysterious region that was related to the death and rebirth of people. That according to many Egyptian priests it was in a part of the sky and others affirmed that it was somewhere in the underworld.
Many affirmed this theory since the God Ra had to travel all over the earth daily through the back of the sky and when night fell the God Ra had to travel the entire Duat in order to be reborn at dawn.
Due to the belief that the Egyptian civilization had, the cosmos in which the Egyptians believed was inhabited by three types of very sensitive divinities. The first were known as the Egyptian gods.
The others were the souls of the deceased who had a place in the realm of the dead and many of them had characteristics of some gods. The last and most important were the pharaohs who had the purpose of being the bridge between the realm of the gods and the human.
Importance of the Pharaoh in the Egyptian Religion
Many specialists and researchers on the Egyptian civilization have debated the degree to which the pharaoh was considered an Egyptian God in the Egyptian religion. Although many have opined that it was unlikely that the Egyptians recognized the pharaoh as a royal authority and at the same time as a divine force.
For which the Egyptians recognized the pharaoh as a human being who was subject to having the weakness of humans. But at the same time she looked at him as if he were a god. Because the power of the divine and that of the monarchy rested on his shoulders. In this way the pharaoh had to act as an intermediary between the Egyptian civilization and the different gods that paid tribute to him in Egypt.
This was a key point to have the Ma'at in control. Since it was used to enforce the laws and justice as the harmony between the entire Egyptian community that existed in order to maintain order and the population to maintain their offerings and rituals to the different Egyptian gods.
Due to these circumstances, the pharaoh had the need and the objective of supervising all the activities that were related to the Egyptian religion. But the life that the pharaoh led of pure prestige could interfere with what was written in the official regulations and in the final stage of the Egyptian New Kingdom the figure of the pharaoh was drastically declined in the Egyptian religion.
Therefore, the Egyptian civilization was closely associated with many of the characteristics of the Egyptian gods and many people identified the pharaoh with the God Horus. Who was in charge of representing the Egyptian monarchy. Also the Egyptian citizens saw the pharaoh as the son of the God Ra. Since the God Ra had to govern and regulate the force of nature while the pharaoh had to regulate the laws in society.
When the stage of the New Egyptian Empire began, civilization began to associate the pharaoh with the God Amun. Since the God Amun was the representative of the supreme force of the cosmos. That's why when the Pharaoh came the moment of his death. In the Egyptian religion he disposed of his body to mummify it and turn it into a kind of earthly deity for the Egyptians.
When they had already made him an earthly deity, they compared him to the Egyptian God Ra. While in other regions of Egypt he was equated with the God Osiris who represented life and rebirth. While others coupled it with the characteristics of the great Sun god Horus. In this way, the so-called mortuary temples were built, so the Egyptian religion used them to pay tribute to the different pharaohs who had already died, as is the case with Shafer.
life after death
One of the most important characteristics in the Egyptian religion is that the civilization had adopted the belief about death and life in the afterlife. That is why they affirmed that every human had a power known as the Ká, which was described as the vital force or power that would leave the body after it died.
As long as the person was alive, the ka was fed by the drink and food that he consumed daily in this way in order to endure in the realm of the dead. The Ka of each person had to continue receiving the different foods that is why in the Egyptian religion offerings and rituals were made to continue giving the different foods to the Ka.
Since if this was not done, the Ka could be consumed and eliminated, while there was also what is known as the Ba, which was defined as the set of characteristics that each person has in spirituality that were unique to each person.
That is why there was a big difference between the Ba and the Ka, so the Ba was always attached to the body even if the person died. Therefore, the funerary rituals that were celebrated had as their main mission to be able to free the body of the deceased from the Ba so that it could move freely in the realm of the dead.
But both aspects, the Ka and the Ba, had to be united so that the soul of the deceased could return to life after having died and that was known as an AKN. But to achieve this, the person's body could not be damaged and had to be preserved in the best way since the Egyptians believed that the Ba always returns to the body of the deceased.
The Ba returned to the body each night in order to receive the new life, so that it could emerge at the beginning of the day as an AKN. But it is necessary to clarify that in the Egyptian religion the only people who had a Ba were the pharaohs because of the connection they had with the Egyptian gods and that is why it could be united with the gods.
While the normal Egyptian civilization or the so-called commoners at the time of death their soul went to a realm that was very dark and totally uninhabited and this was the opposite of life. Some wealthy people who were known as nobles had the power to receive tombs and the resources to maintain them since it was one of the gifts of the pharaoh.
These gifts were made to the nobles because they performed favors for the pharaoh and it was believed that the more favors they performed for the pharaoh, they could bequeath the kingdom of the dead and be reborn again.
In the early days of Egyptian religion one of the most common beliefs was that after the pharaoh died his soul went to heaven and found a destination among the multitude of stars in the sky. But in the course of the Egyptian Old Kingdom that was established between the years (c. 2686-2181 BC), it was established that the figure of the dead pharaoh accompanied the god Ra on his daily journey.
Egyptian Religion and Judgment
At the end of the Old Kingdom (2686-2181 BC) and the beginning of the First Intermediate Period (c. 2181-2055 BC), the Egyptian civilization gradually began to believe that everyone had a Ba, and that all people were capable of having life after death. After that many people began to endow this belief in the new Egyptian empire. The soul of each person had to avoid any supernatural danger that would come from the Duat.
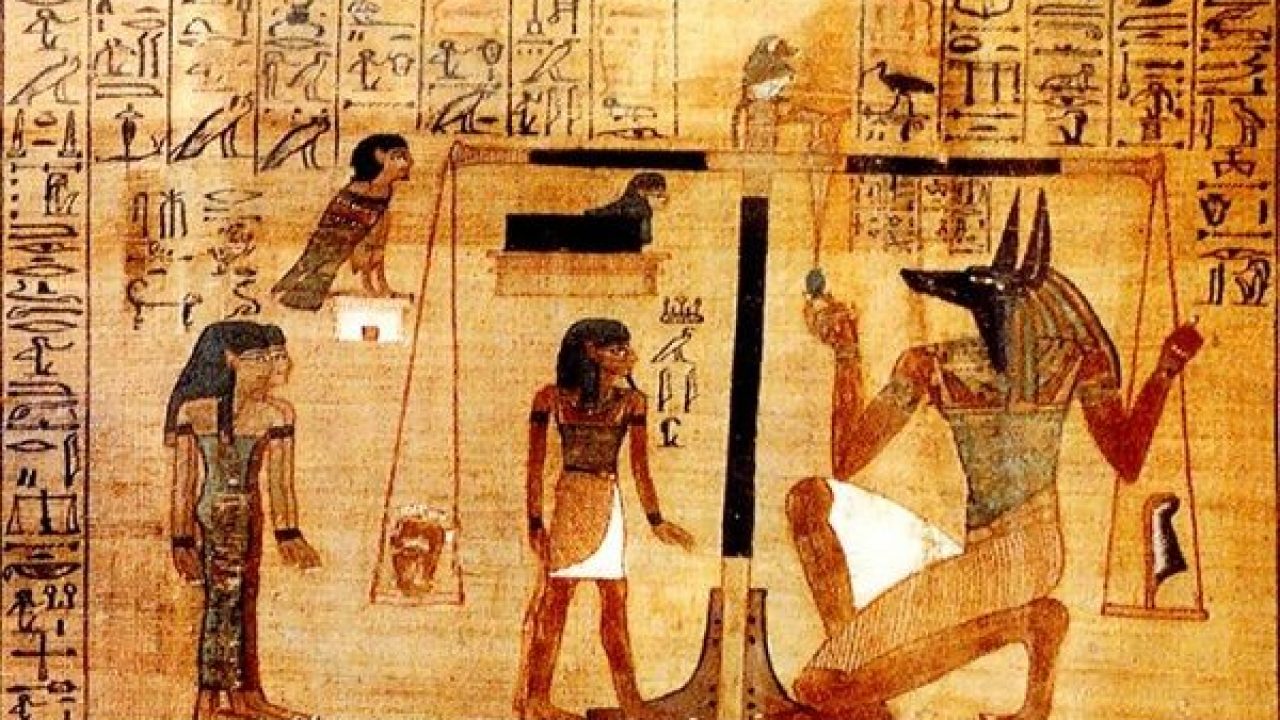
Since at the moment of death the soul would be subjected to a final judgment, this judgment is known in the Egyptian religion as "Weight of Heart"According to the popular belief of the Egyptians, all the gods of the Egyptian pantheon were going to determine what actions of the deceased were good or bad and how their behavior had been during their life according to what was written in the Ma'at.
It was also believed that all the deceased went to the world of the dead that was governed by the God Osiris, it was described as a lush and pleasant world that was between the earth and the underworld. Other Egyptians studied life after death from the vision of the Egyptian God Ra, who walked his daily path with all the souls of those who had died.
Although this method in which the Egyptians believed about the God Ra was widely used by the nobles of the Egyptian civilization, but it extended to some commoners who could believe the same as the nobles. While the time passed between the Middle Kingdoms and the New Kingdom of Egypt, the notion that the AKH was held, the soul of the deceased could travel and be in the world of the living and in a certain way could negatively affect the events that happened in the underworld.
What is written in hieroglyphs
Although in the Egyptian civilization there were not many unified religious scriptures, if many religious texts were produced and on various topics, by having knowledge of the different topics that were dealt with in the Egyptian religion, one can have an understanding about their religion, but at the same time a study must be carried out. study on the different religious practices that they used, for which an analysis will be carried out on various religious issues in Egypt based on the following elements:
Egyptian Mythology: Egyptian mythology is based on a set of metaphorical myths and legends that were intended to explain and illustrate the roles and actions performed by each Egyptian God according to their nature. Depending on how the story was told and emphasis was placed on the details of each event, different perspectives of the situation could be conveyed.
Since all Egyptian history was full of symbology and mystery regarding the different divine events that were presented in history. Therefore, many of the Egyptian stories and myths had countless versions and facts.
Although it should be noted that all Egyptian narratives were never completely written, as they left much to the creativity of the writer or accountant of the work and these works contained many works that gave the myth a more interesting landmark.
Therefore, having knowledge of Egyptian mythology was referred to a set of hymns that specified the qualities and characteristics of the Egyptian gods. In the different hieroglyphs found by the researchers, data on funeral rituals and offerings have been found. That recount the roles that the different Egyptian gods had.
Similarly, much information on Egyptian religion was found in secular religious books. Until the Romans and Greeks recounted some of the most important myths in late Egyptian history.
Among those most related myths were those of the creation of the world, since they are a set of stories that narrate how the world emerges from nothing where there was a dry space in the center of the ocean and everything was chaos and like the sun It is an important part to be able to create life on Earth.
Therefore, the rise of the Egyptian God Ra is also counted. To be able to create order, justice and harmony on Earth. Since that first ascent, thousands of Egyptian stories about the creation of the world have been told, but always with the same meaning and the same moral.
Egyptian history is based on a transformation of the Egyptian God Atum and on all the elements found on earth, a very imaginative discourse of the intellectual God Ptah is also used and with an act of divine power that the God Amun possesses but do it secretly.
But without paying much attention to the different stories that are told, the act of the creation of the world is aimed at complying with the rules and laws of the Egyptian Ma'at and the canons that exist in the cycle of time.
Similarly, it should be noted that one of the most important and widespread myths of the Egyptian religion is the myth of the God Osiris together with that of the Goddess Isis. The myth is based on the fact that the Egyptian God Osiris is the ruler of the entire territory of Egypt. But the God was tricked and killed by his brother the Egyptian God Seth.
This God is associated with chaos and misfortune. But the Goddess Isis who was the sister and at the same time his wife of the God Osiris was able to revive him so that the God Osiris would leave heirs in the land of Egypt. In this way he was the father of the god Horus. For which the God Osiris entered the underworld and became the new God and ruler of the underworld.
When his son the God Horus became older, he decided to fight with his uncle the God of chaos Seth for this to be the king of all the Egyptian territory. This gave the Egyptian religion an identification as they associated the God Seth with chaos. While the God Horus and the God Osiris as the true legitimate rulers of all Egypt.
With this, the Egyptian civilization had a logical basis to be able to carry out the succession of the pharaohs and in the same way have the pharaohs as a foundation to maintain order and justice in Egypt.
In this same way, the pharaohs related the God Osiris with death and reincarnation with the cycles of Egyptian agriculture since the crops were given as the Nile River was flooded. This was known in Egyptian religion as a model for give life to human souls after they perished.
An important point in the Egyptian religion was the journey that the God Ra made every day through the Duat. In this mythical journey the God Ra gets to know the God of the underworld Osiris. When they met this was known as an act of Egyptian regeneration, where life was renewed in the same way the God Ra had many battles with the God Apophis who was a God of evil forces.
This defeat that the God Apophis obtained and the meeting that the God Ra had with the God of the Underworld Osiris gave the God Ra the ascent towards the Sun where every day he had to follow the same path, this was an event that took place every morning on rebirth of good over evil.
Magical texts and rituals: In Egyptian religion, the religious procedures that were written on papyrus in every detail stand out and were used as instructions for other people who were going to perform the ritual or ceremony. The texts where each ritual was described were kept in libraries of the temples or sanctuaries where the different rituals were performed.
In addition, these books were accompanied by many drawings and illustrations detailing the entire procedure of the ceremony or ritual. Although it is necessary to point out that, unlike other books, these illustrations were intended to perpetuate the symbolic rites in the same way so that the Egyptian civilization did not change its form and did not stop performing them.
In this same way the texts that were considered magical in the Egyptian religion were describing the steps of each ritual. Although spells were used for specific purposes in the life of the Egyptians. Despite the fact that these were mundane purposes, they were also protected in the different libraries of the temples and sanctuaries. These purposes were learned by the entire Egyptian population.
Egyptian Prayers and Hymns: In the Egyptian religion, civilization dedicated itself to writing and conceiving an infinity of prayers and hymns which were written in the form of poetry. Although many hymns and prayers were written with a very similar structure, they differed due to the purpose for which they were intended.
For example, hymns were intended to praise the Egyptian gods and many of these hymns were found written on the walls of temples and sanctuaries, many of these hymns were structured in literary formulas that were designed to expose certain natural and mythological aspects and functions. of the Egyptian religion.
In the same way, they extolled the abilities and functions of an Egyptian god, although he expressed himself about the Egyptian religion than any other aspect of the Egyptian civilization, for which they became very interesting during the Egyptian New Kingdom. A period where a very active theological discourse took place.
The prayers were another very important factor in the Egyptian religion but they were written with the same structure as the hymns. And they were written to address the characteristics and functions of a particular Egyptian god but in a more relevant way since they asked for blessings, forgiveness or help for having had a bad streak or illness.
But prayers were used in the Egyptian New Kingdom, since before they were not used much since being able to connect with an Egyptian god was not believed possible by an Egyptian noble or commoner, only the pharaohs had this faculty. And it was even less likely that they could communicate with the Egyptian gods through writing.
During the investigations that have been carried out by specialists and Egyptologists, the prayers are found written in the different statues of the gods as well as in the temples where tributes and ceremonies were paid to them.
The funerary texts: It is important to note that within the Egyptian religion the most important and significant texts that exist and were cared for by the Egyptians for what they represented were the funerary texts whose main purpose was to ensure that the souls of the people who died reach the afterlife. The best way.
The texts that were most cared for were the so-called pyramid texts, these texts contained much information about the large number of spells inscribed within the walls of the ancient royal pyramids dating from the Old Kingdom.
These texts were intended to magically provide the Egyptian pharaohs with the means to keep the Egyptian gods company in the world of the dead or the afterlife. But it is necessary to highlight that funerary spells are found written in a variety of arrangements and combinations and many of them are found written on the walls of the different pyramids.
When the Ancient Egyptian Empire came to an end. A new group of funerary spells began to be performed, which had material found in the walls of the pyramids. Then the Egyptians began to write funerary spells on the tombs. But they were better detailed on the sarcophagi. This collection of spells inscribed on sarcophagi and tombs became known as the Coffin Texts.
Although writings were not found in the royal sarcophagi but in the different tombs of the people of the officials who were not royal. That is why in the Egyptian New Kingdom several funerary texts emerged, of which the best known is the so-called Book of the Dead.
This book contains a series of spells that are used to help the soul of the deceased to overcome the so-called Judgment of Osiris and assist him in the journey through the Duat, the underworld until he can reach the Aaru and obtain the afterlife. Unlike other funerary books, the book of the dead is the one with the most illustrations and vignettes. Therefore, the book was copied to papyrus so that the nobles and commoners had access to it and it could be placed in the tombs when they died.
Many of the funerary texts and sarcophagus texts had a lot of information and detailed descriptions about the underworld and the instructions for the souls to overcome the various dangers that dwelled there. But when the New Kingdom began, the material and information contained in the book of the dead gave rise to the editing and copying of various books on the underworld.
Another of the most important books of the Egyptian religion and the New Kingdom is the Book of the doors, or also known as the Book of the caves. These were books that made representations of what the underworld was like and what the Egyptian God Ra had to go through on his journey through the Duat.
Therefore the journey of the soul of every person who has died and has to pass through the realm of the dead. Although these books were restricted for use in pharaonic tombs. But when the third Egyptian period was born the use of these books was extended in the use of the Egyptian religion.
To the extent that Egypt was modernizing the Egyptian religion, the ancient practices were replaced with newer practices and with better techniques in addition to being scientific. Because the Egyptians dedicated themselves to carrying out studies and scientific advances that were related to the preservation of the body of the deceased.
As they advanced in their practice of mummification, they attained great knowledge and moved on to a higher level of knowledge and excellence in the afterlife.
Egyptian religious practices
The Egyptians, being very believers in the Egyptian religion, carried out religious practices to be able to comply with the gods and be always grateful to them when performing different rituals and ceremonies for these reasons we will tell a little about the religious practices that the Egyptians carried out in the different sacred sites as they are:
The Egyptian Temples: In the Egyptian civilization, being very religious, practically the temples were built from the beginning of the Egyptian civilization and religion. But there were already many Egyptian peoples with their customs and beliefs, the mortuary temples were used to pay tribute to the different spirits of the pharaohs who had already died.
There were also other kinds of temples dedicated to making offerings and rituals to the different Egyptian gods, although it is very difficult to differentiate since the Egyptian monarchy and the gods were closely related and intertwined. Although many of the Egyptian temples were not intended for the worship of the Egyptian gods and pharaohs by the general population. So the common society had its own religious practices.
That is why the temples and sanctuaries that were sponsored by the state or the governors were used as a house for the Egyptian gods, for which the different physical images of the gods were used as intermediaries for the different offerings that the believers of the Egyptian religion gave them. .
Many pharaohs believed that this service was necessary in order to keep the Egyptian gods happy and thus maintain tranquility in the universe and in the cosmos. That is why Egyptian temples and sanctuaries were the center of Egyptian society and the Egyptian government led by the pharaoh used many resources to keep the temple in excellent condition.
Similarly, the pharaohs spent a lot of time as part of their obligation to honor the Egyptian gods. Just as the nobles gave donations to maintain peace in the afterlife. In this way there were temples of a large size. However, many Egyptian gods did not have their own temple or sanctuary, they only built temples to the most important Egyptian gods for the Egyptian religion.
Although it is important to note that many gods according to the Egyptian religion did not have much worship by the pharaoh and the Egyptian people. There were some Egyptian gods that were worshiped a lot by the popular civilization in the different houses but they did not have a particular temple.
The first temples that were built for the Egyptian religion were small houses, and the structures were very simple and impermanent. Although they were designed in the Egyptian Ancient Kingdom as well as in the Egyptian Middle Kingdom. Some of the temples were made of stone but with time they were better elaborated.
But large stones were always used to build the different Egyptian temples. During the period of the New Egyptian Empire, a new design of the temples began to be built, but in a very basic way, which had used common elements that had already been used in the construction of temples in the ancient and middle Egyptian empires.
But in the New Egyptian Empire there were great variations in the plan that was used, many temples could be built and most of the temples that have survived over time is because they were built with this technique.
The technique or plan that was used to build the different Egyptian temples is based on making a central path through all the infrastructure that was known as the path of the procession. Then a series of rooms were made to reach the final sanctuary in that place you could find a large statue of the Egyptian God to whom worship and offerings were rendered.
Although entering the central hall of the temple was intended only for the pharaohs and the high command of the government. As well as the priests who represented the Egyptian religion, since the popular Egyptian population was prohibited from reaching this room. The journey that people had to make from the main entrance of the temple to the main hall or the sanctuary was known as the transit from the earthly world to the realm of the Egyptian gods or the realm of the divine.
This was experienced by the set of mythological symbols that were made on the different walls of the temple as well as in its architecture. After the temple an outer wall could be found. In that space many buildings could be found, as well as workshops and various warehouses to supply what was necessary for the temple.
If the temple was large, you could also find a bookstore where there were several books that had information about the Egyptian religion as well as other books dedicated to the mundane. These bookstores were used as centers for the Egyptians to learn about all the subjects they will need to learn.
The responsibility of carrying out the different rituals fell on the image of the Pharaoh since he was the official representative of Egypt in front of the different Egyptian gods. But those who performed the rites were the Egyptian priests instead of the pharaohs since they were in charge of other major responsibilities.
In the Old and Middle Kingdoms the priests did not have a separate class instead many of the pharaoh's high officials were responsible for performing the ceremonies for several months and some for the whole year dedicated to secular duties.
But when the Egyptian New Kingdom began, the work that the priests did became professionalized and generalized at once. Although many priests who came from town only worked part time and many were state employees. The Pharaoh was the only one who could supervise the furniture and give his approval of the temple.
While the Egyptian religion was gaining a foothold among the Egyptian people, they were all primarily employees of the Pharaoh. But as the fame of the priests grew in the same way, the wealth of the temple became greater until a time came when they wanted to rival the Pharaoh.
When there was a political fragmentation that happened during the Egyptian Third Intermediate Period between the years c. 1070-664 BC C.), The priests of the God Amun, in the so-called city of Karnak. They began to become rulers of some regions of Upper Egypt.
In the different Egyptian temples there were a large number of people working to maintain the temple, since it had the priests, the musicians and the singers of all the ceremonies and rituals. Outside the Egyptian temple there were people who dedicated themselves to work, as is the case with the artisans and farmers who worked on the different farms.
All these people who provided their services to the maintenance of the temples received a salary which came from the same offerings that the people brought to please the Egyptian gods. Therefore, it must be said that the temples were centers that generated economic activities for the pharaoh.
Currently many Egyptian temples remain in their structure and others are already in ruins due to the time that has passed. Although many are already destroyed by the erosion of the walls and the vandalism they have suffered, a pharaoh who was a great promoter of the restoration of the Egyptian temples was Ramses II, but he was also a usurper of the different temples. Among the most important temples of the Egyptian religion are the following:
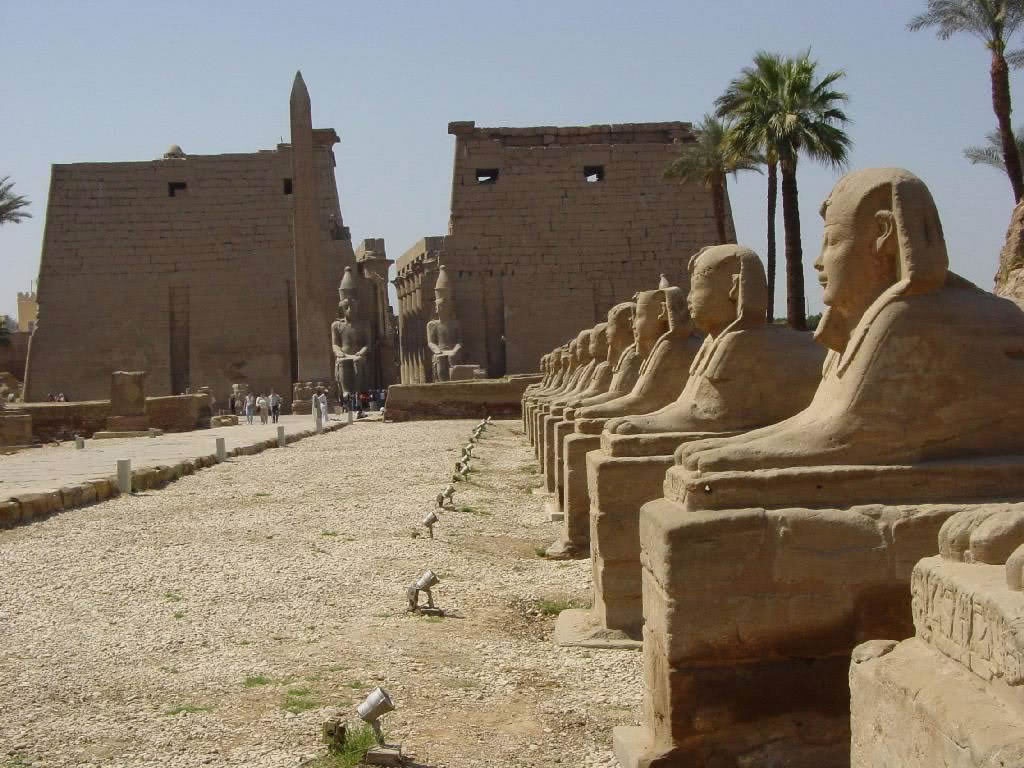
- Deir el-Bahari: group of temples of Mentuhotep II (XNUMXth dynasty), Hatshepsut and Tutmosis III (XNUMXth dynasty). The funerary complex of Hatshepsut, with wide terraced courtyards and a columned structure of great harmony (built about a thousand years before the famous Parthenon in Athens, one of the most beautiful architectural works)
- Karnak - complex of temples, expanded over five hundred years, in Thebes, the capital of ancient Egypt since the Middle Kingdom.
- Luxor: Started by Amenhotep III and expanded by Ramses II, it was the ceremonial center of the Opet festival.
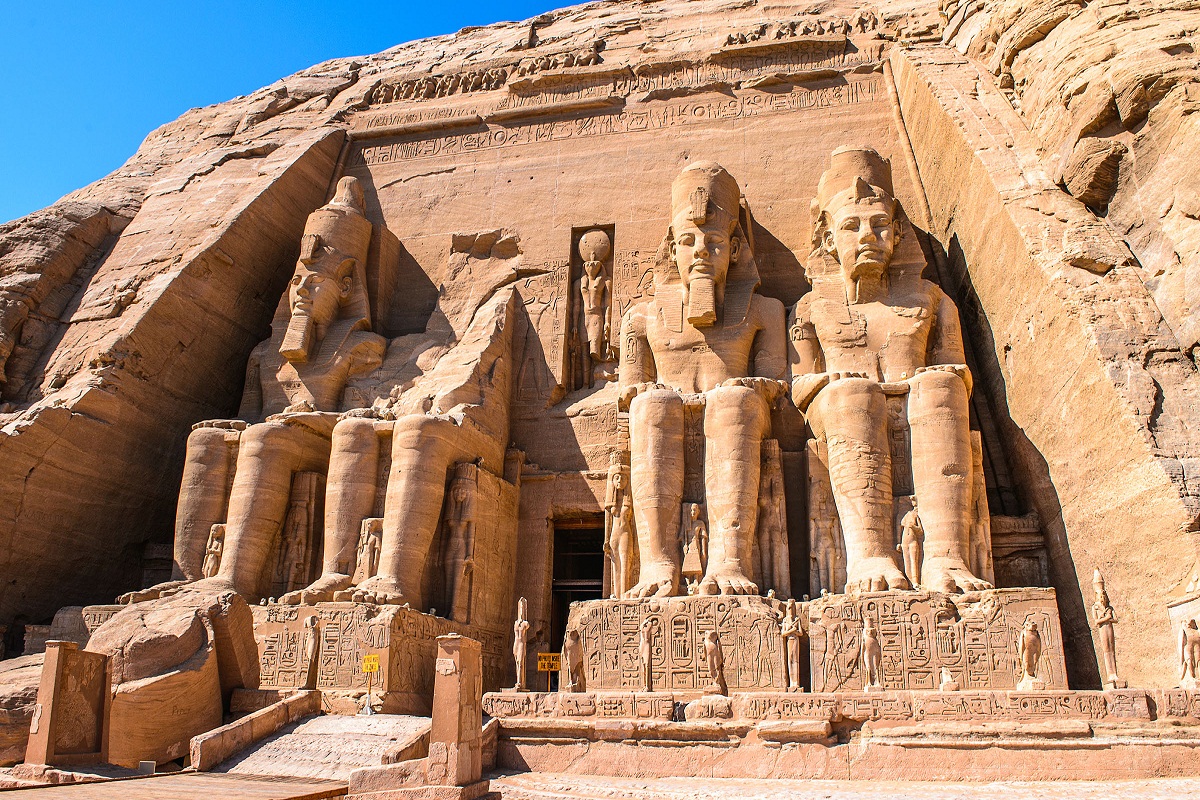
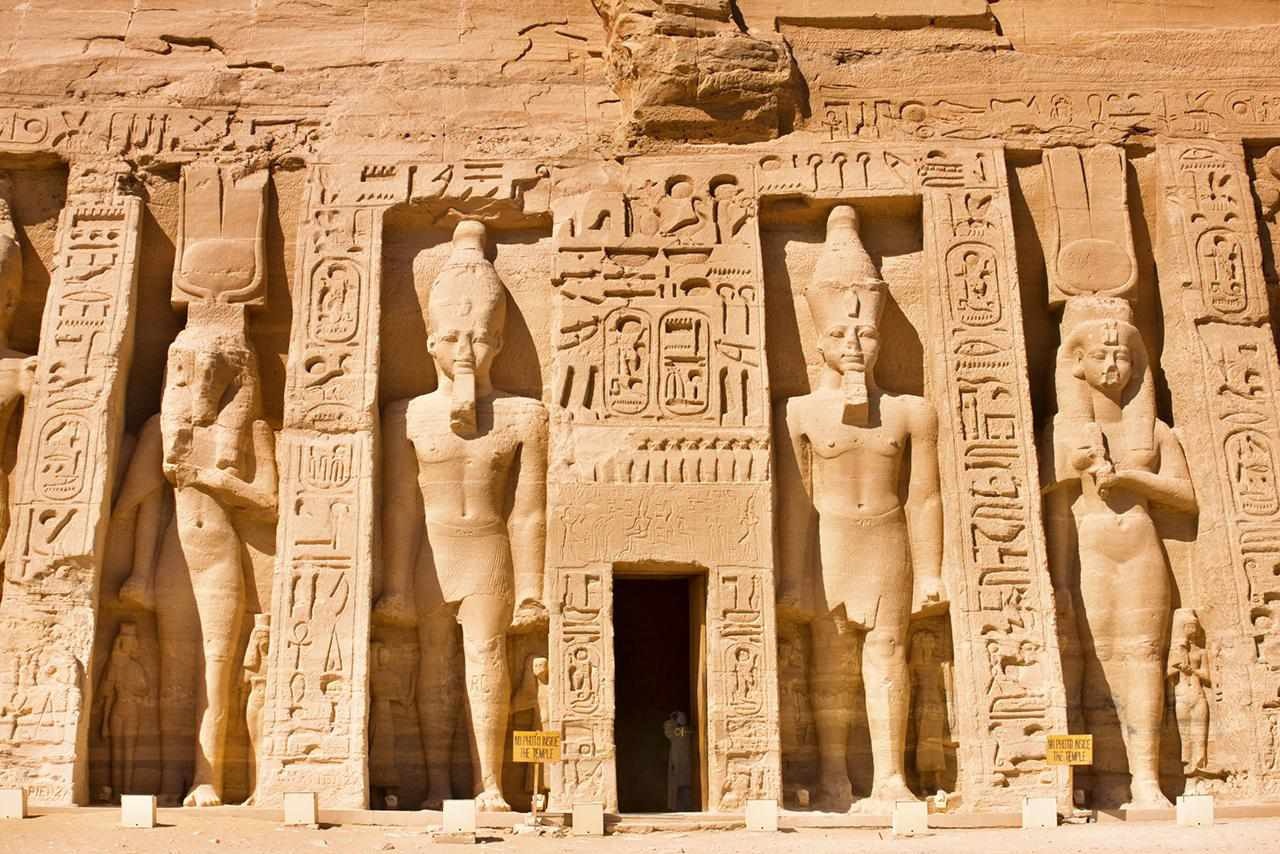
- Abu Simbel: two great temples (speos) of Ramses II, in southern Egypt, on the west bank of the Nile River.
- Abydos: temples of Sethy I and Ramses II. Place of veneration of the first pharaohs, with a large funerary complex.
- The Ramesseum, commemorative temple of Ramses II, next to the Theban necropolis; the main building was dedicated to the funerary cult.
- Medinet Habu: Ramses III memorial temple. Temple complex dating from the New Kingdom.
- Edfu: Ptolemaic temple located between Aswan and Luxor.
- Dendera: temple complex. The main building is the Temple of Hathor.
- Kom Ombo: temple of the region that controlled the trade routes from Nubia to Upper Egypt.
- File Island: temple of Isis (Ast), built in the Ptolemaic era.
Official Egyptian Rituals and Ceremonies: In the Egyptian civilization, due to its Egyptian religious beliefs, the state is obliged to carry out various official rituals and ceremonies that are carried out in the different Egyptian religious temples, since they must worship and offer offerings to the different Egyptian gods. Ceremonies are also performed for the pharaohs who have already died and are related to the gods and the so-called Egyptian divine monarchy.
Among the most important ceremonies and rituals, the coronation ceremony and the Thirst Party stand out, an official state party with the purpose of renewing the strength of the pharaoh that was held periodically during his empire.
During the year, several rituals were performed because the Egyptian religion made rites official throughout the country and several rites were performed in a single temple dedicated to a single Egyptian god, while there were rituals that were practiced daily. But there are ceremonies that were so particular that they were held once a year or on a special occasion.
A ritual that had to be performed at the beginning of the day was the well-known ceremony of offering and gratitude. This ceremony was practiced throughout the Egyptian territory. Where a priest of higher rank or the pharaoh had to wash the statue of some Egyptian god and anoint him with some cream as well as put on him a dress that was very elaborate and then give him a set of offerings.
At the end of the daily rite and the Egyptian god had already consumed his spiritual offering, all the remaining objects were taken to be distributed among the different priests of the temple.
In the Egyptian religion the rituals were in smaller quantity, while the festivals were several with dozens carried out in the year. The festivals were frequent and a set of actions had to be carried out that went beyond giving simple offerings of gratitude to any Egyptian god. Since many festivals had to recreate the scene of the Egyptian legend or myth.
In the same way they had to do some action to be able to eliminate the negative forces or those energies that fed the disorder and chaos in the Egyptian territory. Many of these festivals were led by the highest ranking priests and were held within the temple itself. But the festivals of greater religious relevance such as the so-called Opet festival. That took place in the city of Karnak, it was carried out carrying a procession and carrying the statue of the Egyptian God.
Some commoners who were strong believers in the Egyptian religion accompanied the procession to ask the deity in which they believed in order to resolve their present situation and thus receive some portions of the great offerings that were given to the Egyptian gods on these special occasions.
Animals that worshiped him: In many parts of the Egyptian territory, animals began to be worshiped since the Egyptians believed that they were manifestations of the Egyptian gods, a very particular belief in the Egyptian religion. These animals were selected for some specific targets and sacred marks that indicated the importance of their role in Egyptian society.
Many of these animals maintained this role throughout the Egyptian civilization. A clear example of this was the well-known Apis bull that was highly worshiped in the city of Memphis. This animal was a manifestation of the God Ptah.
While other animals worshiped him for a short time. But this belief of worshiping different animals increased in later times and many priests who ran the temples began to increase the stock of animals worshiped as a divine practice.
A practice that began to develop was in the XNUMXth dynasty when the Egyptians began to mummify any member of a species of animals in order to make a great offering to some Egyptian god, which is why millions of cats, birds and others were found. mummified animals that were buried in the different religious temples of Egypt to honor the gods.
The Oracles: In the Egyptian religion, the pharaohs and some members of the Egyptian society went to the Oracles to ask the different gods for more knowledge and guidance to make the best decisions. Although the Oracles began to be known from the Egyptian New Kingdom. Although they could have appeared much earlier according to some research carried out.
Many Egyptians, including the Pharaoh, went to the oracles to ask a series of questions and these answers were used to settle a legal mess or dispute over a situation. The most commonly used action to use Egyptian oracles was to pose some important question to the image of an Egyptian God and then interpret the answer.
Another method to interpret the answers of the Oracles was to interpret the movement of the animals to which they worshiped or make a query to the statue of some God and wait for the answer of a priest who was the one who spoke for the Egyptian god. This practice gave great influence to the priests in the Egyptian religion since they could interpret the message of the Egyptian gods.
Popular Egyptian Religion: Many of the Egyptian cults were focused on preserving the stability of the Egyptian civilization, so some individuals had their own religious practices that were related to their daily lives. Although this way of practicing the Egyptian religion left very little evidence than the official Egyptian religion because the Egyptian religion that left the most evidence was the richest Egyptian religion in the Egyptian territory.
In the religious practices that were carried out on a daily basis, they included some ceremonies where importance was given to the transitions of life. These were the births since the process of being born was very dangerous. Also the appointment since the name is an important part of the identity of the person.
One of the most important religious practices in the Egyptian popular religion were those that were surrounded by death or the so-called funerary practices because these were very prominent because they were going to ensure the survival of the soul of the deceased and his life after having crossed the most there.
Other practices used by the low-income population is seeking to discern the will of the gods for the people in order to seek self-knowledge. In this practice it was necessary to interpret dreams since they were seen as messages sent by the gods from the realm of the divine.
Many people, not having the possibility of entering the temples of the Egyptian gods, made prayers and gave private offerings to the gods. But this was only reflected as a type of piety that he performed in the Egyptian New Kingdom.
That is why the Egyptians began to use piety when they believed that the gods intervened directly in their prayers and lives to act on what they needed. In this way the Egyptian gods favored people who did good but punished people who did bad and saved people who were merciful to others.
Many of the Egyptian temples were very important for private prayers and offerings, even though more purposeful activities excluded lay people. Many of the practices that the Egyptians carried out were that they donated their goods to the Egyptian gods so that they would fulfill the prayers that the Egyptians made.
When the population could not enter the different temples to fulfill their religious obligations, that is why they began to build small chapels so that people could pray and give thanks for the favors granted.
Magic in Egyptian religion: Magic in the Egyptian religion and was known by the word Heka which meant "the ability to make things happen by indirect means" it was believed that magic was a natural phenomenon of the earth since it was the same energy that was used to the creation of the world and the cosmos.
Magic was the energy that the Egyptian gods used to exert their will and the Egyptians believed that they could also use it, but these practices were closely linked to the Egyptian religion. Although the regular rituals that were done on a daily basis were known as magic.
Also many of the Egyptians used magic for personal purposes even if they caused harm to third parties. That is why magic was considered as a hostile element by itself and its use against other people.
But for many Egyptians, magic was also considered a way to prevent harmful attacks from other people or to eliminate negative energies. But magic was related to the Egyptian priests as many of the books had many magic spells, so the Egyptian priests were scholars of those books.
Many of the priests had other jobs doing magical work as they were hired by lay people. In the same way, other professions in the Egyptian civilization dealt with magic as part of the work, especially the doctors and the so-called scorpion charmers and the artisans who were dedicated to making magical amulets for the Egyptian population.
There are also studies that the peasants made use of simple magic for their purposes since this knowledge was being transmitted orally but there is limited evidence of these studies carried out on simple magic in the Egyptian popular community.
Although it is said that language was closely linked to Egyptian magic to such a degree that the Egyptian God Tot, known as the God of Writing, was the one who invented magic. In this way magic was conceived as spoken or written incantations although they were frequently accompanied by rituals.
That is why the rituals that were performed had to invoke some Egyptian god so that the magic would have effects on the desired purposes. When magic was used, the practitioner was obliged to make use of an Egyptian mythological or religious character. These rituals also used empathetic magic using objects that were believed to have some power such as the magic wand or the different amulets used by the Egyptians.
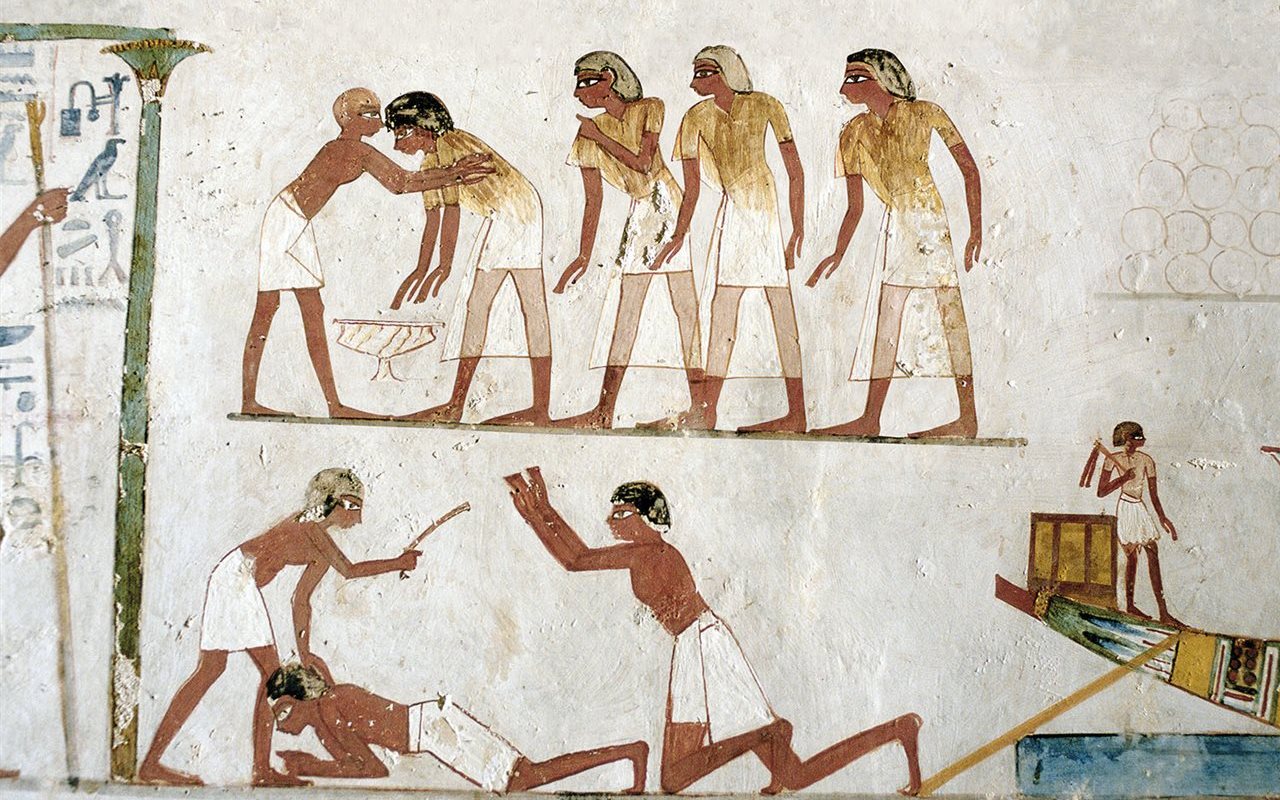
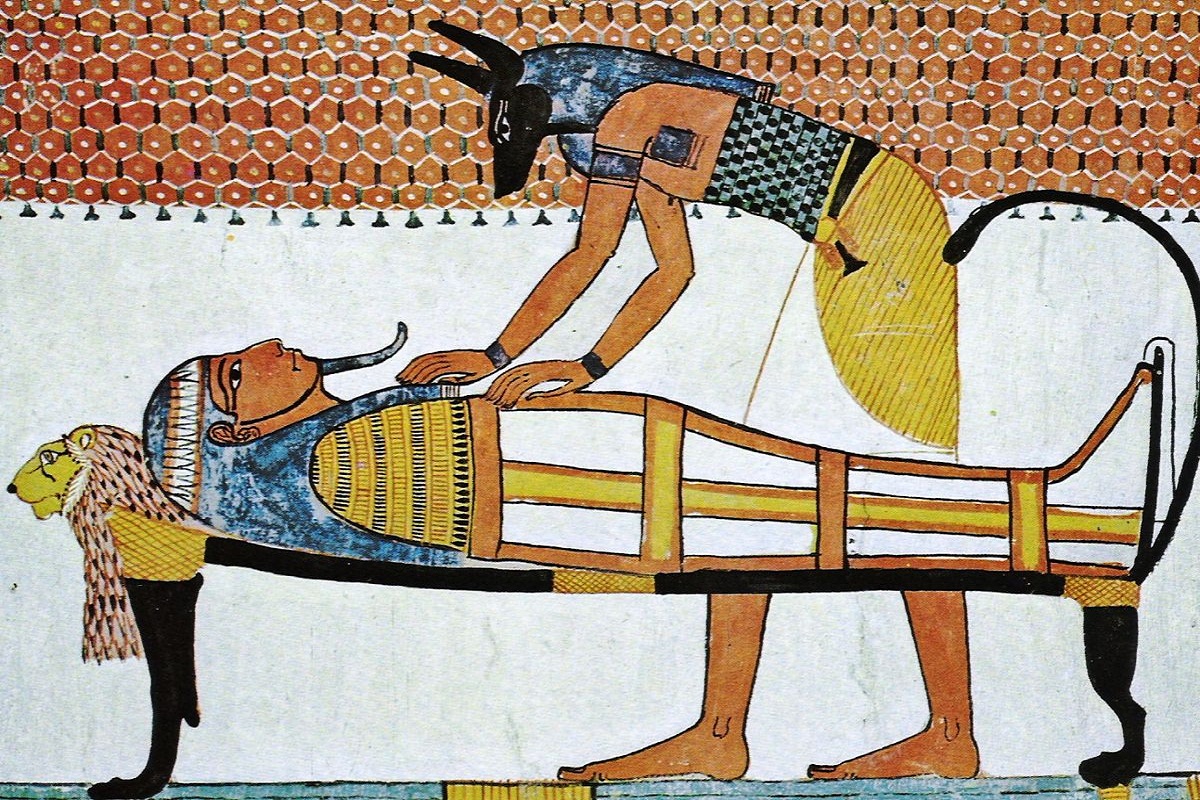
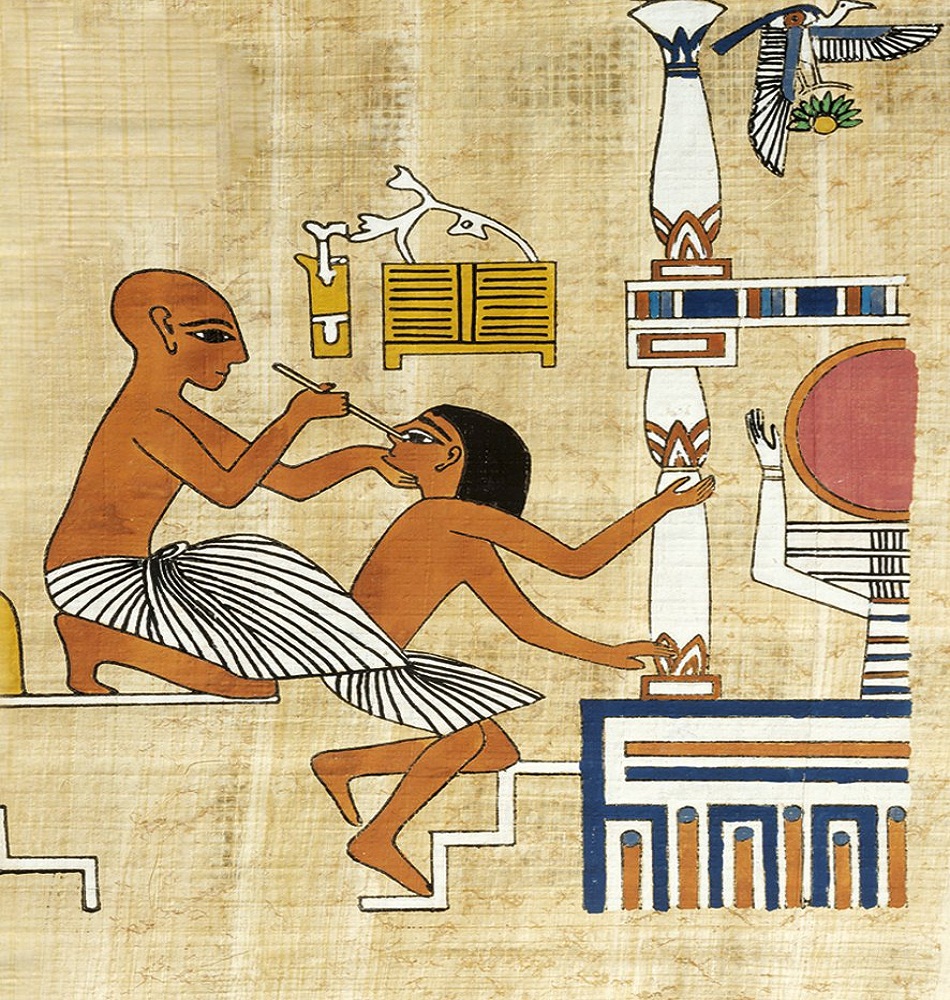
Religious Funeral Practices: These actions were necessary in the Egyptian religion since they were considered very important to give survival to the soul of the deceased. In addition to the preservation of the body, which was an important point in all Egyptian funerary practice. In the first funeral practices that were carried out, the Egyptians left the body of the deceased in the desert since the inclement weather mummified it by itself.
Then, in the period known as the Early Dynastic, tombs began to be used that had greater protection and isolated the body of the deceased from the drying effect of the desert sand but left it to natural decay.
Therefore, the Egyptians began to carry out studies to embalm the corpse and carry out an artificial drying to leave it wrapped and placed in a coffin. The quality of the mummification work depended on the cost and people who could not afford the mummification were buried in desert graves.
When the mummification process of the deceased was carried out, the body was transferred to his house in order to carry out a procession and bury him in a tomb, but he would be watched in the company of family and friends. In addition, several priests attended to offer prayers to the soul.
One of the rituals that the priests had to perform is the well-known opening of the mouth, where they would restore to the deceased the senses that a dead person should have in order to have the abilities of a dead person. After that the mummy was buried in the tomb and proceeded to seal it.
Characteristics of the Egyptian Religion
Being one of the oldest religions in the world and that was practiced for more than 3000 thousand years, it was a religion in which they worshiped various gods and had to worship him. In the Egyptian religion the gods were zoomorphic since they were represented with human bodies and with the head of some animal.
Similarly, in the Egyptian religion, certain animals were considered sacred, such as the cat, the scorpion, the snake, the lion, the falcon, the cow, the bull, the crocodile and the ibis, as well as many others. It is important to note that until they made mummies of the animals that they buried with their owners.
The figure that they had in the Egyptian religion closest to the Egyptian gods was the pharaoh who had the same authority as a king, since according to beliefs he would have blood from the different Egyptian gods. When he died, he was a divine heir of the gods since his mandate lasted a lifetime and beyond death. Among the main characteristics of the Egyptian religion we have:
Polyethist: The Egyptians had a firm belief that there were infinities of gods, each one with some power of nature, that is why they related them to different animals, these gods had the head of the animal and the body of a human. The Egyptian gods intervened in the daily life of every Egyptian.
Offerings: With the beliefs that the Egyptians had, they gave offerings to the different Egyptian gods to keep them happy and not unleash their anger since they caused calamities and many deaths.
Amulets: In the Egyptian religion it was a custom to use amulets from the high hierarchs who were the pharaohs and even the humblest people of the Egyptian civilization in order to eliminate negative energies and have good luck in the actions they perform.
These amulets were designed in stone and contained precious jewels that were worn around the neck and down to the chest of the person. It was also worn on the wrists and ankles.
Cults: In the Egyptian civilization, a place that was had to worship the gods were the temples that were also known as the house of the gods, they were built with large limestone so that they would not be destroyed over time.
Inside the temples there were several rooms intended to bury the bodies of the pharaohs, there was also a large room to worship a particular god and secret passageways that have not yet been deciphered why they were made.
Mummification: As the Egyptians believed that there was life after death, that is why they mummified the bodies of the deceased. This process consisted of removing all the organs of the human body that were placed in a sack called canopies.
The body was then placed on a table to be wrapped in silk cloth to preserve the body and prevent the body from rotting so that it would be ready to meet the soul in the realm of the dead.
If you have found this article on the Egyptian religion important, I invite you to visit the following links: