From ancient Greece to the present day, the Western culture, with the ups and downs of its long journey, it has been based primarily on the principles of freedom, equality, justice, always setting the happiness and well-being of human beings as its fundamental objective.
Western culture
Western culture is the human environment as a result of Western-specific history, institutions, organizations, standards, laws, customs, and values. Between the XNUMXth and XNUMXth century, the colonization, imperialism and economic hegemony of Western countries allowed the exportation of various aspects of the Western way of life in all continents, this phenomenon is called Westernization.
Western culture is based on the ideas of ancient Greek society, ancient Roman culture, and Western Christianity (Catholicism and Protestantism), the synthesis of which is reinforced by Enlightenment writers in the XNUMXth century.
Its fundamental values are freedom, equality, justice, the right to happiness and progress. Western society is based on the principles of individualism, a structuring concept in which individual freedom is considered a right that institutions must protect. Individual freedom structures the economic sector, in particular through the freedom to conduct business and the protection of private property.
In the Western view, religious institutions are separate from political institutions, this principle is called secularism depending on the country in question. Political power is in the hands of individuals, called citizens, according to the heritage of Athenian democracy, it is exercised within the framework of the rule of law, according to the heritage of Roman law.
Religious or philosophical practices are part of individual freedoms and the State is the guarantor of people's freedom to believe or not believe. More generally, freedom of conscience, which includes freedom of religion, is guaranteed by the state and the individual is free to express his or her views on any religious, philosophical, or political ideology. This freedom is called freedom of expression.

Western family organization is based on the nuclear family model, inherited directly from Roman society in which the monogamous couple was at the base of the family structure. Depending on the period, this monogamous couple may have been exclusively heterosexual (medieval period) or both homosexual and heterosexual (ancient Rome, contemporary period).
The West has been draining migration flows since Roman times, this situation has intensified since the 1960s leading to an increase in cultural diversity. The situation of ethnic, racial and sexual minorities and the status of men and women have been in constant evolution since the mid-XNUMXth century with a growing egalitarian trend.
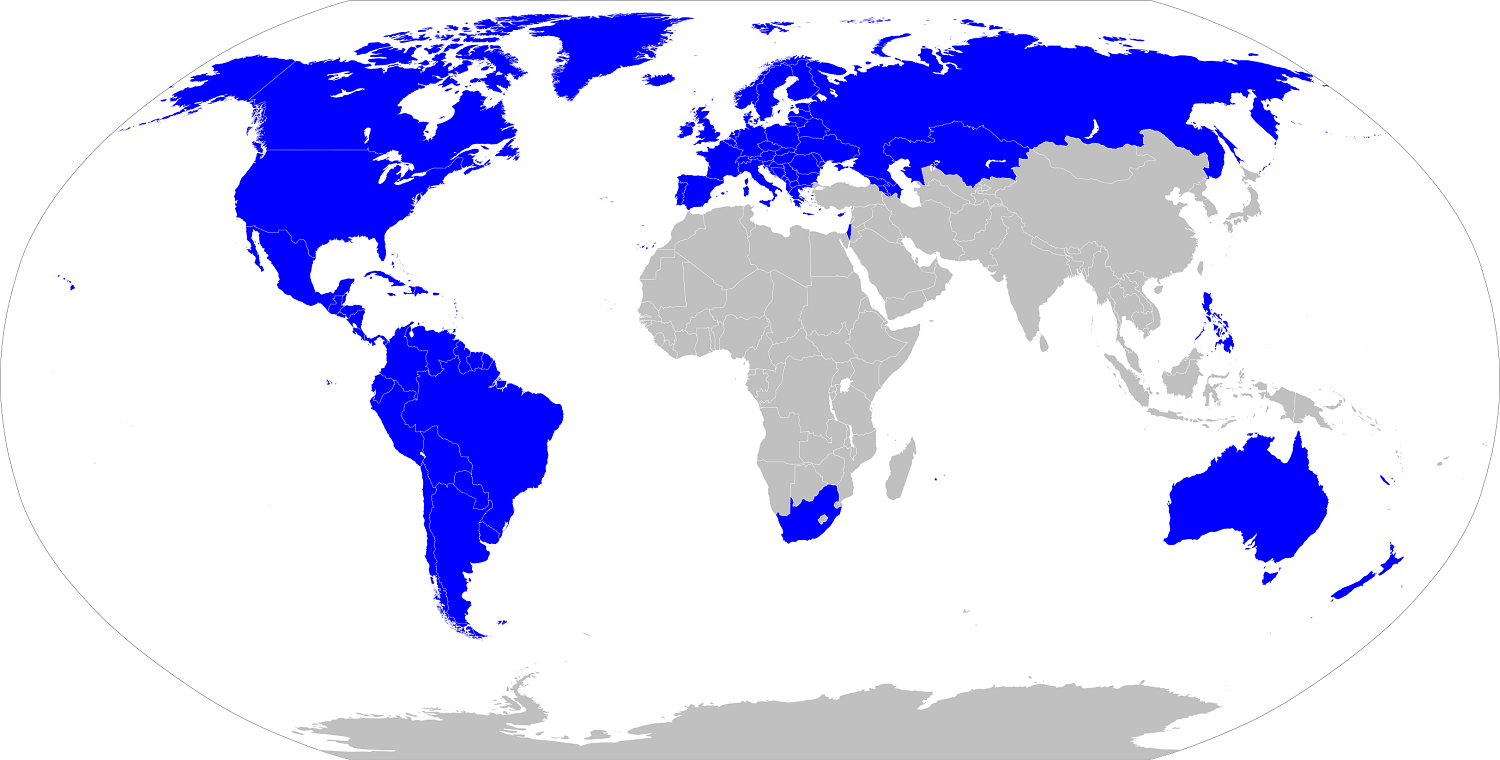
Geographical distribution
Originating in Western Europe, Western culture had spread across several continents through colonization and at the beginning of the XNUMXst century there is a mosaic of societies that have adopted parts of Western culture while maintaining profound differences, especially in religion, values, customs and culture.
Western society is found in former colonies such as the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, most of Latin America, and South Africa. It is also found in the Balkan region mixed with Orthodox and Islamic societies and influences Japanese society.
Although Russia has adopted the philosophy of the Enlightenment in the XNUMXth century under the influence of Peter the Great, the Western character of the culture of this country is controversial. The Slavophile tendency is to consider Soviet culture as a special case for historical reasons, while the Westernist tendency maintains that there is no significant difference between Russian culture and Western culture.
The historical peculiarities of Russia are its role as the engine of the Orthodox Christian Church and the communist political regime from the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917 until the fall of the USSR in 1991.
Colonization
Between the fourteenth and eighteenth centuries England, Spain, Portugal, France, Belgium, Holland, Italy and Germany have colonized the different regions of the world, especially America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia and Oceania. The colonizers arrived in the territory and sought to dominate the indigenous populations, to obtain political, economic and cultural control, often by force, in an illegitimate or deceitful manner. Later, the colonizers banned indigenous religions, customs and languages, and imposed Western values and customs.
The colonizers used Western values, science, history, geography, and culture as a basis of comparison to learn about the populations of the colonized countries and their people. These values, inculcated in schools, governments, and the media, became a way for the colonized to become self-aware. And these values and this way of seeing the world, much more difficult to overthrow than a government, remained after decolonization.
In some colonized regions of the Anglo-Saxon world, notably the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa, the descendants of colonizers, immigrants, and slaves found themselves outnumbered by indigenous populations, who were later marginalized.
In these societies where the colonizers brought their language, their culture and their laws, the local population developed their own economic and political structures and developed an identity based on the coexistence of various cultures and miscegenation. So this identity had the objective of obtaining, sometimes by force, independence from the colonizing country.
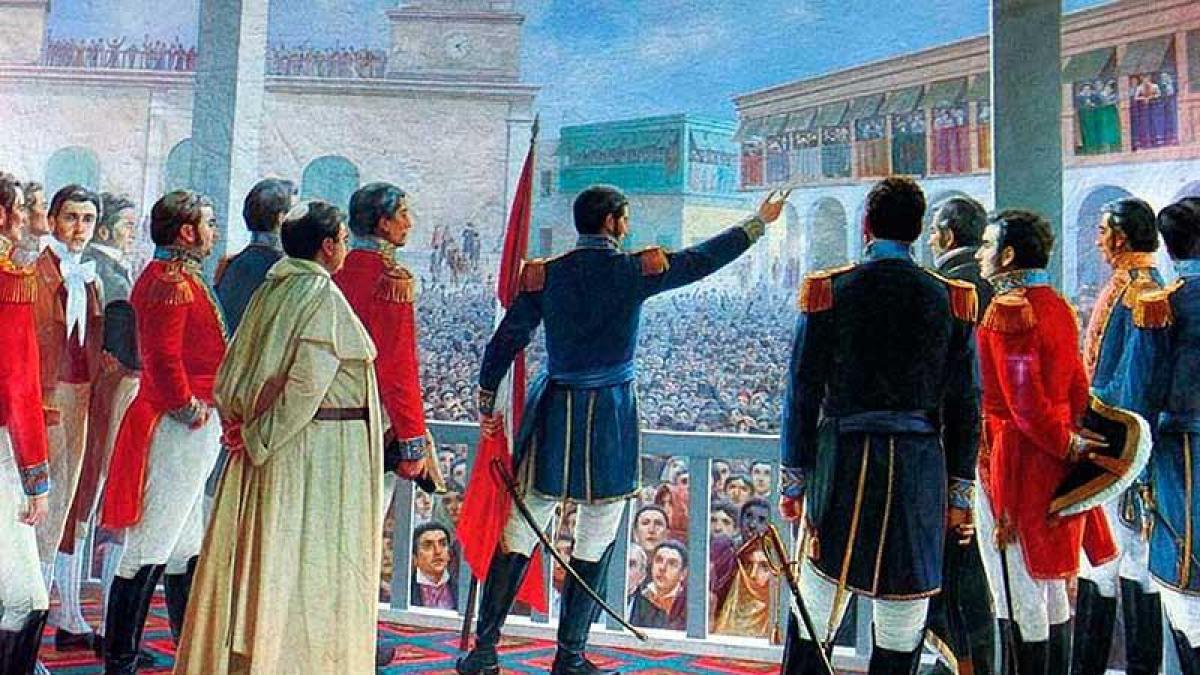

The United States is a nation created by forcibly gaining independence from colonial society in the late 1901th century. The colonial societies of South America achieved independence in the 136th century and Australia in 1760. As a result of the colonization and independence process, there are 86 colonized territories in 1830, 167 in 1938, 33 in 1995 and XNUMX in XNUMX.
Since the end of World War II, the colonizing countries have focused on their activities within their own country, rather than activities outside the colonized territories. As they ceased to be of capital importance to their economy, many colonized territories were returned to the local population.
Left to their own devices, the often very poor former colonies had to build a strong and reliable government while struggling with corruption and instability. Several countries failed in this mission, resulting in a civil war: Cambodia, Afghanistan, Nigeria, Congo and Burma.
foundations of western culture
Western culture is materialistic and hedonistic, especially when it comes to happiness and personal well-being. Its foundations are secularization, capitalism, the free market and modernity. Western culture emphasizes individualism, economic liberalism, and marginalizes the impact of religion on the state and in the public sphere. Leaving the past for the future is a central dynamic in Western culture, and freedom is seen as something everyone is entitled to.
The values and political institutions of XNUMXst century Western culture are inherited from the ideas launched by XNUMXth century writers. Writers who have promoted a democratic, liberal, secular, rational, equitable and humanistic society whose fundamental values are freedom, equality, justice, happiness and progress.

The capitalist economic system, focuses on the search for profit (accumulation of capital) and private enterprise, exists in Western Europe since the fourteenth century, the doctrine of liberalism states that the freedom to exercise capitalism allows it to be more efficient.
Rationalism grants sovereignty to the knowledge acquired through reasoning, for the benefit of the dogmas and a priori. According to the XNUMXth century philosophers “In a rational society everything seems simple, coordinated, uniform and fair; society is based on simple and elementary rules drawn from reason and natural laws”.
Humanism is a reflexive anthropocentrism that emphasizes the human and a vision of the world in which the human has the possibility of being realized by the only forces of nature. In the sixteenth century, humanism paves the way for a renewal of ways of knowing, a reform of education and liberating traditions.
Hedonism, on the other hand, is a doctrine that emphasizes leisure and encourages citizens to enjoy pleasures. Hedonism highlights the leisure of the Roman Empire, that privileged period of time that the rich Romans had, where they could practice leisure activities, entertainment and personal development. In particular games, shows, body treatments, meals and parties.
Secularization is a process of liberation, in which the individual acquires a certain autonomy from religion, takes his destiny in hand and obtains the right to think, to judge independently of the religious. A secular society is independent of the political, moral and scientific and develops its own laws instead of being governed by sacred laws.

In a democratic political regime, the State, bearer of political power, is an instrument of mediation at the service of the population. The individual has a central place and it is he who manages his individual and collective destiny.
The structure of Western culture is marked by modernization, which implies industrialization, urbanization, increased use of schools and media, economic growth, mobility, cultural transformations, political and economic development, social mobilization, integration, and transformation of international relations. . This structure was shaped by the reformation, national revolutions, the industrial revolution, and the cold war.
Modernity
In Western culture, future plans are a central dynamic of society. Society is oriented towards rational and deterministic control of the natural and social environment and each individual is an engine of this process. Being modern is knowing that the destiny of everything is to end up outdated.
Modernity is associated with the notion of progress: from the past to the future, in a process of constant change. Modernity offers the hope of progress, civilization and emancipation and is inseparable from nostalgia, rootlessness, fragmentation and uncertainty. Inheritance of the Enlightenment, the responsibility to advance towards a better future goes hand in hand with human nature considered eternal and absolute.
Certain cultural or technological products are commonly called modern: movies, planes, buildings. These objects, recognized as bearers of modernity, suggest that modernity is more of a cultural fact than a period in history.

Modernization is a pillar of Western culture. The Industrial Revolution not only shaped but accelerated modernization in close collaboration with Western ideology, economic, political and financial systems. The globalization of the economy is marked by a technical-economic interdependence that places information as the most precious asset.
At the dawn of the XNUMXst century, the values of progress have never been stronger, and the prospect of the future is a fascinating subject. At the same time, social and economic problems such as overpopulation, the depletion of natural resources and the deterioration of the natural environment are emerging and all have their roots in the advancement of science and technology.
Human beings, whether wise, greedy or violent, find themselves at the controls of machines that enhance their capabilities and allow nature to be molded according to their expectations and their image.
Appeared in the mid-twentieth century, computers have changed Western society. These machines are used in companies, scientific circles, public administration and many families. Many companies claim to have become dependent on these machines which are also used in scientific circles to accelerate research and progress.
Freedom
Freedom is a strong value in Western culture and the word is used as a slogan in political and economic discourse. In the West, freedom is seen as something natural, something that every human being seeks, simply because he is human.
Comparatively, outside the West, freedom is a value far from being desirable, compared to other values of much greater importance such as honor, glory, piety or harmony with nature. So much so that the word freedom does not exist in some languages. In Japanese and Korean languages, the word freedom is borrowed from Chinese and has the pejorative meaning of lack of rules and avoidance.

In Western culture, there is widespread agreement about the value of freedom, but much disagreement about its definition, which revolves around personal freedoms, sovereignty, and civil rights:
Individual freedom is that everyone can do what they want without being hampered or restricted by others as long as they stay within limits where no one bothers to do the same.
The sovereignty of a people or a nation is that the people can do what its members want, regardless of the wishes of other people.
Civil law is the freedom of every person to participate in the exercise of the political life of the nation. Civil law requires adequate political institutions, the most common being democracy.
Democracia
Democratic political regimes in Western Europe are based on a competition of political parties: communities that carry out political actions to promote their own interests. The parties seek to obtain the support of the population that allows them to recruit members for the national assembly, the collective that exercises power in common with other institutions.
All Western European countries use political parties as intermediaries between the people and the government. The personalities recruited by the parties, responsible for national political decisions, have a great impact on society.
Even small countries like Switzerland go through intermediaries. The political regime of this country allows the inhabitants to make political decisions without going through the parties, however such a procedure is too cumbersome to be used for all government decisions.

In the mass politics of Western Europe, political parties are pitted against the secret opinions of each universal suffrage voter. The differences of opinion are noted by the votes and are at the origin of the political organization of the nation.
Economy
In Western societies, the government controls the military, legal, administrative, productive, and cultural institutions, while civil society is made up of private communities controlled by volunteers and regulated by the free market: businesses, communities, cultural or religious associations, and the media. Communication.
Civil society depends on the economy, whose vitality allows the creation of communities. Freedom of association creates links between people and prevents alienation and disorganization in a society conducive to individualization, competition and loneliness
Changes in the labor market have made it possible for people from lower social classes to acquire goods that were previously the exclusive property of the middle class: television, washing machine, vacuum cleaner and stereo. The changes also caused an increase in wages and a reduction in the working day, which opened the way to the leisure market. The products of popular culture such as music, sports and the media have become commercial objects and have developed concerts, sporting events and mass tourism.
The most visible symbol of change in society is the automobile: before World War II, only the wealthy owned one, the number of cars on the road in Europe rose from 5 million in 1948 to 45 million in 1960.
Here are some links of interest: