Probably one of the most beautiful natural phenomena on our planet, as well as one of the most difficult to explain: The Northern Lights. These not only make up an almost surreal landscape in our skies, they are also the object of astronomical studies that would explain the operation of the terrestrial electromagnetic field.
Surely, like us, at some point you have marveled at the impressive spectacle that the northern lights can produce in the skies of the Earth's poles. They seem to recreate a scene from a science fiction movie or the view of the sky on some strange planet outside our solar system.
But they're not really the stuff of science fiction, and they're definitely not a divine sign either (as many ancient cultures believed). In fact, the northern lights they are produced on Earth, due to the excitation of the particles of our own atmosphere by the effect of solar winds.
If you would love to see a northern lights and want to know everything about this interesting topic, be sure to read our article until the end, where we will teach you what are the northern lights and other important aspects related to them.
If you want to know much more about the wonders that inhabit our universe, then you should not miss our article on the Hubble telescope, the eye that looks into space.
What is the Northern Lights?
The Northern Lights are a phenomenon of natural luminescence that occurs at night in the skies of the northern hemisphere of the earth.
The lights projected in the sky are truly impressive because they are wave-shaped and seem to move slowly, this was a feature that amazed and puzzled the inhabitants of the countries where this phenomenon is visible for centuries.
Although it is a multi-colored spectacle, the Northern Lights appear to be predominantly green in color. This happens because green is the color of the chemical reaction when ionizing an oxygen particle, which happens to be the most common molecular element in that area of our atmosphere.
However, the aurora borealis tends to gradually change color (pink, red, blue) as the radiation from the solar winds excites other denser or less abundant molecules in the atmosphere such as hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen.
Curious fact: ¡ NOT ALL AURORAS ARE BOREAL!
In general terms, this phenomenon does not only occur at the north pole of the earth, it also occurs at the south pole, in which case, the phenomenon has been dubbed as aurora australis
Both phenomena together are known as polar lights, however, "northern Lights" they are vastly more popular than their twins to the south, simply because they are so much easier to spot and can be seen from so many more countries.
Aurora Borealis: origin of the name
Even though "dawn" by itself refers todawn", this name is given in honor of Dawn, the Roman goddess who embodied the sunrises.
On the other hand, “Boreal” is derived from the Greek word "Boreas", whose translation would be “northern hemisphere”.
How are northern lights formed?
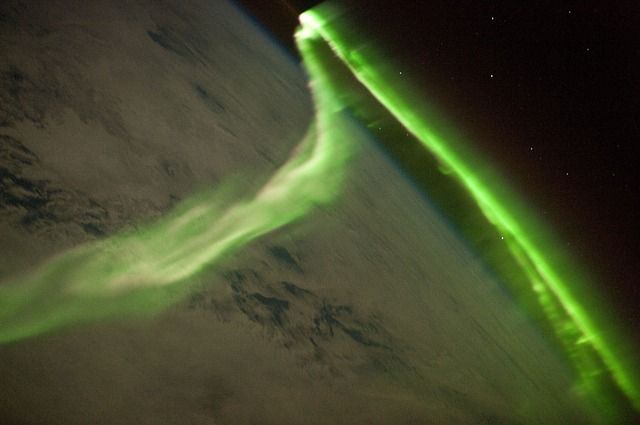

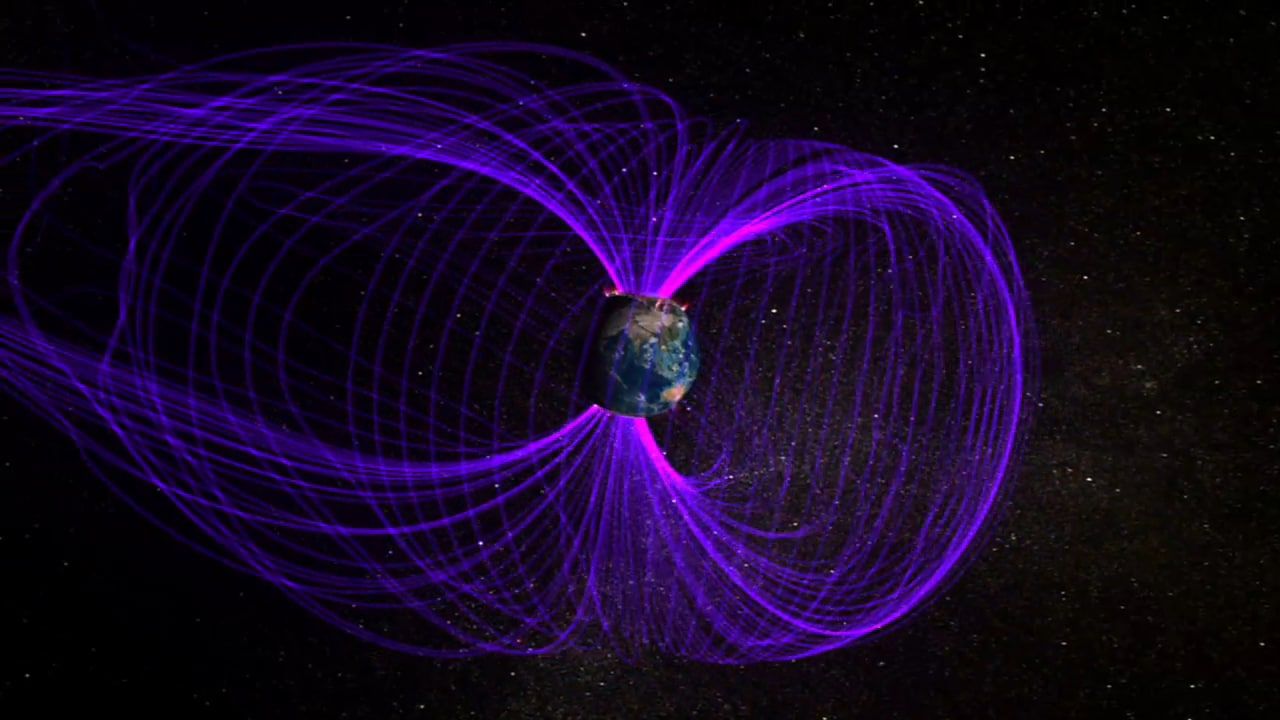
The image, taken by the International Space Station, shows what the electromagnetic field of the Earth's magnetosphere looks like when it is excited by solar winds, producing the Northern Lights.
The polar auroras (northern and austral lights) are generated as a product of the excitation exerted by the radiation brought by the solar winds on the gas molecules present in our atmosphere.
This process occurs because the solar winds are "moved" towards the terrestrial poles
upon impact with our planet's magnetosphere, an invisible shield formed by mineral activity in the planet's core and which functions as a force field against solar UV radiation.
When these winds reach the terrestrial poles, their radiation excites the gas particles, causing them to gain an additional electron, which generates a massive energetic reaction, which is expressed in our environment with flashes of light.
Depending on the intensity of the winds, the position of the earth and the amount and type of ionized particles, the characteristics of the Northern Lights can change, always taking different forms, moving in different ways and even gradually changing the color hue.
Why are they seen at the poles and not all over the planet?
Why the polar auroras can only be seen at the terrestrial poles and not all over the planet is one of the most common questions related to this topic. After all, the magnetosphere surrounds the entire Earth sphere.
To make it easier to understand, we will explain it as follows:
Although the magnetosphere surrounds our planet, it would not have the spherical shape corresponding to the earth, instead it would be like a parabolic oval, flat in front and very elongated in the rear part of the planet in relation to the sun.
This occurs because the force of the solar winds exerts pressure on the force field, stretching it backwards. Something similar to what would happen if we surround a stone impacted by the flow of water from a river with a bubble.
Therefore, the closest point (lowest height) of the magnetosphere in relation to the earth's surface occurs right at the two polar axes of the planet, going down to levels where the concentration of gaseous molecules in the atmosphere is much more abundant (between 100 and 300 km above sea level).
When and where to see the Northern Lights?
Due to its beauty and unique condition on the planet, seeing the northern lights has become an activity of tourist interest. Tens of thousands of people travel each year to countries in northern latitudes, where they could see this impressive play of lights in the sky.
However, hunting the Northern Lights is not necessarily an easy task…or cheap.
The northern lights are a completely unpredictable phenomenon, because our instruments cannot calculate the probability of formation of a polar light at a given time and place.
However, if we know certain conditions that can make seeing the Northern Lights much more likely in a given location.
What does it take to see a northern lights?
- The auroras can only be seen with the naked eye during winter; Fortunately, winter at the North Pole is very long.
- They can only be observed at latitudes above the polar circle line
- The best time to see the Northern Lights is between the months of October and March.
- Choose places with little terrestrial light pollution.
Where are the Northern Lights best seen?
There are several Nordic destinations that seem ideal for expeditions in search of the perfect Northern Lights. Of all, possibly the northern lights norway is the most famous of all, since this country receives many visitors a year for this purpose.
Some of the destinations where you can see the northern lights are:
- North Cape – Norway
- Aurora Sky Station – Swedish Lapland
- Urho Kekkonen – Finland
- Lofoten Island – Norway
- Fairbanks–Alaska
- Yellowknife – Canada
- Shetland Islands – UK
Northern lights in ancient times
For many Nordic cultures, the Northern Lights went from being a mystery to an important part of their culture and religious beliefs. In fact, before their scientific understanding, the polar lights, like comets, were related to natural disasters, bad omens and the wrath of some gods.
The Sami, indigenous Norwegians
A Sami legend (a people originally from the Lapland peninsula, north of Norway) tells that the formation of the northern lights is produced by the trail of fire left by the heavenly fox crossing the skies at night.
For the Sami, the trail left by the flaming fox's tail would mark the passage from the terrestrial plane to the other world.
In fact, the word to identify the Northern Lights in Finnish is “revontulette”, which literally means: Fire Fox.
In Greenland...
The Greenlandic Eskimo people believed that the path of light in the night sky was produced by the procession of souls to the other world due to wars. therefore, the appearance of the northern lights during the end of the year was taken as a harbinger of war.
for the Inuit
The Inuit are also an indigenous Eskimo people. These are native to the northernmost regions of North America, especially Alaska.
For the Inuit, the northern lights were as common as seeing the stars at night can be for us, so these are closely related to their customs and beliefs.
In their culture, the northern lights represent the flow of energy that transports the souls of the dead to the afterlife, so they venerate it and there are even several stories about shamans who have made "astral travel" to the northern lights.
However, the clash of discoveries and modern science has relegated the Inuit tradition to little more than a few folk stories and legends.