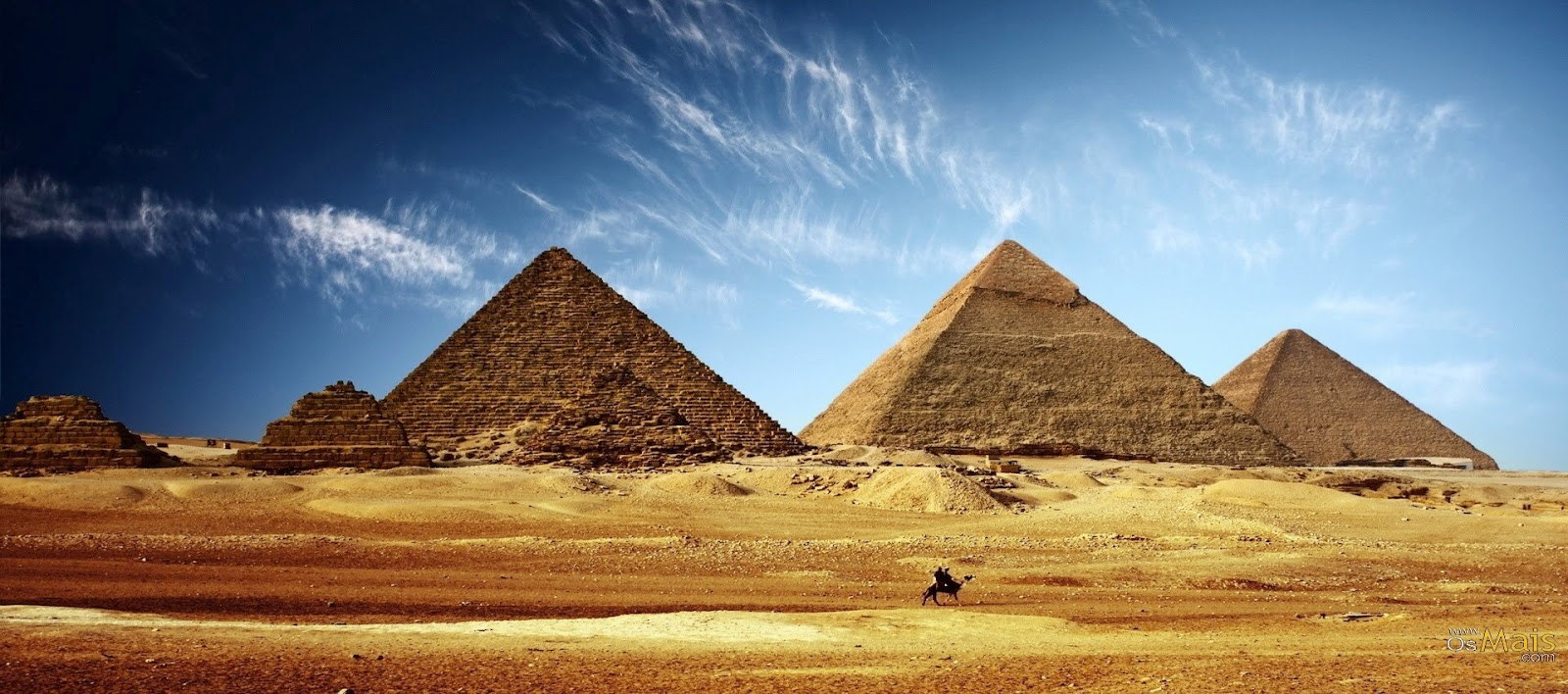
With a history developed on the banks of the Nile River through thousands of years, full of hieroglyphs, pyramids, sphinxes, pharaohs, wars, uprisings and betrayals, the peculiar Characteristics of Egyptian culture fascinate with their mysterious beauty and complexity. Do not miss this interesting article!

Characteristics of Egyptian culture
The civilization of Ancient Egypt, which arose around four thousand years before Christ, was one of the oldest in the world. Favorable natural conditions contributed to the early development of culture and art in Ancient Egypt. At this time, the Egyptians knew how to make fine jewelry from precious metals, writing appeared, and scientific knowledge gradually began to accumulate.
The characteristics of Egyptian culture are so unique that Egypt left a huge cultural heritage to the world civilization, works of its art were exported to different parts of the world in ancient times and widely copied by masters from other countries.
history of egyptian culture
There are three main sources of knowledge about the characteristics of Egyptian culture: texts written by Greek writers, the Bible and other Jewish religious books written since the XNUMXth century BC, and the most important sources which are documents, inscriptions, and objects directly from Ancient Egypt.
Due to the lack of a source base today, one cannot be one hundred percent sure of the absolute dates of this or that event in history. Most of the facts can only be narrated. So, the beginning of the ancient Egyptian civilization is the beginning of the early dynastic period, which occurred, according to modern Egyptologists, in the fourth millennium BC.
The end of classical Egypt is known with certainty: it is 31 BC. C., when the last Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, Caesarion, ended the reign and Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire.
The history of Ancient Egypt is usually divided into several stages. Modern Egyptology in the history of Egypt reveals that:
prehistoric egypt
It is a period in the history of Egypt from the appearance of man to the formation of the Egyptian agricultural civilization.
Predynastic period (XNUMXth-XNUMXth millennium BC)
The period of the final decomposition of tribal relations, the formation of a socially differentiated society and the emergence of the first slave states of ancient Egypt.
early kingdom
It is the first dynastic period in the history of the ancient Egyptian state, the period of the reign of the I and II dynasties of the pharaohs. It lasted from 3120 to 2649 BC
the ancient kingdom
It is the period that covers the reign of the pharaohs of the III-VI dynasties. At this time, a strong centralized state was formed in Egypt, there was an economic, political-military and cultural flourishing of the country
First transition period
During the reign of the VII and VIII dynasties, the power of the pharaohs of Memphis was only nominal, political anarchy reigned in Egypt. Power passed into the hands of monarchs.
middle kingdom
It is the era between 2040 and 1783 (or 1640) BC. C., which explains the reign of the dynasties of the pharaohs Manetho XI – XII, originating from Thebes. Moment of a new emergence, but with relatively weak centralization of the ancient Egyptian state.
Second transition period
After the fall of the XNUMXth dynasty, Egypt crumbles into independent nomes.
new kingdom
It is the era of greatest flourishing of the ancient Egyptian state, known for the largest number of monuments, which are the basis of the entire heritage of the civilization of the pharaohs, whose subjects made up 20% of the world population. This is the period of the reign of three important dynasties: XVIII, XIX, XX.
The third transition period
The division of Egypt led to the disintegration of a single real economy, the basis of state centralization.
Late Period or Late Kingdom
It covers the reign of the pharaohs of the XXVI-XXX dynasties (664 – 332 BC). This is a period of struggle for the restoration of independence from Egypt, strong wars and foreign invasions, which ended with the conquest of the country by the Persian Empire and then by Alexander the Great.
Ptolemaic period
The Ptolemaic period or Hellenism is a period in the history of the Mediterranean, mainly the eastern one, which extends from the death of Alexander the Great (323 BC) until the definitive establishment of Roman rule in these territories, which is usually dated from the fall of Hellenistic Egypt. , headed by the Ptolemaic dynasty (30 BC).
language and writing
Scientists know the ancient Egyptian language from the large number of preserved inscriptions of hieroglyphic writing, made on stone and papyrus. The Egyptian language is one of the oldest languages in the world that had a written language; the earliest surviving ancient texts date back to the turn of the fourth and third millennia BC.
From this period, Egyptian writing had both signs representing words and signs denoting combinations of consonants, in addition, alphabetic signs for single consonants and generalized determiners, pictorially hinting to which circle of concepts the word belongs. Accountants use huge amounts: ten thousand, a hundred thousand and even a million, for which they had their own words and signs. The writing of the Egyptians was divided into several types:
Hieroglyphs
It is a figurative writing supplemented with phonetic signs, that is, it combines elements of ideographic, syllabic and phonetic letters. Hieroglyphs used to be carved in stone, there are also linear hieroglyphs for wooden sarcophagi and papyrus.
hieratics
This is an early form of cursive writing, which arose during the XNUMXst Dynasty when hieroglyphic characters were applied with a brush to papyrus, stone, or leather, as a result of which the characters received a more rounded cursive shape.
demotics
It is a type of simplified cursive writing. Signs were written horizontally from right to left, from even more simplified signs, sometimes continuous.
ancient egyptian literature
Literature is one of the characteristics of Egyptian culture, written from the pharaonic period of Ancient Egypt to the end of Roman rule, along with Sumerian literature, it is considered the world's first literature. For three thousand years, the Egyptians have created a rich fiction, developed its various genres.
In the Old Kingdom period (XNUMXth to XNUMXnd centuries BC), literary creativity included funerary texts, letters, religious hymns and poems, and memorable autobiographical texts recounting the careers of prominent nobles. Only in the early Middle Kingdom (XNUMXst to XNUMXth centuries BC) was narrative literature created. It was a 'revolution', which, according to RB Parkinson, was brought about by the rise of the intellectual class of scribes, a new sense of cultural identity, very high levels of literacy, and easier access to written material.
Fine arts
For more than 3500 years, artists have adhered to forms and canons that developed during the time of the Old Kingdom, following a strict set of principles that persist even during periods of foreign influence and internal change.
One of the characteristics of Egyptian culture is that these artistic standards are expressed in simple lines, shapes, a characteristic flat projection of figures, without specifying spatial depth, which created a sense of order and balance in the composition.
Images and text were closely intertwined on tomb and temple walls, stelae, and statues. The paints were obtained from minerals such as iron ore (red and yellow ochre), copper ores (blue and green), soot or charcoal (black), and limestone (white). They could be mixed with gum arabic to determine viscosity and broken into pieces that can be moistened with water if necessary.
Painting
In Ancient Egypt, all reliefs were brightly colored, the least of all images were in palaces, temples and tombs, there were drawings only on the surface. Many of the pictorial manifestations of ancient Egypt have survived thanks to the arid climate. The stone surface was prepared for painting, a thick layer of earth with a softer layer of plaster on top, then limestone, and the paint lay flat. The construction pigments were normally minerals to protect the images from sunlight.
The composition of the paint was heterogeneous: egg tempera, various viscous substances and resins. Ultimately, the fresco mural was never produced or used. Instead, paint was used on a layer of dry plaster, a so-called mural al seco. Above the painting was covered with a layer of varnish or resin to preserve the image for a long time.
The small images made with this technique are well preserved, although they are practically not found on large statues. Most often, using similar methods, small statues were painted, especially wooden ones.
Sculpture
Ancient Egyptian sculpture is one of the most distinctive and strictly canonically developed areas of Egyptian culture features. The sculpture was created and developed to represent the ancient Egyptian gods, pharaohs, kings and queens in physical form. Statues of gods and pharaohs were placed in public view, as a rule, in open spaces and outside temples. Statues generally retain the original shape of the block or piece of wood from which they were carved.
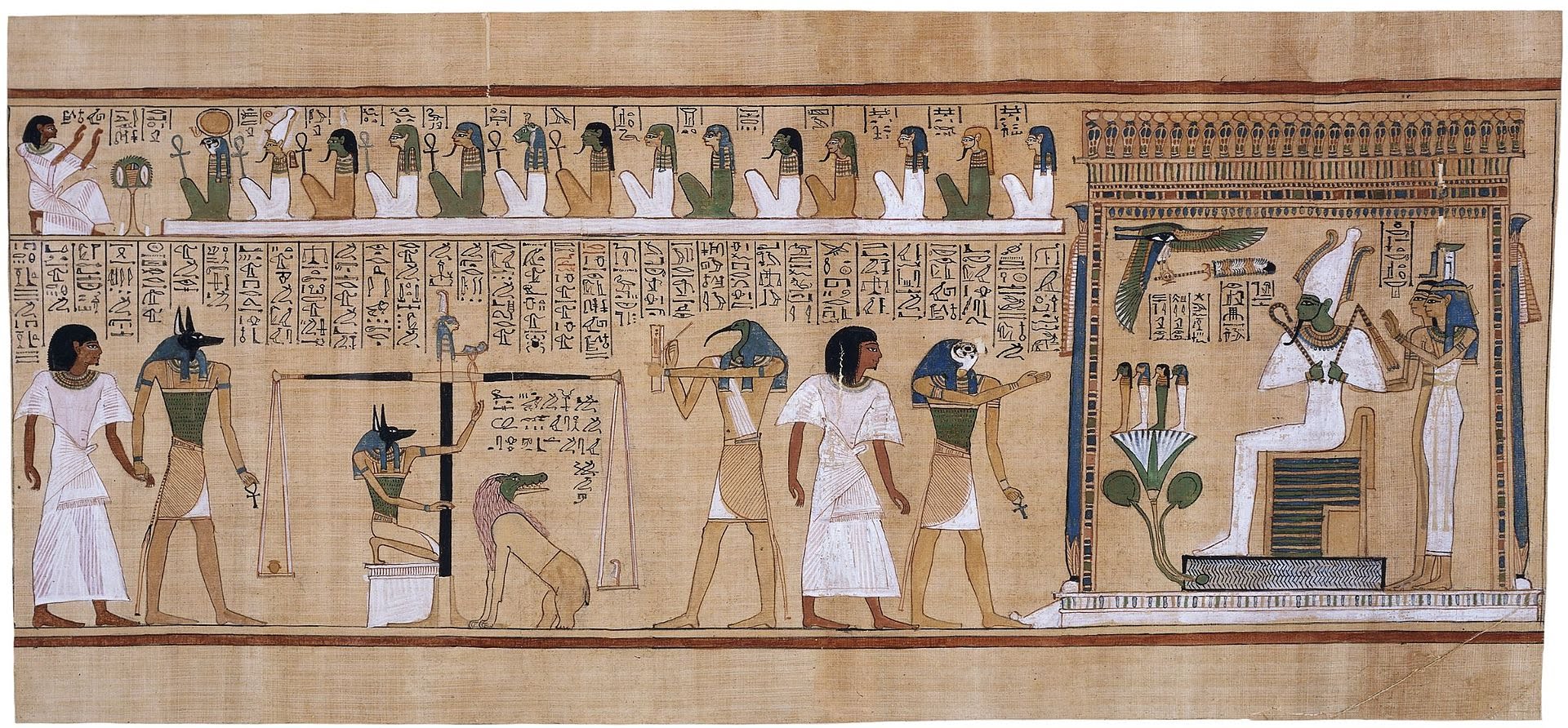
religion and mythology
In ancient Egypt, there was no common religion, but rather a wide variety of local cults dedicated to certain deities. Most of them were monotheistic in nature (focusing on the worship of one deity and acknowledging others), which is why the Egyptian religion is considered polytheistic.
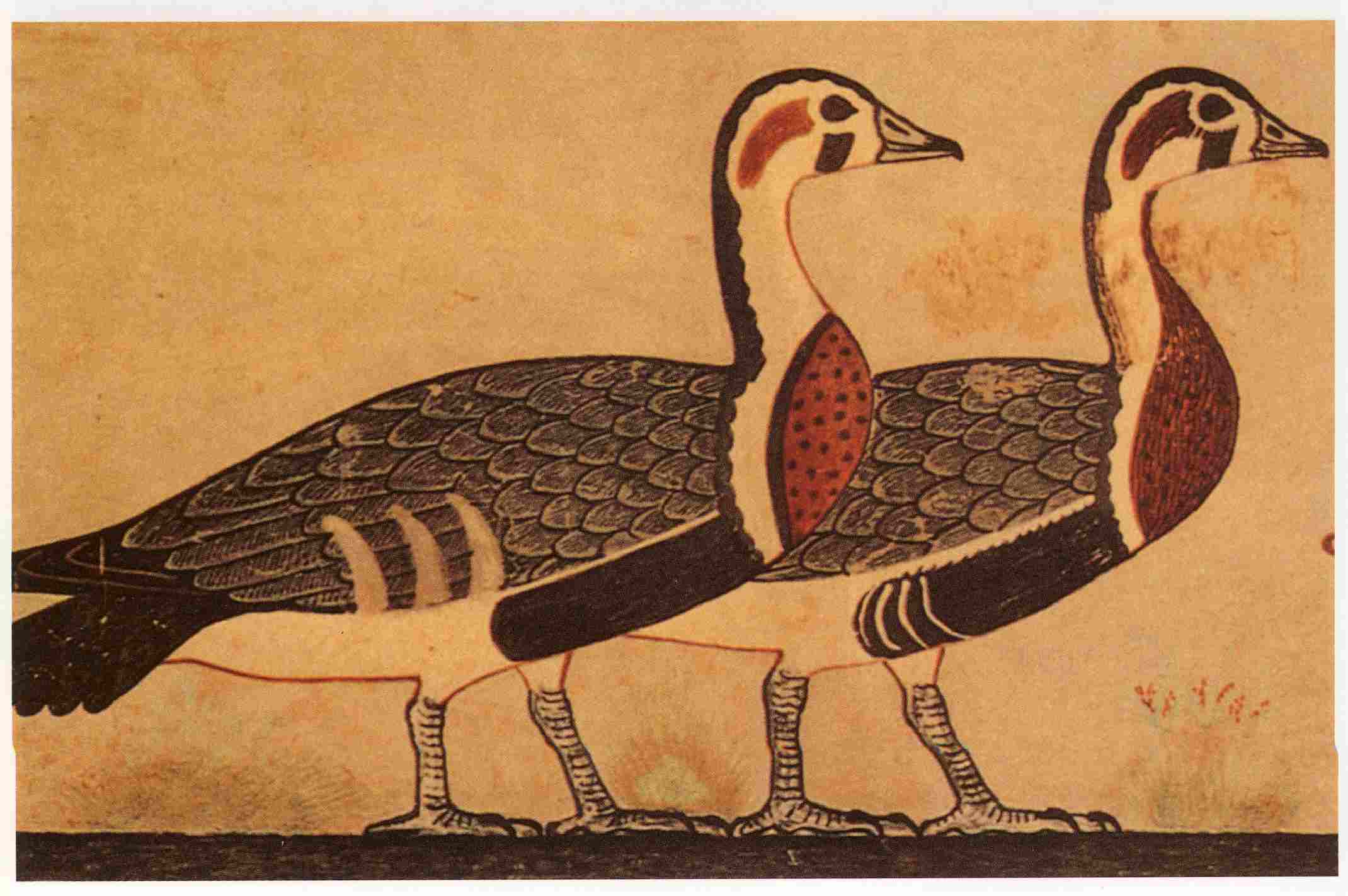
The deities worshiped in various localities personify natural forces and social phenomena. The sky was represented by a woman or a cow, the earth and the air - by male deities. God Thoth was the patron saint of writing and witchcraft, and the goddess Maat personified truth. Natural phenomena were perceived as the relationship of various deities. Some gods in ancient times were worshiped by the Egyptians in the form of animals or birds.
The Egyptians associated the Horus Falcon with the idea of a powerful heavenly deity. The falcon was depicted in tribal standards, it is also shown bringing Narmer victory over Lower Egypt. After the formation of the state, Horus acts as the constant patron of the pharaohs.
The fusion of the cult of Horus with that of the king was also facilitated by the fact that with the development of the cult of Osiris as the deceased pharaoh. In different periods, the most revered were the deities of Ra and then Amun, Osiris, Isis, Set, Ptah, Anubis were identified with him.
In the fourteenth century BC, Pharaoh Amenhotep IV (Akhenaten) carried out important religious reforms, he was the one who introduced the cult of Aton. Akhenaten practiced a single cult (henotheism) of Aten not because he did not believe in the existence of other gods, but because he refrained from worshiping any god except Aten. Akhenaten's reform was not only religious, but also cultural, comprehensive. After his death, Amun once again became the supreme deity of the cult.
Daily life
The main diet consisted of bread and beer and is supplemented with vegetables such as onions and garlic and fruits such as dates and figs. On feast days wine and meat were served. There were many varieties of bread and buns, differing in flour, shape, degree of baking and additives in the dough, for which honey, milk, fruits, eggs, fat, butter, dates, etc. were used. Dairy products were known: cream, butter, cottage cheese. The Egyptians used honey or carob as sweeteners for drinks and foods.
The Egyptians placed great emphasis on appearance and personal hygiene. They washed themselves with river water using animal fat soap paste and chalk. To maintain cleanliness, men shaved their entire bodies and used perfumes to combat unpleasant odors and ointments to soothe the skin.
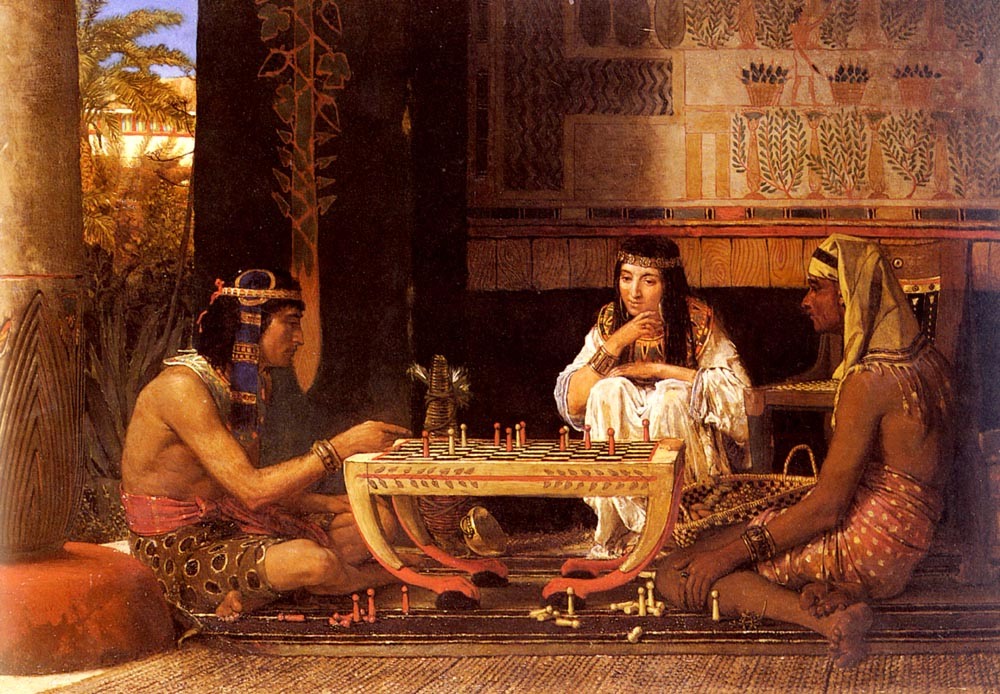
Scientists know that the inhabitants of Ancient Egypt loved to play board games, but their rules did not survive. Play equipment was made from various types of wood along with other materials. Various toys, ball games, and juggling were popular with children, and evidence of the popularity of wrestling was also found. Wealthy people practiced hunting (including the use of specially trained dogs) and navigation.
The musical instruments of ancient Egypt were the harp and the flute. During the New Kingdom period, the Egyptians played bells, tambourines, drums, and lyres imported from Asia. The wealthy hosted receptions with professional musicians.
Legacy
Ancient Egypt has left a huge legacy of world civilization, its works of art in ancient times were exported to various parts of the world and widely copied by craftsmen from other countries. Egyptian culture greatly influenced the ancient Romans. The cult of the goddess Isis was widespread in Rome. Egyptian sculptural portraiture, landscape painting, obelisks and other elements of architecture, lions and sphinxes were perceived by ancient art, and through it by European art.
The culture and civilization of ancient Egypt laid the foundation for the subsequent cultural development of many peoples. Peculiar architectural forms: majestic pyramids, temples, palaces and obelisks, have inspired the imagination of travelers and explorers for many centuries. Egyptian masters created beautiful wall paintings and statues, mastered glass and earthenware production methods, poets and writers created new forms in literature.
Among the scientific achievements of the ancient Egyptians are the creation of an original writing system, mathematics, practical medicine, astronomical observations, and the calendar that arose on its basis. The interest in the monuments, artifacts and archaeological excavations in Ancient Egypt, which arose at the end of the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries, led to the creation of the science of Egyptology and the emergence of certain trends in fashion.
Here are some links of interest: